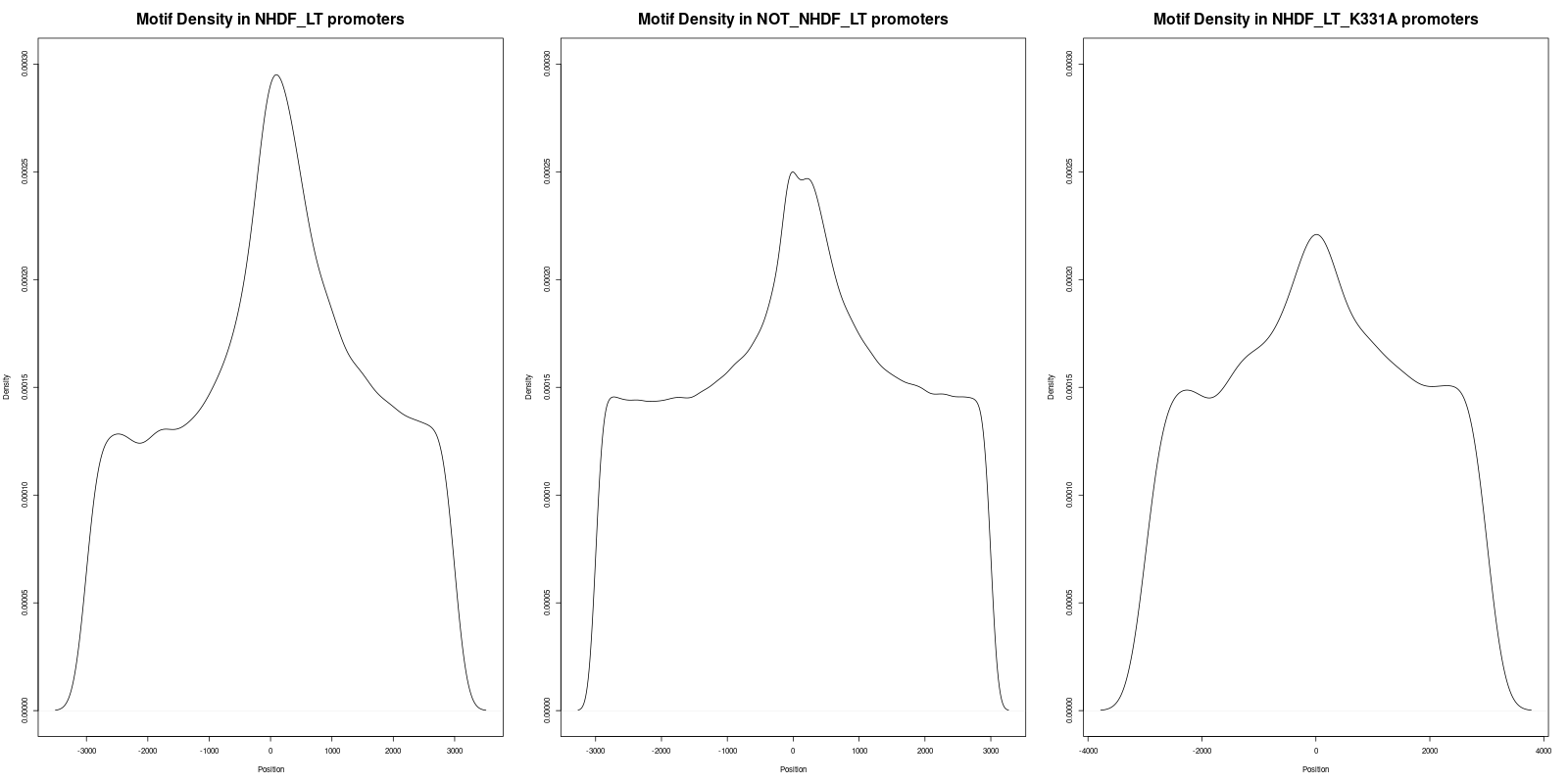
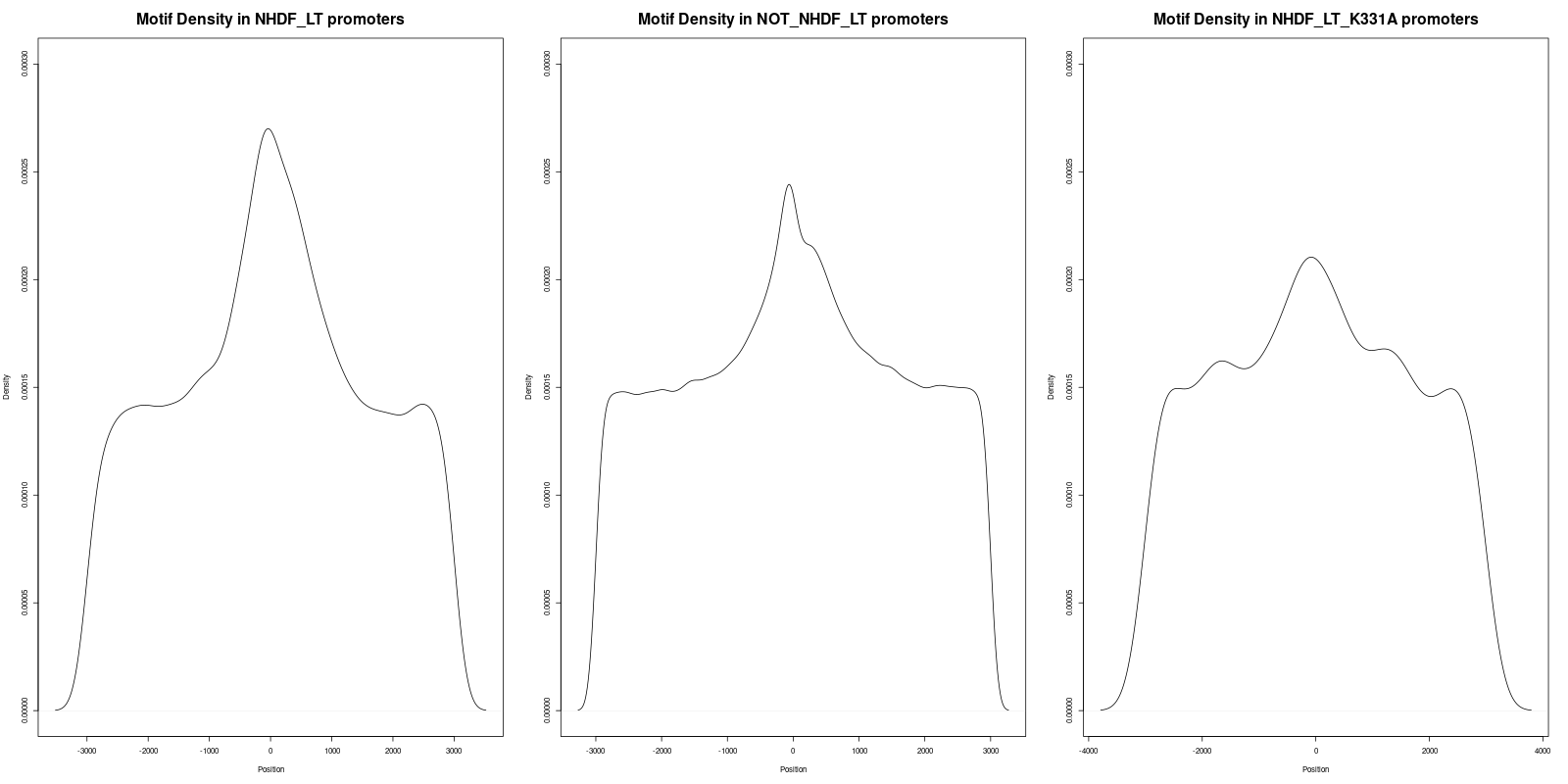
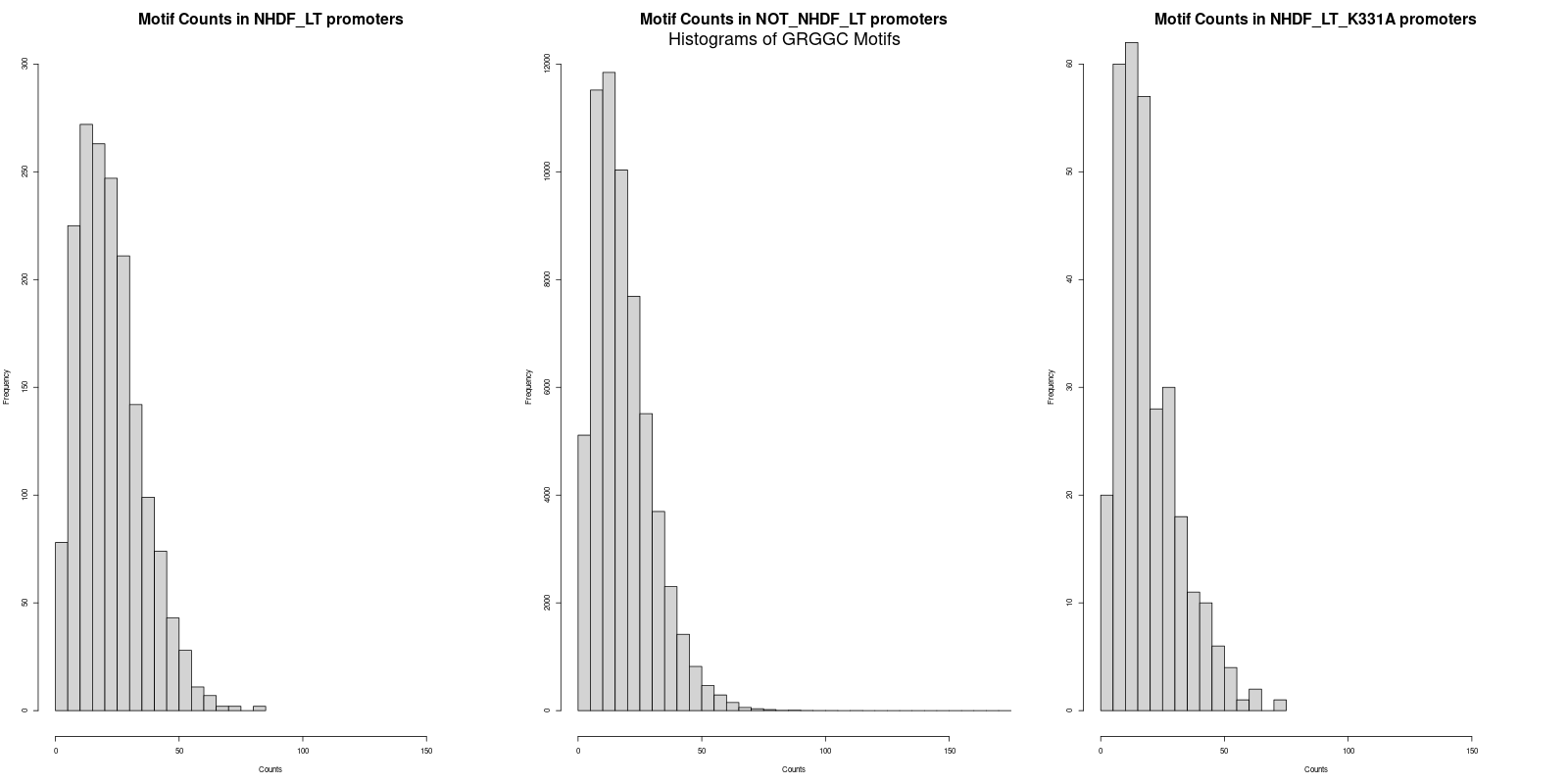
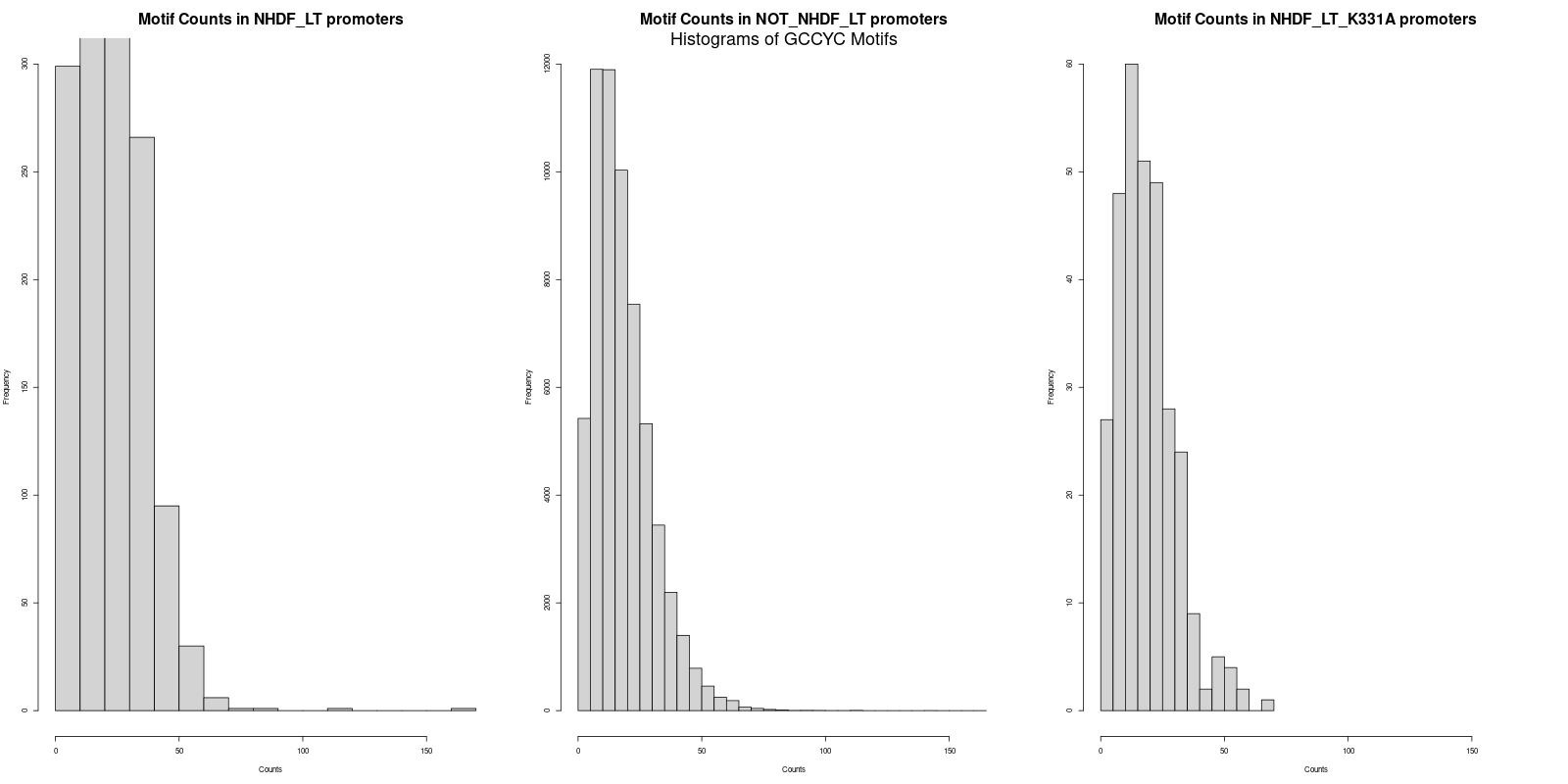
-
nextflow
#under hamm ln -s /home/jhuang/Tools/nf-core-rnaseq-3.12.0/ rnaseq #Debug the following error: added "--minAssignedFrags 0 \\" to modules/nf-core/salmon/quant/main.nf option "salmon quant" and added "--min_mapped_reads 0" in the nextflow command (rnaseq_2021) jhuang@hamm:~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_RNASeq$ /usr/local/bin/nextflow run rnaseq/main.nf --input samplesheet.csv --outdir results_JN707599 --fasta JN707599.fasta --gtf JN707599.gtf -profile test_full -resume --max_memory 124.GB --max_time 2400.h --save_reference --aligner star_salmon --gtf_extra_attributes gene_id --gtf_group_features transcript_id --featurecounts_group_type gene_id --featurecounts_feature_type transcript --skip_rseqc --skip_dupradar --skip_preseq --skip_biotype_qc --skip_deseq2_qc --skip_multiqc --min_mapped_reads 0 (rnaseq_2021) jhuang@hamm:~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_RNASeq$ /usr/local/bin/nextflow run rnaseq/main.nf --input samplesheet.csv --outdir results_LT --fasta JN707599.fasta --gtf LT.gtf -profile test_full -resume --max_memory 124.GB --max_time 2400.h --save_reference --aligner star_salmon --gtf_extra_attributes gene_id --gtf_group_features transcript_id --featurecounts_group_type gene_id --featurecounts_feature_type transcript --skip_rseqc --skip_dupradar --skip_preseq --skip_biotype_qc --skip_deseq2_qc --skip_multiqc --min_mapped_reads 0 (rnaseq_2021) jhuang@hamm:~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_RNASeq$ /usr/local/bin/nextflow run rnaseq/main.nf --input samplesheet.csv --outdir results_sT --fasta JN707599.fasta --gtf sT.gtf -profile test_full -resume --max_memory 124.GB --max_time 2400.h --save_reference --aligner star_salmon --gtf_extra_attributes gene_id --gtf_group_features transcript_id --featurecounts_group_type gene_id --featurecounts_feature_type transcript --skip_rseqc --skip_dupradar --skip_preseq --skip_biotype_qc --skip_deseq2_qc --skip_multiqc --min_mapped_reads 0 #DEBUG #V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI,V_8_4_2_p602_d8_DonorI.fastq.gz,,auto #V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI,V_8_5_1_602and604_d3_DonorI.fastq.gz,,auto #V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII,V_8_5_2_602and604_d3_DonorII.fastq.gz,,auto #mamba install -c bioconda rsem #mamba install fq -
construct DESeqDataSet including host+viral gene expressions
# Import the required libraries library("AnnotationDbi") library("clusterProfiler") library("ReactomePA") library(gplots) library(tximport) library(DESeq2) library("org.Hs.eg.db") library(dplyr) library(tidyverse) setwd("~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_immune_evasion_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq/results_JN707599/star_salmon") # Define paths to your Salmon output quantification files files <- c("V_8_0_mock_DonorI" = "./V_8_0_mock_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_0_mock_DonorII" = "./V_8_0_mock_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII" = "./V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII" = "./V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII" = "./V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII" = "./V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI" = "./V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI" = "./V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI" = "./V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI" = "./V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII" = "./V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII" = "./V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII" = "./V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII" = "./V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI" = "./V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI" = "./V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI" = "./V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI" = "./V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII" = "./V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI" = "./V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI" = "./V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI" = "./V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII" = "./V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII" = "./V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI" = "./V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI/quant.sf", "V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII" = "./V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII/quant.sf", "V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI" = "./V_8_5_1_sTplusLT_d3_Donor1/quant.sf", "V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII" = "./V_8_5_2_sTplusLT_d3_Donor2/quant.sf") # Import the transcript abundance data with tximport txi <- tximport(files, type = "salmon", txIn = TRUE, txOut = TRUE) column_names <- colnames(txi$counts) output_string <- paste(column_names, collapse = ", ") cat(output_string, "\n") #"V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII","V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI","V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII" col_order <- c("V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII","V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI","V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII") #reordered.txi <- txi[,col_order] identical(column_names,col_order) condition = as.factor(c("untreated","untreated", "p601_d3","p604_d3", "p601_d8","p604_d8", "p601_d3","p604_d3","p601_d8","p604_d8", "p600_d3","p605_d3","p600_d8", "p605_d8", "p600_d3","p605_d3","p600_d8","p605_d8", "p602_d8","p602_d8", "p600and601_d9d12", "p604and605_d9d12","p600and601_d9d12","p604and605_d9d12", "p602_d3","p602_d3", "p602and604_d3","p602and604_d3")) batch = as.factor(c("200420", "200420", "190927", "190927", "190927", "190927", "190228", "190228", "190228", "190228", "191008", "191008", "191008", "191008", "190228", "190228", "190228", "190228", "200817", "200817", "200420", "200420", "200817", "200817", "210302", "210302", "210504","210504")) ids = as.factor(c("untreated_DonorI","untreated_DonorII", "p601_d3_DonorII","p604_d3_DonorII", "p601_d8_DonorII","p604_d8_DonorII", "p601_d3_DonorI","p604_d3_DonorI","p601_d8_DonorI","p604_d8_DonorI", "p600_d3_DonorII","p605_d3_DonorII","p600_d8_DonorII", "p605_d8_DonorII", "p600_d3_DonorI","p605_d3_DonorI","p600_d8_DonorI","p605_d8_DonorI", "p602_d8_DonorII","p602_d8_DonorI", "p600and601_d12_DonorI", "p604and605_d12_DonorI","p600and601_d9_DonorII","p604and605_d9_DonorII", "p602_d3_DonorI","p602_d3_DonorII", "p602and604_d3_DonorI","p602and604_d3_DonorII")) donor = as.factor(c("DonorI","DonorII", "DonorII","DonorII", "DonorII","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorI","DonorI","DonorI", "DonorII","DonorII","DonorII","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorI","DonorI","DonorI", "DonorII","DonorI", "DonorI", "DonorI","DonorII","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorII")) # Define the colData for DESeq2 #colData = data.frame(row.names=column_names, condition=condition, donor=donor, batch=batch, ids=ids) colData <- data.frame(condition=condition, donor=donor, row.names=names(files)) # -- transcript-level count data (for virus) -- # Create DESeqDataSet object dds <- DESeqDataSetFromTximport(txi, colData=colData, design=~condition+donor) write.csv(counts(dds), file="transcript_counts.csv") # -- gene-level count data (for virus) -- # Read in the tx2gene map from salmon_tx2gene.tsv tx2gene <- read.table("salmon_tx2gene.tsv", header=FALSE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) # Set the column names colnames(tx2gene) <- c("transcript_id", "gene_id", "gene_name") # Remove the gene_name column if not needed tx2gene <- tx2gene[,1:2] # Import and summarize the Salmon data with tximport txi <- tximport(files, type = "salmon", tx2gene = tx2gene, txOut = FALSE) dds <- DESeqDataSetFromTximport(txi, colData=colData, design=~condition+donor) #dds <- dds[rowSums(counts(dds) > 3) > 2, ] #60605-->26543 write.csv(counts(dds, normalized=FALSE), file="gene_counts.csv") # -- merge the raw counts of human and microbe -- setwd("~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_immune_evasion_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq/results/featureCounts") d.raw<- read.delim2("merged_gene_counts_2_f3_f5.txt",sep="\t", header=TRUE, row.names=1) colnames(d.raw)<- c("V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII", "V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI", "V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII") #26364 col_order <- c("V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII", "V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII", "V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII", "V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI", "V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII", "V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII", "V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI", "V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI", "V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI", "V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII", "V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII", "V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI", "V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII") reordered.raw <- d.raw[,col_order] write.csv(reordered.raw, file="merged_gene_counts_2_f3_f5_reordered.txt") # Confirm the identification of the headers of two files before merging! #kate ./results/featureCounts/merged_gene_counts_2_f3_f5_reordered.txt #"","V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII","V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI","V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII" #results_JN707599/star_salmon/gene_counts.csv #"","V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII","V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI","V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII" #cat ../Data_Denise_RNASeq/results/featureCounts/merged_gene_counts_2_f3_f5_reordered.txt ../Data_Denise_RNASeq/results_JN707599/star_salmon/gene_counts.csv > merged_gene_counts.csv #~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py merged_gene_counts.csv -d',' -o raw_gene_counts.xls; setwd("~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_immune_evasion_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq_Merged/") d.raw <- read.csv("merged_gene_counts.csv", header=TRUE, row.names=1) dds <- DESeqDataSetFromMatrix(countData=d.raw, colData=colData, design=~condition+donor) dim(counts(dds)) head(counts(dds), 10) rld <- rlogTransformation(dds) # draw simple pca and heatmap library(gplots) library("RColorBrewer") #mat <- assay(rld) #mm <- model.matrix(~condition, colData(rld)) #mat <- limma::removeBatchEffect(mat, batch=rld$batch, design=mm) #assay(rld) <- mat # -- pca -- png("pca.png", 1200, 800) plotPCA(rld, intgroup=c("condition")) dev.off() # -- heatmap -- png("heatmap.png", 1200, 800) distsRL <- dist(t(assay(rld))) mat <- as.matrix(distsRL) hc <- hclust(distsRL) hmcol <- colorRampPalette(brewer.pal(9,"GnBu"))(100) heatmap.2(mat, Rowv=as.dendrogram(hc),symm=TRUE, trace="none",col = rev(hmcol), margin=c(13, 13)) dev.off() -
(corrected of last step) construct DESeqDataSet including host+viral gene expressions
column_names <- colnames(d.raw) col_order <- c("V_8_0_mock_DonorI","V_8_0_mock_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d3_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p601_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_5_p604_d8_DonorII","V_8_1_6_p601_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d3_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p601_d8_DonorI","V_8_1_6_p604_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_3_p600_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d3_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_3_p605_d8_DonorII","V_8_2_4_p600_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d3_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI","V_8_2_4_p605_d8_DonorI","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorII","V_8_4_1_p602_d8_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p600and601_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_1_p604and605_d12_DonorI","V_8_3_2_p600and601_d9_DonorII","V_8_3_2_p604and605_d9_DonorII","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorI","V_8_4_2_p602_d3_DonorII","V_8_5_1_p602and604_d3_DonorI","V_8_5_2_p602and604_d3_DonorII") identical(column_names,col_order) condition = as.factor(c("untreated","untreated", "p601_d3","p604_d3", "p601_d8","p604_d8", "p601_d3","p604_d3","p601_d8","p604_d8", "p600_d3","p605_d3","p600_d8", "p605_d8", "p600_d3","p605_d3","p600_d8","p605_d8", "p602_d8","p602_d8", "p600and601_d9d12", "p604and605_d9d12","p600and601_d9d12","p604and605_d9d12", "p602_d3","p602_d3", "p602and604_d3","p602and604_d3")) batch = as.factor(c("200420", "200420", "190927", "190927", "190927", "190927", "190228", "190228", "190228", "190228", "191008", "191008", "191008", "191008", "190228", "190228", "190228", "190228", "200817", "200817", "200420", "200420", "200817", "200817", "210302", "210302", "210504","210504")) ids = as.factor(c("untreated_DonorI","untreated_DonorII", "p601_d3_DonorII","p604_d3_DonorII", "p601_d8_DonorII","p604_d8_DonorII", "p601_d3_DonorI","p604_d3_DonorI","p601_d8_DonorI","p604_d8_DonorI", "p600_d3_DonorII","p605_d3_DonorII","p600_d8_DonorII", "p605_d8_DonorII", "p600_d3_DonorI","p605_d3_DonorI","p600_d8_DonorI","p605_d8_DonorI", "p602_d8_DonorII","p602_d8_DonorI", "p600and601_d12_DonorI", "p604and605_d12_DonorI","p600and601_d9_DonorII","p604and605_d9_DonorII", "p602_d3_DonorI","p602_d3_DonorII", "p602and604_d3_DonorI","p602and604_d3_DonorII")) donor = as.factor(c("DonorI","DonorII", "DonorII","DonorII", "DonorII","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorI","DonorI","DonorI", "DonorII","DonorII","DonorII","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorI","DonorI","DonorI", "DonorII","DonorI", "DonorI", "DonorI","DonorII","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorII", "DonorI","DonorII")) colData <- data.frame(condition=condition, donor=donor, row.names=column_names) setwd("~/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq_Merged_Corrected/") d.raw <- read.csv("merged_gene_counts_corrected.csv", header=TRUE, row.names=1) dds <- DESeqDataSetFromMatrix(countData=d.raw, colData=colData, design=~condition+donor) dim(counts(dds)) head(counts(dds), 10) rld <- rlogTransformation(dds) # draw simple pca and heatmap library(gplots) library("RColorBrewer") #mat <- assay(rld) #mm <- model.matrix(~condition, colData(rld)) #mat <- limma::removeBatchEffect(mat, batch=rld$batch, design=mm) #assay(rld) <- mat # -- pca -- png("pca.png", 1200, 800) plotPCA(rld, intgroup=c("condition")) dev.off() # -- heatmap -- png("heatmap.png", 1200, 800) distsRL <- dist(t(assay(rld))) mat <- as.matrix(distsRL) hc <- hclust(distsRL) hmcol <- colorRampPalette(brewer.pal(9,"GnBu"))(100) heatmap.2(mat, Rowv=as.dendrogram(hc),symm=TRUE, trace="none",col = rev(hmcol), margin=c(13, 13)) dev.off() -
select the differentially expressed genes
#untreated_DonorI,untreated #untreated_DonorII,untreated #p601_d3_DonorII,mCherry control #p604_d3_DonorII,sT #p601_d8_DonorII,mCherry control #p604_d8_DonorII,sT #p601_d3_DonorI,mCherry control #p604_d3_DonorI,sT #p601_d8_DonorI,mCherry control #p604_d8_DonorI,sT # #p600_d3_DonorII,GFP control #p605_d3_DonorII,LTtr #p600_d8_DonorII,GFP control #p605_d8_DonorII,LTtr #p600_d3_DonorI,GFP control #p605_d3_DonorI,LTtr #p600_d8_DonorI,GFP control #p605_d8_DonorI,LTtr #p602_d3_DonorI,LT #p602_d3_DonorII,LT #p602_d8_DonorII,LT #p602_d8_DonorI,LT # #p600and601_d12_DonorI,GFP+mCherry control #p604and605_d12_DonorI,sT+LTtr #p600and601_d9_DonorII,GFP+mCherry control #p604and605_d9_DonorII,sT+LTtr # #p602and604_d3_DonorI,sT+LT #p602and604_d3_DonorII,sT+LT #CONSOLE: mkdir /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_immune_evasion_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq_Merged/degenes #---- relevel to control ---- dds$condition <- relevel(dds$condition, "p601_d3") dds = DESeq(dds, betaPrior=FALSE) resultsNames(dds) clist <- c("p604_d3_vs_p601_d3") dds$condition <- relevel(dds$condition, "p600_d3") dds = DESeq(dds, betaPrior=FALSE) resultsNames(dds) clist <- c("p605_d3_vs_p600_d3") dds$condition <- relevel(dds$condition, "p600_d3") dds = DESeq(dds, betaPrior=FALSE) resultsNames(dds) clist <- c("p602_d3_vs_p600_d3") dds$condition <- relevel(dds$condition, "p601_d8") dds = DESeq(dds, betaPrior=FALSE) resultsNames(dds) clist <- c("p604_d8_vs_p601_d8") dds$condition <- relevel(dds$condition, "p600_d8") dds = DESeq(dds, betaPrior=FALSE) resultsNames(dds) clist <- c("p605_d8_vs_p600_d8") dds$condition <- relevel(dds$condition, "p600_d8") dds = DESeq(dds, betaPrior=FALSE) resultsNames(dds) clist <- c("p602_d8_vs_p600_d8") library(biomaRt) listEnsembl() listMarts() #--> total 69, 27 GRCh38.p7 and 39 GRCm38.p4 #ensembl <- useEnsembl(biomart = "ensembl", dataset = "hsapiens_gene_ensembl", version="104") #GRCh37.p13 ensembl <- useEnsembl("ensembl","hsapiens_gene_ensembl", host="https://grch37.ensembl.org") datasets <- listDatasets(ensembl) # -- 1. export res_df containing both human and virus genes -- #for (i in clist) { i<-clist[1] contrast = paste("condition", i, sep="_") res = results(dds, name=contrast) res <- res[!is.na(res$log2FoldChange),] res_df <- as.data.frame(res) write.csv(as.data.frame(res_df[order(res_df$pvalue),]), file = paste(i, "all.txt", sep="-")) up <- subset(res_df, padj<=0.05 & log2FoldChange>=2) down <- subset(res_df, padj<=0.05 & log2FoldChange<=-2) write.csv(as.data.frame(up[order(up$log2FoldChange,decreasing=TRUE),]), file = paste(i, "up.txt", sep="-")) write.csv(as.data.frame(down[order(abs(down$log2FoldChange),decreasing=TRUE),]), file = paste(i, "down.txt", sep="-")) #} # -- 2. annatete human genes 'geness_res', note that the virus genes in that is ignored in the process since they are not in the database -- #> dim(geness) [1] 21938 9 using GRCh38.p7 #> dim(geness) [1] 23517 9 using GRCh37.p13 #for (i in clist) { #i<-clist[1] contrast = paste("condition", i, sep="_") res = results(dds, name=contrast) res <- res[!is.na(res$log2FoldChange),] geness <- getBM(attributes = c('ensembl_gene_id', 'external_gene_name', 'gene_biotype', 'entrezgene_id', 'chromosome_name', 'start_position', 'end_position', 'strand', 'description'), filters = 'external_gene_name', values = rownames(res), mart = ensembl) geness_uniq <- distinct(geness, ensembl_gene_id, .keep_all= TRUE) #merge by column by common colunmn name, in the case "GENEID" res$geneSymbol = rownames(res) #identical(rownames(res), rownames(geness_uniq)) res_df <- as.data.frame(res) geness_res <- merge(geness_uniq, res_df, by.x="external_gene_name", by.y="geneSymbol") dim(geness_res) #22044 15 rownames(geness_res) <- geness_res$ensembl_gene_id geness_res$ensembl_gene_id <- NULL #} # -- 3. prepare annatete virus genes -- virus_genes <- c("LT", "sT", "VP1", "VP2", "VP3") virus_rows <- res_df[rownames(res_df) %in% virus_genes, ] virus_rows$external_gene_name <- rownames(virus_rows) virus_rows$chromosome_name <- "JN707599" # Define default values based on data type default_values <- list( character = NULL, numeric = 0, integer = 0L, logical = FALSE ) # Ensure that virus_rows has the same columns as geness_res for (col in colnames(geness_res)) { if (!col %in% colnames(virus_rows)) { data_type <- class(geness_res[[col]])[1] default_value <- default_values[[data_type]] virus_rows[[col]] <- rep(default_value, nrow(virus_rows)) } } missing_cols <- setdiff(colnames(geness_res), colnames(virus_rows)) for (col in missing_cols) { virus_rows[[col]] <- NA # Or another default value as appropriate } # Reorder columns in virus_rows to match the order in geness_res virus_rows <- virus_rows[, colnames(geness_res), drop = FALSE] # -- 4. merge them together -- #for (i in clist) { merged_df <- rbind(geness_res, virus_rows) merged_df_sorted <- as.data.frame(merged_df[order(merged_df$padj),]) write.csv(merged_df_sorted, file = paste(i, "all_annotated.txt", sep="-")) up <- subset(merged_df_sorted, padj<=0.05 & log2FoldChange>=2) down <- subset(merged_df_sorted, padj<=0.05 & log2FoldChange<=-2) viral <- merged_df_sorted[merged_df_sorted$external_gene_name %in% c("LT", "sT", "VP1", "VP2", "VP3"), ] write.csv(as.data.frame(up[order(up$log2FoldChange,decreasing=TRUE),]), file = paste(i, "up_annotated.txt", sep="-")) write.csv(as.data.frame(down[order(abs(down$log2FoldChange),decreasing=TRUE),]), file = paste(i, "down_annotated.txt", sep="-")) write.csv(as.data.frame(viral), file = paste(i, "viral_annotated.txt", sep="-")) #} # -- 5. draw graphics -- library(ggrepel) #geness_res <- read.csv(file = "p605_d8_vs_p600_d8-all_annotated.txt", sep=",", row.names=1) #i<-"p605_d8_vs_p600_d8" geness_res <- merged_df_sorted # Color setting geness_res$Color <- ifelse(geness_res$padj > 0.05 | abs(geness_res$log2FoldChange) < 2, "gray", ifelse(geness_res$log2FoldChange > 0, "red", "blue")) # Predefined genes colored in green predefined_genes <- c("LT", "sT", "VP1", "VP2", "VP3") geness_res$Color[geness_res$external_gene_name %in% predefined_genes] <- "green" geness_res$invert_Padj <- (-log10(geness_res$padj)) * sign(geness_res$log2FoldChange) top_g <- unique(c(geness_res[order(geness_res$invert_Padj, decreasing = TRUE), 'external_gene_name'][1:200], geness_res[order(geness_res$invert_Padj, decreasing = FALSE), 'external_gene_name'][1:200])) # Define the original and compressed ranges original_range <- c(80, 115) compressed_range <- c(80.0, 90.0) # Calculate breaks for the y-axis y_breaks_below <- seq(0, 80, by=5) y_breaks_compressed <- c(80.0, 90.0) y_breaks_above <- c() y_breaks <- c(y_breaks_below, y_breaks_compressed, y_breaks_above) y_labels_below <- seq(0, 80, by=5) y_labels_compressed <- c(80, 115) y_labels_above <- c() y_labels <- c(y_labels_below, y_labels_compressed, y_labels_above) # Adjust the p-values based on the ranges geness_res$adjusted_pvalue <- with(geness_res, ifelse(-log10(padj) > original_range[1] & -log10(padj) <= original_range[2], ((-log10(padj) - original_range[1]) / (original_range[2] - original_range[1])) * (compressed_range[2] - compressed_range[1]) + compressed_range[1], ifelse(-log10(padj) > original_range[2], -log10(padj) - (original_range[2] - original_range[1]) + (compressed_range[2] - compressed_range[1]), -log10(padj)))) # Create the plot png(paste(i, "png", sep="."), width=1000, height=1000) ggplot(geness_res, aes(x = log2FoldChange, y = adjusted_pvalue, color = Color, label = external_gene_name)) + geom_vline(xintercept = c(2, -2), lty = "dashed", size = 1.5) + geom_hline(yintercept = -log10(0.05), lty = "dashed", size = 1.5) + geom_point(size = 3) + labs(x = "log2(Fold change)", y = "-log10(P-adj)", color = "Significance") + scale_color_identity() + geom_text_repel(data = subset(geness_res, external_gene_name %in% top_g & padj < 0.05 & (abs(log2FoldChange) >= 2)), size = 7, point.padding = 0.15, color = "black", min.segment.length = .1, box.padding = .2, lwd = 2) + theme_bw(base_size = 24) + theme(legend.position = "bottom") + #annotate("rect", xmin = -Inf, xmax = Inf, ymin = compressed_range[1], ymax = compressed_range[1], linetype = "dashed", color = "grey") + #annotate("rect", xmin = -Inf, xmax = Inf, ymin = compressed_range[2], ymax = compressed_range[2], linetype = "dashed", color = "grey") + #annotate("text", x = -Inf, y = compressed_range[1], label = "/", hjust = 0, size = 10) + #annotate("text", x = -Inf, y = compressed_range[2], label = "/", hjust = 0, size = 10) + scale_y_continuous(breaks = sort(y_breaks), labels = sort(y_labels)) dev.off() #Under DIR degenes under KONSOLE and delete "start_position","end_position","strand" and so on. #~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py viral_gene_counts.csv p604_d8_vs_p601_d8-viral_annotated.txt p605_d8_vs_p600_d8-viral_annotated.txt p602_d8_vs_p600_d8-viral_annotated.txt p604_d3_vs_p601_d3-viral_annotated.txt p605_d3_vs_p600_d3-viral_annotated.txt p602_d3_vs_p600_d3-viral_annotated.txt -d$',' -o viral_raw_counts_and_comparisons.xls; #dpt: days post-transfection
Author Archives: gene_x
ChIP-seq using HOMER (-stype histone, macs2 or SICER + custom getDifferentialPeaksReplicates_broad[narrow].pl)
-
nextflow processing data
(chipseq) jhuang@hamm:/mnt/h1/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/Histone-ChIP_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public$ nextflow run NGI-ChIPseq/main.nf --reads '/mnt/h1/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/Histone-ChIP_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/Raw_Data/*.fastq.gz' --genome hg38 --macsconfig macs.config --saveReference --saveAlignedIntermediates --singleEnd --blacklist_filtering -profile standard --project NHDF_enhancer_analysis_hg38 -resume ./picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam ./picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam -
make homer directories and findPeaks with HOMER under (conda homer, but note that homer is installed under Tools manually!)
#HOMER will be installed in the same directory that you place the configureHomer.pl program. configureHomer.pl will attempt to check for required utilities and alert you to missing programs. 1. mkdir ~/Tools/homer; cd ~/Tools/homer 2. wget http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/configureHomer.pl 3. Run the configureHomer.pl script to install homer: perl configureHomer.pl -install 4. Add the homer/bin directory to your executable path. For example, edit your ~/.bashrc file to include the line: PATH=$PATH:/home/jhuang/Tools/homer/bin/ 5. Reset your terminal so that the changes to the PATH variable take effect: source ~/.bashrc #jhuang@hamm:~/Tools/homer/bin$ wget http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/configureHomer.pl #configureHomer.pl -install #chmod +x /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/homer/bin/configureHomer.pl #ls ~/miniconda3/envs/homer/bin #echo $PATH #If /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/homer/bin is not in the output, you'll need to add it to your $PATH. chmod +x ~/Tools/homer/configureHomer.pl ./configureHomer.pl -install hg38 ./configureHomer.pl -list #conda update -n base -c defaults conda conda create -n homer conda activate homer #(NOT_USE!) conda install -c bioconda homer mamba install r-essentials bioconductor-deseq2 mamba install samtools #bioconductor-edger wget #http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/introduction/update.html #http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/introduction/install.html conda install -c bioconda ucsc-bedgraphtobigwig # install bedGraphToBigWig on @homer conda install -c bioconda macs2 conda install -c anaconda pandas #under (myperl) on computer @hamburg mkdir homer bigWigs macs2 sicer cd homer #Why do I need give "-genome hg38" in makeTagDirectory? If you don't provide a genome with the -genome option, HOMER will only count the number of tags in each region without any genomic context or sequence information. #So, it is essential to include this information when creating a tag directory if you plan to perform any genome-based analysis. makeTagDirectory p600_601_d12_D1_input ../results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p600_601_d9_D2_input ../results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p602_d8_D1_input ../results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p602_d8_D2_input ../results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3 ../results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3 ../results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3 ../results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3 ../results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p600_601_d12_D1_H3K27me3 ../results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p600_601_d9_D2_H3K27me3 ../results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p602_d8_D1_H3K27me3 ../results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory p602_d8_D2_H3K27me3 ../results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 for sample in p600_601_d12_D1_input p600_601_d9_D2_input p602_d8_D1_input p602_d8_D2_input p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3 p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3 p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3 p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3 p600_601_d12_D1_H3K27me3 p600_601_d9_D2_H3K27me3 p602_d8_D1_H3K27me3 p602_d8_D2_H3K27me3; do makeUCSCfile ${sample} -bigWig /home/jhuang/REFs/hg38.chromSizes -o auto -style chipseq #-pseudo 1 -norm 1e7 -normLength 100 -fsize 1 mv ${sample}/${sample}.ucsc.bigWig ../bigWigs/ done #Note that normLength should possibly read the fragmentation length from phantompeakqualtools. Easier to set all libraries to the default value: 100. #To normalize to a fragment length of 150, you would use -normLength 150. #To turn off normalization, you would use -normLength 0. # -- not necessary any more: using MACS2 and SICER instead of using findPeaks ------------------------> go STEPs 4.1 and 5.1. # #factor (transcription factor ChIP-Seq, uses -center, output: peaks.txt, default) # #histone (histone modification ChIP-Seq, region based, uses -region -size 500 -L 0, regions.txt) # for sample in p601_d8_D1 p601_d8_D2 p604_d8_D1 p604_d8_D2; do # #Finding peaks of size 1000, no closer than 2000 # findPeaks ${sample}_H3K4me3 -style factor -size 1000 -o auto -i ${sample}_input # #-minDist <#> (minimum distance between peaks, default: peak size x2) # #findPeaks ${sample}_H3K27me3 -style histone -region -size 3000 -minDist 5000 -o auto -i ${sample}_input # #findPeaks ${sample}_H3K27ac -style factor -size 200 -minDist 200 -o auto -i ${sample}_input # #findPeaks ${sample}_H3K4me1 -style histone -region -size 1000 -minDist 2500 -o auto -i ${sample}_input # done ./p601_d8_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt ./p601_d8_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt ./p604_d8_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt ./p604_d8_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt ./p601_d8_D1_H3K27me3/regions.txt ./p601_d8_D2_H3K27me3/regions.txt ./p604_d8_D1_H3K27me3/regions.txt ./p604_d8_D2_H3K27me3/regions.txt for dir in p601_d8_D1_H3K4me3 p601_d8_D2_H3K4me3 p604_d8_D1_H3K4me3 p604_d8_D2_H3K4me3; do awk -v OFS='\t' '{print $2, $3, $4, $1, $6}' ./${dir}/peaks.txt > ${dir}_peaks.bed grep -v "#" ${dir}_peaks.bed | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > ${dir}_sorted_peaks.bed done for dir in p601_d8_D1_H3K27me3 p601_d8_D2_H3K27me3 p604_d8_D1_H3K27me3 p604_d8_D2_H3K27me3; do awk -v OFS='\t' '{print $2, $3, $4, $1, $6}' ./${dir}/regions.txt > ${dir}_regions.bed grep -v "#" ${dir}_regions.bed | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > ${dir}_sorted_regions.bed done #DEBUG: why the bam files so small? makeTagDirectory NHDF-Ad_Control_r1 /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/results/picard/NHDF_Control_r1.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory NHDF-Ad_Control_r2 /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/results/picard/NHDF_Control_r2.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory NHDF-Ad_H3K27ac_r1 /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/results/picard/NHDF_H3K27ac_r1.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory NHDF-Ad_H3K27ac_r2 /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/results/picard/NHDF_H3K27ac_r2.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory NHDF-Ad_H3K4me1_r1 /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/results/picard/NHDF_H3K4me1_r1.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 makeTagDirectory NHDF-Ad_H3K4me1_r2 /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/results/picard/NHDF_H3K4me1_r2.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 NHDF-Ad_Control_r1 NHDF-Ad_Control_r2 NHDF-Ad_H3K27ac_r1 NHDF-Ad_H3K27ac_r2 NHDF-Ad_H3K4me1_r1 NHDF-Ad_H3K4me1_r2 > (myperl) environments for HOMER, ~/Tools/diffreps/bin/diffReps.pl, MACS2, ~/Tools/SICER1.1/SICER/SICER.sh
2.5. diffbind (NOT_USED) https://hbctraining.github.io/Intro-to-ChIPseq/lessons/08_diffbind_differential_peaks.html #–>identifying statistically significantly differentially bound sites https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-022-02686-y
#samplesheet.csv
#SampleID, Condition, Peaks, Counts
#Sample1, Control, sample1_peaks.bed, sample1.bam
#Sample2, Treatment, sample2_peaks.bed, sample2.bam
library(DiffBind)
samples <- dba(sampleSheet="samplesheet.csv")3.0. combine the diffReps.pl and HOMER annotatePeaks.pl, so we can use for hg38 and mm10 and so on (IMPORTANT, DON’T NEED –gname hg38, run diffReps.pl –> bed_file –> annotatePeaks.pl it with HOMER)
#Dynamic regions were defined as MACS (H3K4me3, H3K27ac) or SICER (H3K4me1, H3K27me3) peaks overlapping significantly (≥ 2-fold change, adjusted P-value ≤ 0.05) up- or down-regulated differentially enriched regions from diffReps in the three pairwise comparisons WAC vs mock, WA314 vs mock and WAC vs WA314.
#STEP1
#--> not given "--gname hg38"
## Step4: Annotate differential sites.
#unless($noanno or $gname eq ''){
# `region_analysis.pl -i $report -r -d refseq -g $gname`;
#}
## Step5: Look for hotspots.
#unless($nohs){
# my $hotspot = $report . '.hotspot';
# `findHotspots.pl -d $report -o $hotspot`;
#}
~/Tools/diffreps/bin/diffReps.pl -tr ../results/picard/V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bed ../results/picard/V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bed -co ../results/picard/V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bed ../results/picard/V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bed --report output_results --chrlen /home/jhuang/REFs/hg38.chromSizes --nsd sharp --noanno
~/Tools/diffreps/bin/diffReps.pl -tr ../results/picard/V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bed ../results/picard/V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bed -co ../results/picard/V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bed ../results/picard/V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bed --report p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_diff_out --chrlen /home/jhuang/REFs/hg38.chromSizes --nsd sharp --noanno
~/Tools/diffreps/bin/diffReps.pl --treatment ./results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bed ./results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bed --btr ./results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bed ./results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bed --control ./results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bed ./results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_H3K27me3.dedup.sorted.bed --bco ./results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bed ./results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bed --report p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_diff_out --chrlen /home/jhuang/REFs/hg38.chromSizes --nsd broad --mode block --window 10000 --gap 30000 --noanno
#I have utilized 'diffReps' for this analysis because the methods I previously mentioned in my last email were not effective in identifying sites with statistically significant differential binding. 'diffReps' appears to be a more suitable tool for our needs. Below is the command I used. It's important to note that 'diffReps' typically requires replicates as input and outputs a set of peaks/regions.
#STEP2
#replace Chr to '#Chr'
grep -v "#" output_results | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > output_results_
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $1, $2, $3, "diffreps_peak_"NR, $12}' output_results_ > H3K4me3.bed
#grep -v "#" H3K4me3.bed | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > H3K4me3_sorted_peaks.bed
grep -v "#" p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_diff_out | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_diff_out_
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $1, $2, $3, "diffreps_peak_"NR, $12}' p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_diff_out_ > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3.bed
grep -v "#" p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_diff_out | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_diff_out_
awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $1, $2, $3, "diffreps_peak_"NR, $12}' p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_diff_out_ > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3.bed
#STEP3 (under myperl) peak calling macs2 for narrow peaks, CISER for broad peaks!
#process the output of diffReps.pl to BED file.
annotatePeaks.pl H3K4me3.bed hg38 > H3K4me3_annotated_peaks.txt
annotatePeaks.pl p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3.bed hg38 > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_annotated_peaks.txt
annotatePeaks.pl p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3.bed hg38 > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_annotated_peaks.txt
(head -n 1 p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_annotated_peaks.txt && tail -n +2 p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_annotated_peaks.txt | sort -t "_" -k 3 -n) > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_annotated_peaks_.txt
(head -n 1 p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_annotated_peaks.txt && tail -n +2 p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_annotated_peaks.txt | sort -t "_" -k 3 -n) > p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_annotated_peaks_.txt
~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_annotated_peaks_.txt -d$'\t' -o p602_vs_p600_601_H3K4me3_annotated_peaks.xls
~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_annotated_peaks_.txt -d$'\t' -o p602_vs_p600_601_H3K27me3_annotated_peaks.xls4.0. combine macs2 to getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl
replace the initial peak identification by using your MACS2 output.
#http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/ngs/diffExpression.html
#getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl = findPeaks + annotatePeaks.pl + getDiffExpression.pl
#annotatePeaks.pl tss hg38 -raw -d H3K4me3-Mock-rep1/ H3K4me3-Mock-rep2/ H3K4me3-WNT-rep1/ H3K4me3-WNT-rep3/ > countTable.peaks.txt
Here's an outline of how we might be able to replace the initial peak identification by using your MACS2 output.
#TODO: using MACS call peaks of the data H3K27ac.4.1. MACS2 peak calling
# -- macs2 --> bed --> annotatePeaks.pl
conda activate homer
cd macs2
macs2 callpeak -t ../results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -c ../results/picard/V_8_3_1_p600_601_d12_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bam -f BAM -g hs -n p600_601_d12_D1 -q 0.05
macs2 callpeak -t ../results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -c ../results/picard/V_8_3_2_p600_601_d9_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bam -f BAM -g hs -n p600_601_d9_D2 -q 0.05
macs2 callpeak -t ../results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -c ../results/picard/V_8_4_2_p602_d8_D1_input.dedup.sorted.bam -f BAM -g hs -n p602_d8_D1 -q 0.05
macs2 callpeak -t ../results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3.dedup.sorted.bam -c ../results/picard/V_8_4_1_p602_d8_D2_input.dedup.sorted.bam -f BAM -g hs -n p602_d8_D2 -q 0.05
awk 'OFS="\t" {print $1, $2, $3, $4, $5}' p600_601_d12_D1_peaks.narrowPeak > p600_601_d12_D1_peaks.bed
awk 'OFS="\t" {print $1, $2, $3, $4, $5}' p600_601_d9_D2_peaks.narrowPeak > p600_601_d9_D2_peaks.bed
awk 'OFS="\t" {print $1, $2, $3, $4, $5}' p602_d8_D1_peaks.narrowPeak > p602_d8_D1_peaks.bed
awk 'OFS="\t" {print $1, $2, $3, $4, $5}' p602_d8_D2_peaks.narrowPeak > p602_d8_D2_peaks.bed
#annotatePeaks.pl p601_d8_D1_peaks.bed hg38 > p601_d8_D1_annotated_peaks.txt
#annotatePeaks.pl p601_d8_D2_peaks.bed hg38 > p601_d8_D2_annotated_peaks.txt
#annotatePeaks.pl p604_d8_D1_peaks.bed hg38 > p604_d8_D1_annotated_peaks.txt
#annotatePeaks.pl p604_d8_D2_peaks.bed hg38 > p604_d8_D2_annotated_peaks.txt4.2. Convert your MACS2 peaks to HOMER-compatible format. You can do this manually or with a script. For example:
It’s possible to use more information from the MACS2 output file to create a more informative peaks.txt file for HOMER. However, it’s important to note that some information that HOMER needs for its differential peak analysis is not available in the MACS2 output (such as Normalized Tag Count, Control Tags, and others). But we can certainly map more of the available MACS2 columns to the corresponding HOMER columns.
#The following awk command can be used to convert more MACS2 information into the HOMER format:
cd macs2
#awk 'BEGIN{OFS="\t"}{print $1,$2,$3,"Peak_"NR,$5,$6,$7,$8,$9,$10}' macs2_peaks.bed > macs2_peaks.txt
awk 'BEGIN{OFS="\t"} NR > 1 {print $10, $1, $2, $3, "+", "0", "0", $6, $6, "0", $8, $5, $9, "0", "0"}' p600_601_d12_D1_peaks.xls > p600_601_d12_D1_macs2_peaks.txt
awk 'BEGIN{OFS="\t"} NR > 1 {print $10, $1, $2, $3, "+", "0", "0", $6, $6, "0", $8, $5, $9, "0", "0"}' p600_601_d9_D2_peaks.xls > p600_601_d9_D2_macs2_peaks.txt
awk 'BEGIN{OFS="\t"} NR > 1 {print $10, $1, $2, $3, "+", "0", "0", $6, $6, "0", $8, $5, $9, "0", "0"}' p602_d8_D1_peaks.xls > p602_d8_D1_macs2_peaks.txt
awk 'BEGIN{OFS="\t"} NR > 1 {print $10, $1, $2, $3, "+", "0", "0", $6, $6, "0", $8, $5, $9, "0", "0"}' p602_d8_D2_peaks.xls > p602_d8_D2_macs2_peaks.txt
This command will:
* Skip the header line (NR > 1)
* Map the MACS2 peak name ($10) to the HOMER PeakID
* Map the MACS2 chromosome, start, and end ($1, $2, $3) to the HOMER chr, start, end
* Use a placeholder "+" for the HOMER strand
* Use a placeholder "0" for the HOMER Normalized Tag Count and Focus Ratio
* Map the MACS2 pileup ($6) to the HOMER findPeaks Score and Total Tags
* Use a placeholder "0" for the HOMER Control Tags
* Map the MACS2 fold_enrichment ($8) to the HOMER Fold Change vs Control
* Map the MACS2 abs_summit ($5) to the HOMER p-value vs Control
* Map the MACS2 -log10(qvalue) ($9) to the HOMER Fold Change vs Local
* Use a placeholder "0" for the HOMER p-value vs Local and Clonal Fold Change
This script is limited by the differences in the information provided by MACS2 and HOMER. While it makes use of as much information as possible from the MACS2 output, some columns in the HOMER format still have to be filled with placeholder values.4.3. Associate the converted peak files with their respective tag directories. In HOMER, peak files can be associated with a tag directory by placing them in the tag directory with the filename “peaks.txt”.
#mv homer/p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt homer/p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3/peaks_raw.txt
#mv homer/p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt homer/p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3/peaks_raw.txt
#mv homer/p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt homer/p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3/peaks_raw.txt
#mv homer/p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt homer/p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3/peaks_raw.txt
cp macs2/p600_601_d12_D1_macs2_peaks.txt homer/p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt
cp macs2/p600_601_d9_D2_macs2_peaks.txt homer/p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt
cp macs2/p602_d8_D1_macs2_peaks.txt homer/p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt
cp macs2/p602_d8_D2_macs2_peaks.txt homer/p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt
#33896 p600_601_d12_D1_peaks.bed
#47977 p600_601_d9_D2_peaks.bed
#59049 p602_d8_D1_peaks.bed
#33730 p602_d8_D2_peaks.bed
#CHECK and DELETE headers including "name ..." in the new peaks.txt files!
#Repeat this for each of your tag directories.4.4. The program getDifferentialPeaksReplicates will essentially perform 3 steps, in the step 2 was modified.
First, it will pool the target tag directories and input directories separately into pooled experiments and perform an initial peak identification (using findPeaks). Pooling the experiments is generally more sensitive than trying to merge the individual peak files coming from each experiment (although this can be done using the “-use
#-- Successful modification of the script getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl (Explain how to archieve getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl, only for DEBUG, for calculation directly run getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl!) --
#The -d parameter in the mergePeaks function in HOMER is used to specify the maximum distance between peak centers
#change Max distance to merge to 30000 bp in getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl
#mergePeaks -d 500 [100,1000] temp_sorted | sort
#conda list homer #4.11
mergePeaks -d 2000 p600_601_d12_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt p600_601_d9_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt > mergePeaks_res1.txt # get 37569 records
mergePeaks -d 2000 p602_d8_D1_H3K4me3/peaks.txt p602_d8_D2_H3K4me3/peaks.txt > mergePeaks_res2.txt # get 44076 records
#(homer) jhuang@hamburg:~/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung/results_chipseq_histone_hg38/H3K4me3_H3K27ac__H3K27me3_H3K9me3/homer$
#getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl -use How to Create a New User on Ubuntu Server?
-
Restricting User ‘malawi’ from Installing System-wide Programs and Verifying Permissions
chmod o-rx /home/jhuang ls -ld /home/jhuang cd /home/jhuang groups malawi sudo deluser malawi sudo jhuang@hamm:~$ groups malawi #malawi : malawi jhuang@hamm:~$ groups jhuang #jhuang : jhuang adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare docker -
Ensuring Full Permissions for User ‘malawi’ in Their Home Directory
#chmod -R u=rwx,go= /home/malawi ls -ld /home/malawi #drwxr-xr-x sudo chown malawi:malawi /home/malawi #sudo chmod 700 /home/malawi #sudo chmod -R 700 /home/malawi sudo chmod 755 /home/malawi sudo chmod -R 755 /home/malawi ls -ld /home/malawi -
Protecting Other Users’ Directories from Access by ‘malawi’
sudo chmod o-rx /home/jhuang sudo chmod o-rx /mnt/h1/jhuang #for dir in /home/*; do # if [ -d "$dir" ]; then # sudo chmod o-rx "$dir" # fi #done ls -ld /home/jhuang -
Changing User Passwords
sudo passwd malawi passwd -
Changing User Passwords
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("SeuratObject") install.packages("Seurat") -
#(NOT GOOD) from 775 to o-rx #sudo chmod o-rx /mnt/h1/jhuang #sudo chmod -R o-rx /mnt/h1/jhuang #sudo chmod o-rx /home/jhuang #sudo chmod -R o-rx /home/jhuang #from 775 to 750 sudo chmod 750 /mnt/h1/jhuang sudo chmod -R 750 /mnt/h1/jhuang sudo chmod 750 /home/jhuang sudo chmod -R 750 /home/jhuang #END -
install r and r-seurat with miniconda3
mkdir -p ~/miniconda3 wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -O ~/miniconda3/miniconda.sh bash ~/miniconda3/miniconda.sh -b -u -p ~/miniconda3 rm -rf ~/miniconda3/miniconda.sh ~/miniconda3/bin/conda init bash conda create -n r -c bioconda r r-seurat conda activate r #> .libPaths() #[1] "/home/malawi/miniconda3/envs/r/lib/R/library" if (!requireNamespace("remotes", quietly = TRUE)) install.packages("remotes") remotes::install_github("satijalab/seurat-data") conda deactivate conda activate r R library(Seurat) library(SeuratData) library(ggplot2) library(patchwork) library(dplyr)
Processing Spatial Transcriptomics Data Using Space Ranger
Using spaceranger to process spatial transcriptomics data involves several steps, from preparing the necessary input files to running the analysis and interpreting the results. Below, I’ll provide a comprehensive example of how to use spaceranger for processing a hypothetical dataset.
Prerequisites:
Install Space Ranger: Make sure spaceranger is installed on your system. You can download it from the 10x Genomics website.
Required Data: You need three key pieces of data:
- Spatial Gene Expression FASTQ files: These are generated by the sequencing instrument.
- Spatial Gene Expression Image: An image of the tissue section.
- Spatial Gene Expression Slide and Capture Area: This information is usually provided by the manufacturer.Example Workflow:
-
Prepare Input Files
Ensure you have the following files:
- FASTQ files: Usually named something like SampleName_S1_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz, SampleName_S1_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz.
- A tissue image file, like tissue_hires_image.png.
- A slide and capture area file, often provided by the manufacturer.
-
Create a Reference Dataset
If you don’t already have a reference dataset for your species of interest, you can create one using the spaceranger mkref command. For example:
spaceranger mkref --genome=GRCh38 --fasta=GRCh38.fasta --genes=genes.gtf --nthreads=8 --memgb=64Replace GRCh38.fasta and genes.gtf with the paths to your genome FASTA and gene annotation GTF files, respectively.
-
Running Space Ranger
The core of the spaceranger workflow is the count command, which aligns reads, generates feature-barcode matrices, and performs spatial analysis. The command looks something like this:
spaceranger count --id=sample_output \ --transcriptome=/path/to/refdata-cellranger-GRCh38-3.0.0 \ --fastqs=/path/to/fastqs \ --sample=SampleName \ --image=/path/to/tissue_hires_image.png \ --slide=V19J01-123 \ --area=A1 \ --nthreads=16 \ --memgb=64 --id: The name of the output folder. --transcriptome: Path to the reference dataset. --fastqs: Path to the folder containing FASTQ files. --sample: Name of the sample. --image: Path to the high-resolution tissue image. --slide and --area: Slide and capture area information. --nthreads and --memgb: Specify computational resources. -
Analyze Output
Once the spaceranger count command is complete, it will generate an output directory (sample_output in this case) containing several files, including:
- Feature-barcode matrices
- Analysis files (clustering, dimensionality reduction, etc.)
- Images showing gene expression overlaid on the tissue image
-
Further Analysis
The resulting data can be further analyzed using tools like Seurat (R), Scanpy (Python), or Loupe Browser (from 10x Genomics).
Additional Notes:
Always refer to the specific version of the spaceranger documentation you are using, as commands and options might vary slightly between versions.
Ensure your computational environment has enough resources (CPU, memory) to handle the dataset size.
This workflow is a basic example. Depending on your specific experiment and data, additional steps or modifications might be necessary.Prepare the databases for vrap
-
I used an strategy, at first annotate the contigs using the virus-speicific data and bacteria-speicific data, then using more general databases nt and nr. The results are as attached. For some samples, for examples S5, which we can detected several contigs as gammaherpesvius. For the bacteria, it is more conversed.
# -- txid10239 (Virus) and Taxonomy ID: 2 (Bacteria) -- # -- Virus -- #TODO: from 1,100,000 --> 1,288,629 (up to 2020/07/01); bacteria we can use refseq (up to 2020/07/01)! #--virus bacteria-refseq-fasta, then virus sequences, virus protein as default database, then nt and nr! #TODO!: download bact_nt_db and use in '--virus bact_nt_db'! # pip install ncbi-genome-download # ncbi-genome-download -F fasta bacteria # ncbi-genome-download -F fasta virus # https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/microbes/ # https://www.biostars.org/p/9503245/ -
download bacteria refseq with datasets
#https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/docs/v1/download-and-install/ The NCBI Datasets datasets command line tools are datasets and dataformat . #datasets download genome bacteria --assembly-source refseq --dehydrated --filename bacteria_refseq.zip ~/Tools/datasets download genome bacteria --assembly-source refseq --dehydrated --exclude-protein --exclude-genomic-cds --exclude-rna --exclude-gff3 --filename bacteria_refseq_fasta.zip ~/Tools/datasets download genome taxon bacteria #2,231,190 ~/Tools/datasets download genome taxon bacteria --assembly-source refseq --dehydrated --exclude-protein --exclude-genomic-cds --exclude-rna --exclude-gff3 --filename bacteria_refseq.zip #325,471 #~/Tools/datasets download genome taxon virus #97,281 records #~/Tools/datasets download genome taxon virus --assembly-source refseq --dehydrated --exclude-protein --exclude-genomic-cds --exclude-rna --exclude-gff3 --filename virus_refseq.zip #14,992 #Unzip the file unzip bacteria_refseq.zip -d bacteria_refseq unzip virus_refseq.zip -d virus_refseq #Rehydrate the file: I'm recommending the dehydrated option because it's actually faster and more reliable, despite the additional steps. By default, the data package includes genomic, transcript, protein and cds sequences, in addition to gff3. If you only need the genomic fasta sequences, you can use this command instead: ~/Tools/datasets rehydrate --directory bacteria_refseq/ ~/Tools/datasets rehydrate --directory virus_refseq/ #29984 -
run vrap.py with –host genome.fa –virus bacteria_refseq [default viral_db up to 2020_07_01] -n nt -r nr
# -- Virus -- vrap/vrap.py -1 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20430/635290002_CMV_S4_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20430/635290002_CMV_S4_R2_001.fastq.gz -o CMV_S4_unbiased2 --host /home/jhuang/REFs/genome.fa -n /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nt -a /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nr -t 40 -l 200 vrap/vrap.py -1 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20431/635850623_EBV_S5_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20431/635850623_EBV_S5_R2_001.fastq.gz -o EBV_S5_unbiased2 --host /home/jhuang/REFs/genome.fa -n /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nt -a /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nr -t 40 -l 200 # -- Control -- vrap/vrap.py -1 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20428/neg_control_S2_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20428/neg_control_S2_R2_001.fastq.gz -o neg_control_S2_unbiased2 --host /home/jhuang/REFs/genome.fa -n /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nt -a /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nr -t 40 -l 200 # -- Bacteria -- vrap/vrap.py -1 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20427/635031018_E_faecium_S1_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20427/635031018_E_faecium_S1_R2_001.fastq.gz -o E_faecium_S1_unbiased2 --host /home/jhuang/REFs/genome.fa -n /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nt -a /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nr -t 40 -l 200 vrap/vrap.py -1 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20429/635724976_S_aureus_epidermidis_S3_R1_001.fastq.gz -2 ../231114_VH00358_62_AACYCYWM5_cfDNA/p20429/635724976_S_aureus_epidermidis_S3_R2_001.fastq.gz -o S_aureus_epidermidis_S3_unbiased2 --host /home/jhuang/REFs/genome.fa -n /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nt -a /mnt/h1/jhuang/blast/nr -t 40 -l 200 #END
ChIP-seq using HOMER (-style factor, findPeaks + default getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl)
-
nextflow ChIP-seq run for NHDF_p783
#under Raw_Data for ChIP-seq ln -s ./230306_NB501882_0417_AHMVHHBGXN/2023_022_nf_denise/nf859/3_NHDF_Donor_1_p783_input_S5_R1_001.fastq.gz p783_input_DonorI.fastq.gz ln -s ./230306_NB501882_0417_AHMVHHBGXN/2023_022_nf_denise/nf860/4_NHDF_Donor_2_p783_input_S6_R1_001.fastq.gz p783_input_DonorII.fastq.gz ln -s ./230306_NB501882_0417_AHMVHHBGXN/2023_022_nf_denise/nf861/5_NHDF_Donor_1_p783_ChIP_S7_R1_001.fastq.gz p783_ChIP_DonorI.fastq.gz ln -s ./230306_NB501882_0417_AHMVHHBGXN/2023_022_nf_denise/nf862/6_NHDF_Donor_2_p783_ChIP_S8_R1_001.fastq.gz p783_ChIP_DonorII.fastq.gz #'hg38' { bwa = "/home/jhuang/REFs/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/BWAIndex/" # blacklist = "/home/jhuang/REFs/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/blacklists/hg38-blacklist.bed" # gtf = "/home/jhuang/REFs/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Annotation/Genes/genes.gtf" # } ln -s /home/jhuang/Tools/NGI-ChIPseq/ . (chipseq) nextflow run NGI-ChIPseq/main.nf --reads '/home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/Raw_Data/*.fastq.gz' --genome hg38 --macsconfig macs.config --singleEnd --blacklist_filtering -profile standard --project Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung --outdir results_LT_DNA_Bindung_hg38 -resume #By the way: nextflow RNA-seq run for NHDF_p783 (NOT the topics of the post). #under Raw_Data for RNA-seq cp ~/DATA/Data_Denise_tx_epi_MCPyV_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq/Raw_Data/V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI.fastq.gz ./ cp ~/DATA/Data_Denise_tx_epi_MCPyV_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_RNASeq/Raw_Data/V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII.fastq.gz ./ #under Raw_Data_p783_RNAseq for RNA-seq ln -s ../Raw_Data/V_8_2_4_p600_d8_DonorI.fastq.gz ctrl_DonorI.fastq.gz ln -s ../Raw_Data/V_8_2_3_p600_d8_DonorII.fastq.gz ctrl_DonorII.fastq.gz ln -s ../Raw_Data/230306_NB501882_0417_AHMVHHBGXN/2023_022_nf_denise/nf857/1_NHDF_Donor_1_p783_S1_R1_001.fastq.gz p783_DonorI.fastq.gz ln -s ../Raw_Data/230306_NB501882_0417_AHMVHHBGXN/2023_022_nf_denise/nf858/2_NHDF_Donor_2_p783_S2_R1_001.fastq.gz p783_DonorII.fastq.gz #Note that we need to regenerate MultiQC.html after ignoring 'Biotype Counts', since --fcGroupFeaturesType gene_name cannot generate the real biotype counts! (rnaseq_2021) nextflow run rnaseq --reads '/home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/Raw_Data_p783/RNA_seq/*.fastq.gz' --fasta "/home/jhuang/REFs/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa" --gtf "/home/jhuang/REFs/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Annotation/Genes/genes.gtf" --bed12 "/home/jhuang/REFs/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Annotation/Genes/genes.bed" --singleEnd -profile standard --aligner star --saveReference -resume --saveAlignedIntermediates --skip_rseqc --skip_dupradar --skip_genebody_coverage --skip_preseq --skip_edger --fcGroupFeaturesType gene_name -
nextflow ChIP-seq run for data of truncated LT-Ag + sT expression of WaGa and HEK293
#160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX cat ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_input_1_10_p197_1/293_input_1_10_p197_1_GTAGAG_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_input_1_10_p197_1/293_input_1_10_p197_1_GTAGAG_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz > HEK293_Input_p197_r1.fastq.gz cat ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_input_1_10_p197_2/293_input_1_10_p197_2_GTCCGC_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_input_1_10_p197_2/293_input_1_10_p197_2_GTCCGC_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz > HEK293_Input_p197_r2.fastq.gz cat ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_input_1_10_p197_3/293_input_1_10_p197_3_GTGAAA_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_input_1_10_p197_3/293_input_1_10_p197_3_GTGAAA_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz > HEK293_Input_p197_r3.fastq.gz cat ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_lt_p197_1/293_lt_p197_1_TAGCTT_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_lt_p197_1/293_lt_p197_1_TAGCTT_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz > HEK293_LT_p197_r1.fastq.gz cat ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_lt_p197_2/293_lt_p197_2_GGCTAC_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_lt_p197_2/293_lt_p197_2_GGCTAC_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz > HEK293_LT_p197_r2.fastq.gz cat ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_lt_p197_3/293_lt_p197_3_AGTCAA_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz ../160719_SN7001212_0156_AC8K76ACXX/Sample_293_lt_p197_3/293_lt_p197_3_AGTCAA_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz > HEK293_LT_p197_r3.fastq.gz #140117_SN7001212_0097_AC3ECBACXX cat ../140117_SN7001212_0097_AC3ECBACXX/Sample_waga_igg/waga_igg_TAGCTT_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz ../140117_SN7001212_0097_AC3ECBACXX/Sample_waga_igg/waga_igg_TAGCTT_L004_R1_001.fastq.gz > WaGa_IgG.fastq.gz cat ../140117_SN7001212_0097_AC3ECBACXX/Sample_waga_lt/waga_lt_GGTAGC_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz ../140117_SN7001212_0097_AC3ECBACXX/Sample_waga_lt/waga_lt_GGTAGC_L004_R1_001.fastq.gz > WaGa_LT.fastq.gz ln -s /home/jhuang/Tools/NGI-ChIPseq/ . (chipseq) nextflow run NGI-ChIPseq/main.nf --reads '/home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/LTtr-ChIP/Raw_Data/*.fastq.gz' --genome hg38 --macsconfig macs.config --singleEnd --blacklist_filtering -profile standard --project Denise_LTtr_DNA_Bindung --outdir results_LTtr_DNA_Bindung_hg38 -resume -
makeTagDirectory
conda activate myperl mkdir results_ChIPseq_K331A_hg38/homer; cd results_ChIPseq_K331A_hg38/homer #makeTagDirectory <output directory> <input file> -genome hg38 for sample in p783_ChIP_DonorI p783_ChIP_DonorII p783_input_DonorI p783_input_DonorII; do makeTagDirectory ${sample} ../picard/${sample}.dedup.sorted.bam -genome hg38 done -
generate bigwigs
#makeUCSCfile peaks.txt -f peaks.bed -o auto -noadj -bigWig sample.bw -genome hg38 for sample in p783_ChIP_DonorI p783_ChIP_DonorII p783_input_DonorI p783_input_DonorII; do makeUCSCfile ${sample} -pseudo 1 -bigWig /home/jhuang/REFs/hg38.chromSizes -o auto -style chipseq -norm 1e7 -normLength 100 -fsize 1 done mv ./p783_ChIP_DonorI/p783_ChIP_DonorI.ucsc.bigWig ./p783_ChIP_DonorI/LT_K331A_DI.bigWig mv ./p783_ChIP_DonorII/p783_ChIP_DonorII.ucsc.bigWig ./p783_ChIP_DonorII/LT_K331A_DII.bigWig mv ./p783_input_DonorI/p783_input_DonorI.ucsc.bigWig ./p783_input_DonorI/LT_K331A_DI_input.bigWig mv ./p783_input_DonorII/p783_input_DonorII.ucsc.bigWig ./p783_input_DonorII/LT_K331A_DII_input.bigWig -
peak calling, get peaks.txt
#findPeaks <tag directory> -i <input file> -o <output file> -genome hg38 findPeaks p783_ChIP_DonorI -style factor -o auto -i p783_input_DonorI findPeaks p783_ChIP_DonorII -style factor -o auto -i p783_input_DonorII cp ../reproduce_2023/tagDirectories/ ./ cd homer ln -s ../tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor1 ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor2 ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor1_Input ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor2_Input ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r1 ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r2 ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r1_Input ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r2_Input ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/HEK293_LT+sT_r2 ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/HEK293_LT+sT_r3 ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/HEK293_LT+sT_r2_Input ./ ln -s ../tagDirectories/HEK293_LT+sT_r3_Input ./ findPeaks NHDF_LT_Donor1 -style factor -o auto -i NHDF_LT_Donor1_Input findPeaks NHDF_LT_Donor2 -style factor -o auto -i NHDF_LT_Donor2_Input findPeaks Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r1 -style factor -o auto -i Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r1_Input findPeaks Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r2 -style factor -o auto -i Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r2_Input findPeaks HEK293_LT+sT_r2 -style factor -o auto -i HEK293_LT+sT_r2_Input findPeaks HEK293_LT+sT_r3 -style factor -o auto -i HEK293_LT+sT_r3_Input -
peak calling using getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl
cp -r ../../reproduce_2023/tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor1_Input ./ cp -r ../../reproduce_2023/tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor2_Input ./ cp -r ../../reproduce_2023/tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor1 ./ cp -r ../../reproduce_2023/tagDirectories/NHDF_LT_Donor2 ./ #-annStats annStats.txt conda activate myperl getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl -t p783_ChIP_DonorI p783_ChIP_DonorII -i p783_input_DonorI p783_input_DonorII -genome hg38 -use peaks.txt > peaks_K331A_LT.txt mv peaks_K331A_LT.txt peaks_NHDF_K331A_LT.txt getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl -t NHDF_LT_Donor1 NHDF_LT_Donor2 -i NHDF_LT_Donor1_Input NHDF_LT_Donor2_Input -genome hg38 -use peaks.txt > peaks_NHDF_LT.txt getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl -t Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r1 Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r2 -i Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r1_Input Pfsk-1B_LT+sT_r2_Input -genome hg38 -use peaks.txt > peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt getDifferentialPeaksReplicates.pl -t HEK293_LT+sT_r2 HEK293_LT+sT_r3 -i HEK293_LT+sT_r2_Input HEK293_LT+sT_r3_Input -genome hg38 -use peaks.txt > peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt -
merge peaks: tried 0, 200, 500, 1000, 2000
#http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/ngs/mergePeaks.html mergePeaks -d 1000 peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt peaks_NHDF_LT.txt -prefix celllines -venn celllines.txt -matrix celllines #-- generate bed files -- awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' peaks_NHDF_LT.txt > peaks_NHDF.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt > peaks_HEK293.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt > peaks_PFSK-1.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt > peaks_HEK293_only.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt > peaks_HEK293_NHDF.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt > peaks_NHDF_only.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt > peaks_PFSK-1_only.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt > peaks_PFSK-1_HEK293.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt > peaks_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF.bed; awk 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $2,$3,$4,$1,$6}' celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt > peaks_PFSK-1_NHDF.bed; #-- annotate the peaks -- annotatePeaks.pl peaks_NHDF_LT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_NHDF.txt annotatePeaks.pl peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_HEK293.txt annotatePeaks.pl peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_HEK293_only.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_HEK293_NHDF.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_NHDF_only.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_only.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_HEK293.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt_peaks_HEK293_LT+sT.txt_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF.txt annotatePeaks.pl celllines_peaks_PFSK-1_LT+sT.txt_peaks_NHDF_LT.txt hg38 > annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_NHDF.txt mkdir ../beds_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF; for sample in peaks_HEK293_only peaks_PFSK-1_only peaks_NHDF_only peaks_HEK293 peaks_PFSK-1 peaks_NHDF peaks_PFSK-1_HEK293 peaks_PFSK-1_NHDF peaks_HEK293_NHDF peaks_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF; do grep -v "cmd" ${sample}.bed > ../beds_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF/${sample}_.bed done #Chr Start End PeakID (cmd=annotatePeaks.pl common_peaks_NHDF.txt hg38) Peak Score Strand ~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py celllines.txt annotatedPeaks_HEK293_only.txt annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_only.txt annotatedPeaks_NHDF_only.txt annotatedPeaks_HEK293.txt annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1.txt annotatedPeaks_NHDF.txt annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_HEK293.txt annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_NHDF.txt annotatedPeaks_HEK293_NHDF.txt annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF.txt -d$'\t' -o annotatedPeaks_PFSK-1_HEK293_NHDF.xls #IMPORTANT: DELETE the column 'Strand' marked with '+' in the merged Excel file!
Small RNA processing
Small RNA sequencing is a type of RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) that specifically targets and sequences small RNA molecules in a sample.
RNA-seq is a technique that uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment, capturing a snapshot of the transcriptome.
Small RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), play crucial roles in gene regulation. They typically range from 20 to 30 nucleotides in length.
-
prepare raw data
#mv Data_Ute_smallRNA_3/bundle_v1 Data_Ute_smallRNA_5 ln -s ../Data_Ute_smallRNA_3/bundle_v1 . #OLD MKL_1_wt_1_221216.fastq.gz -> ../221216_NB501882_0404_AHLVNMBGXM/ute/nf796/MKL_1_wt_1_S16_R1_001.fastq.gz #OLD MKL_1_wt_2_221216.fastq.gz -> ../221216_NB501882_0404_AHLVNMBGXM/ute/nf797/MKL_1_wt_2_S17_R1_001.fastq.gz ln -s ./230623_newDemulti_smallRNAs/210817_NB501882_0294_AHW5Y2BGXJ_smallRNA_Ute_newDemulti/2021_nf_ute_smallRNA/nf655/MKL_1_derived_EV_miRNA_S1_R1_001.fastq.gz 2021_August_nf655_MKL-1_EV-miRNA.fastq.gz ln -s ./230623_newDemulti_smallRNAs/210817_NB501882_0294_AHW5Y2BGXJ_smallRNA_Ute_newDemulti/2021_nf_ute_smallRNA/nf657/WaGa_derived_EV_miRNA_S2_R1_001.fastq.gz 2021_August_nf657_WaGa_EV-miRNA.fastq.gz ln -s ./230623_newDemulti_smallRNAs/220617_NB501882_0371_AH7572BGXM_smallRNA_Ute_newDemulti/2022_nf_ute_smallRNA/nf774/0403_WaGa_wt_S1_R1_001.fastq.gz 2022_August_nf774_0403_WaGa_wt.fastq.gz ln -s ./230623_newDemulti_smallRNAs/220617_NB501882_0371_AH7572BGXM_smallRNA_Ute_newDemulti/2022_nf_ute_smallRNA/nf780/0505_MKL1_wt_S2_R1_001.fastq.gz 2022_August_nf780_0505_MKL-1_wt.fastq.gz ln -s ./230623_newDemulti_smallRNAs/221216_NB501882_0404_AHLVNMBGXM_smallRNA_Ute_newDemulti/2022_nf_ute_smallRNA/nf796/MKL-1_wt_1_S1_R1_001.fastq.gz 2022_November_nf796_MKL-1_wt_1.fastq.gz ln -s ./230623_newDemulti_smallRNAs/221216_NB501882_0404_AHLVNMBGXM_smallRNA_Ute_newDemulti/2022_nf_ute_smallRNA/nf797/MKL-1_wt_2_S2_R1_001.fastq.gz 2022_November_nf797_MKL-1_wt_2.fastq.gz ln -s ./230602_NB501882_0428_AHKG53BGXT/demulti_new/nf876/1002_WaGa_sT_Dox_S1_R1_001.fastq.gz 2023_June_nf876_1002_WaGa_sT_Dox.fastq.gz ln -s ./230602_NB501882_0428_AHKG53BGXT/demulti_new/nf887/2312_MKL_1_scr_DMSO_S2_R1_001.fastq.gz 2023_June_nf887_2312_MKL-1_scr_DMSO.fastq.gz -
main run
mkdir our_out # -qc -ra TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGGAACTCCAGTCAC -rb 4 #NOT_USED # -mic -mtool Blast -mdb viruses #IGNORING Microbe Module since it is very time-consuming! #jhuang@hamburg:~/DATA/Data_Ute/Data_Ute_smallRNA_5$ java -jar COMPSRA.jar -ref hg38 -qc -ra TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGGAACTCCAGTCAC -rb 4 -rh 20 -rt 20 -rr 20 -rlh 8,17 -aln -mt star -ann -ac 1,2,3,4,5,6 -mic -mtool Blast -mdb viruses -in 2021_August_nf655_MKL-1_EV-miRNA.fastq.gz -out ./our_out/ for sample in 2021_August_nf655_MKL-1_EV-miRNA 2021_August_nf657_WaGa_EV-miRNA 2022_August_nf774_0403_WaGa_wt 2022_August_nf780_0505_MKL-1_wt 2022_November_nf796_MKL-1_wt_1 2022_November_nf797_MKL-1_wt_2 2023_June_nf876_1002_WaGa_sT_Dox 2023_June_nf887_2312_MKL-1_scr_DMSO; do mkdir our_out/${sample}/ java -jar COMPSRA.jar -ref hg38 -rh 20 -rt 20 -rr 20 -rlh 8,17 -aln -mt star -ann -ac 1,2,3,4,5,6 -in ${sample}.fastq.gz -out ./our_out/ done -
prepare Data_Ute/Data_Ute_smallRNA_4/sample.list
2021_August_nf655_MKL-1_EV-miRNA 2021_August_nf657_WaGa_EV-miRNA 2022_August_nf774_0403_WaGa_wt 2022_August_nf780_0505_MKL-1_wt 2022_November_nf796_MKL-1_wt_1 2022_November_nf797_MKL-1_wt_2 2023_June_nf876_1002_WaGa_sT_Dox 2023_June_nf887_2312_MKL-1_scr_DMSO -
extract the raw counts and perform statistical test on pre-defined groups.
#The following results calculate raw counts (Note: If you only want to merge the count files, you can use -fm -fms.) java -jar COMPSRA.jar -ref hg38 -fun -fm -fms 1-8 -fdclass 1,2,3,4,5 -fdann -pro COMPSRA_MERGE -inf ./sample.list -out ./our_out/ #The following command calculate statistical test after defining case and control. java -jar COMPSRA.jar -ref hg38 -fun -fd -fdclass 1,2,3,4,5,6 -fdcase 1-2 -fdctrl 3-6 -fdnorm cpm -fdtest mwu -fdann -pro COMPSRA_DEG -inf ./sample.list -out ./our_out/ sed -i -e 's/_August/-08/g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_November/-11/g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_June/-06/g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_STAR_Aligned_miRNA.txt//g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA.txt #sed -i -e 's/_piRNA.txt//g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_piRNA.txt #sed -i -e 's/_tRNA.txt//g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_tRNA.txt #sed -i -e 's/_snoRNA.txt//g' COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snoRNA.txt #sed -i -e 's/_snRNA.txt//g' COMPSRA_DEG_0_snRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_August/-08/g' COMPSRA_DEG_0_miRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_November/-11/g' COMPSRA_DEG_0_miRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_June/-06/g' COMPSRA_DEG_0_miRNA.txt sed -i -e 's/_STAR_Aligned_miRNA.txt//g' COMPSRA_DEG_0_miRNA.txt import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA.txt', sep='\t', index_col=0) df = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 9']) # Assuming df is your DataFrame df.loc['Sum'] = df.sum(numeric_only=True) df.to_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA_.txt', sep='\t') df = pd.read_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_piRNA.txt', sep='\t', index_col=0) df = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 9']) df.loc['Sum'] = df.sum(numeric_only=True) df.to_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_piRNA_.txt', sep='\t') df = pd.read_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snoRNA.txt', sep='\t', index_col=0) df = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 9']) df.loc['Sum'] = df.sum(numeric_only=True) df.to_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snoRNA_.txt', sep='\t') df = pd.read_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snRNA.txt', sep='\t', index_col=0) df = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 9']) df.loc['Sum'] = df.sum(numeric_only=True) df.to_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snRNA_.txt', sep='\t') df = pd.read_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_tRNA.txt', sep='\t', index_col=0) df = df.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 9']) df.loc['Sum'] = df.sum(numeric_only=True) df.to_csv('COMPSRA_MERGE_0_tRNA_.txt', sep='\t') #samtools flagstat **.bam #47217410 + 0 in total (QC-passed reads + QC-failed reads) #45166321 + 0 mapped (95.66% : N/A) #2051089 + 0 in total (QC-passed reads + QC-failed reads) #TODO: check the microRNA in the paper mentioned in which position? #Single publications on EVs as transport vehicles for specific miRNAs in the pathogenesis of Merkel cell carcinoma have also been reported, such as miR-375 and its function in proliferation ~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA_.txt \ COMPSRA_MERGE_0_piRNA_.txt \ COMPSRA_MERGE_0_tRNA_.txt \ COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snoRNA_.txt \ COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snRNA_.txt \ -d$'\t' -o raw_counts.xls; # sorting the DEG table, change the sheet labels to 'miRNA_between_columns_B-C_and_columns_D-G' ~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py COMPSRA_DEG_0_miRNA.txt -d$'\t' -o normalized_and_significance_test_miRNA.xls; ##merging the row counts and statical values #cut -f1-1 COMPSRA_MERGE_0_snoRNA.txt > f1_MERGE #cut -f1-1 COMPSRA_DEG_0_snoRNA.txt > f1_DEG #cut -f1-1 COMPSRA_MERGE_0_miRNA.txt > f1_MERGE #cut -f1-1 COMPSRA_DEG_0_miRNA.txt > f1_DEG #diff f1_MERGE f1_DEG -
calculate the number of total reads, total human reads and total non-human reads.
for sample in 2021_August_nf655_MKL-1_EV-miRNA 2021_August_nf657_WaGa_EV-miRNA 2022_August_nf774_0403_WaGa_wt 2022_August_nf780_0505_MKL-1_wt 2022_November_nf796_MKL-1_wt_1 2022_November_nf797_MKL-1_wt_2 2023_June_nf876_1002_WaGa_sT_Dox 2023_June_nf887_2312_MKL-1_scr_DMSO; do echo "--------------- ${sample} ---------------" samtools flagstat ./${sample}/${sample}_STAR_Aligned.out.bam samtools flagstat ./${sample}/${sample}_STAR_Aligned_UnMapped.bam done
COMPSRA was composed of five functional modules: Quality Control, Alignment, Annotation, Microbe and Function. They are integrated into a pipeline and each module can also process independently.
-
Quality Control: To deal with fastq files and filter out the adapter sequences and reads with low quality.
- FASTQ files from the small RNA sequencing of biological samples are the default input.
- First, the adapter portions of a read are trimmed along with any randomized bases at ligation junctions that are produced by some small RNA-seq kits (e.g., NEXTflexT M Small RNA-Seq kit). The adapter sequences, typically situated at the 3′ (3-prime) end, vary across different kits. Some commonly employed adapter sequences are listed below:
- TruSeq Small RNA (Illumina) TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGG
- Small RNA Kits V1 (Illumina) TCGTATGCCGTCTTCTGCTTGT
- Small RNA Kits V1.5 (Illumina) ATCTCGTATGCCGTCTTCTGCTTG
- NEXTflex Small RNA Sequencing Kit v3 for Illumina Platforms (Bioo Scientific) TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGG
- LEXOGEN Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit (Illumina) TGGAATTCTCGGGTGCCAAGGAACTCCAGTCAC
- The read quality of the remaining sequence is evaluated using its corresponding Phred score.
- Poor quality reads are removed according to quality control parameters set in the command line (-rh 20 –rt 20 –rr 20).
- Users can specify qualified reads of specific length intervals for input into subse-quent modules.
-
Alignment:
- To align the clean reads to the reference genome. COMPSRA uses STAR as its default RNA sequence aligner with default parameters which are customizable on the command line.
- Qualified reads from the QC module output are first mapped to the human genome hg19/hg38, and then aligned reads are quantified and annotated in the Annotation Module.
- Reads that could not be mapped to the human genome are saved into a FASTA file for input into the Microbe Module.
-
Annotation:
- To annotate different kinds of circulating RNAs based on the alignment result.
- COMPSRA currently uses several different small RNA databases for annotating human genome mapped reads and provides all the possible annotations:
- miRBase (Kozomara and Griffiths-Jones, 2011) for miRNA;
- piRNABank (Sai Lakshmi and Agrawal, 2008);
- piRBase (Zhang, et al., 2014) and piRNACluster (Rosenkranz, 2016) for piRNA;
- gtRNAdb (Chan and Lowe, 2016) for tRNA;
- GENCODE release 27 (Harrow, et al., 2012) for snRNA and snoRNA;
- circBase (Glazar, et al., 2014) for circular RNA.
- To conform the different reference human genome versions in these databases, we use an automatic LiftOver created by the UCSC Genome Browser Group.
- All the databases used are already pre-built, enabling speedy annotation.
-
Microbe:
- To predict the possible species of microbes existed in the samples.
- The qualified reads that could not be mapped to the human genome in the Alignment Module are aligned to the nucleotide (nt) database (Coordinators, 2013) from UCSC using BLAST.
- The four major microbial taxons archaea, bacteria, fungi and viruses are supported.
-
Function:
- To perform differential expression analysis and other functional studies to be extended.
- The read count of each RNA molecule that is identified in the Annotation Module is outputted as a tab-delimited text file according to RNA type.
- With more than one sample FASTQ file inputs, the output are further aggregated into a data matrix of RNA molecules as rows and samples as columns showing the read counts of an RNA molecule across different samples.
- The user can mark each sample FASTQ file column as either a case or a control in the command line, and perform a case versus control differential expression analysis for each RNA molecule using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test (Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test) as the default statistical test.
Density of motif plots and its statistical tests
-
plot peaks
@Input: the peak bed-files @Output: peak_tss_distances_NHDF_.xlsx peak_tss_distances_NHDF_.txt peak_distribution_NHDF_.csv peak_distribution_NHDF_.png @RUN: python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_NHDF_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa @RUN: python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_HEK293_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa @RUN: python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_PFSK-1_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa @RUN: python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_K331A_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa -
filtering the cloeset genes when the absolute values of Distance to TSS is smaller than or equal to 3000 using python.
@Input: peak_tss_distances_NHDF_.txt @RUN: python3 filter_genes_with_peaks.py peak_tss_distances_NHDF_.txt import pandas as pd import argparse def filter_and_save_genes(input_file): # Read the dataframe df = pd.read_csv(input_file, sep='\t') # Convert Distance to TSS to absolute values df['Distance to TSS'] = df['Distance to TSS'].abs() # Filter dataframe where Distance to TSS <= 3000 filtered_df = df[df['Distance to TSS'] <= 3000] # Get the list of gene names gene_names = filtered_df['Closest Gene (Gene name)'].tolist() # Join the gene names with a comma gene_names_string = ','.join(gene_names) # Print the gene names print(gene_names_string) # Save the gene names to a text file #with open('gene_names.txt', 'w') as file: # file.write(gene_names_string) # Convert the list of gene names to a DataFrame gene_names_df = pd.DataFrame(gene_names, columns=['Gene Name']) # Save the DataFrame to an Excel file gene_names_df.to_excel('gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_NHDF.xlsx', index=False) if __name__ == '__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Process some integers.') parser.add_argument('input_file', help='The path to the input file') args = parser.parse_args() filter_and_save_genes(args.input_file) -
draw venn diagrams based on the gene names
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib_venn import venn2, venn3 # Read the gene names from the Excel files df1 = pd.read_excel('gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_NHDF.xlsx') # generated in the STEP 2 df2 = pd.read_excel('gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_K331A.xlsx') #df2 = pd.read_excel('gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_HEK293.xlsx') df3 = pd.read_excel('gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_PFSK-1.xlsx') # Create sets from the gene names set1 = set(df1['Gene Name']) set2 = set(df2['Gene Name']) set3 = set(df3['Gene Name']) venn2([set1, set2], set_labels=('NHDF LT', 'NHDF LT K331A')) #, set_colors=('skyblue', 'lightgreen') #venn3([set1, set2, set3], set_labels=('NHDF LT', 'HEK293 LT+sT', 'PFSK-1 LT+sT')) plt.title('Genes with Peaks in Promoter', fontsize=16) plt.xticks(fontsize=12) plt.yticks(fontsize=12) plt.savefig('Venn_Diagram_of_Genes_with_Peaks_in_Promoter_NHDF_vs_K331A.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight') # Save the Venn diagram as an image file plt.show() # Display the Venn diagram -
extract the promoter seqeuences, generating promoter_sequences_3000_3000.fasta
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # ./1_generate_promoter_sequences.py /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db #improve the code to exact alsogene_type except for ensemble_ids and gene_symbol, and save them in the heads. # # Create the database from the GTF file # gtf_file = 'gencode.v43.annotation.gtf' # db_file = 'gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db' # db = gffutils.create_db(gtf_file, dbfn=db_file, force=True, merge_strategy='merge', verbose=True) import gffutils from pyfaidx import Fasta import argparse from Bio import SeqIO from Bio.SeqRecord import SeqRecord from Bio.Seq import Seq def extract_promoter_sequences(gencode_db, genome_records, upstream_length=3000, downstream_length=3000): db = gffutils.FeatureDB(gencode_db, keep_order=True) promoters = [] for gene in db.features_of_type('gene'): #CDS gene_type = gene.attributes.get('gene_type', [''])[0] #if gene_type == 'protein_coding': if True: if gene.strand == '+': promoter_start = max(gene.start - upstream_length, 1) promoter_end = gene.start + downstream_length - 1 else: # gene.strand == '-' promoter_start = gene.end - downstream_length + 1 promoter_end = min(gene.end + upstream_length, len(genome_records[gene.chrom])) promoter_seq = str(genome_records[gene.chrom][promoter_start-1:promoter_end]) if gene.strand == '-': promoter_seq = str(Seq(promoter_seq).reverse_complement()) gene_symbol = gene.attributes.get('gene_name', [''])[0] gene_type = gene.attributes.get('gene_type', [''])[0] #20042 in which gene_type == 'protein_coding', while 62703 all types. header = f"{gene.id} | Symbol: {gene_symbol} | Type: {gene_type}" #header = f"{gene_symbol}" #record = SeqRecord(Seq(promoter_seq.upper()), id=gene.id, description=gene_symbol) record = SeqRecord(Seq(promoter_seq.upper()), id=gene.id, description=header) promoters.append(record) return promoters if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Plot peak distribution around TSS.') parser.add_argument('gencode_db', type=str, help='Path to the gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db file') args = parser.parse_args() genome_records = Fasta('/ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa') promoter_sequences = extract_promoter_sequences(args.gencode_db, genome_records) SeqIO.write(promoter_sequences, "promoter_sequences_3000_3000.fasta", "fasta") -
find motifs in promoters, generating the file
#!/usr/bin/env python3 #./2_find_motifs_in_promoters.py import re from Bio import SeqIO def find_motif_frequency_and_distribution(fasta_file, output_file, motif_1="GRGGC", motif_2="GCCYC"): motif_1 = motif_1.replace("R", "[AG]").replace("Y", "[CT]") motif_2 = motif_2.replace("R", "[AG]").replace("Y", "[CT]") promoter_sequences = SeqIO.parse(fasta_file, "fasta") with open(output_file, 'w') as f: f.write("PromoterID\tGene_Symbol\tGene_Type\tMotif_GRGGC_Count\tMotif_GCCYC_Count\tMotif_GRGGC_Center_Positions\tMotif_GCCYC_Center_Positions\n") for promoter in promoter_sequences: header_parts = promoter.description.split("|") promoter_id = header_parts[0].strip() gene_symbol = header_parts[1].strip() gene_type = header_parts[2].strip() motif1_positions = [(m.start() + len(motif_1) // 2 - 3000) for m in re.finditer(motif_1, str(promoter.seq))] motif2_positions = [(m.start() + len(motif_2) // 2 - 3000) for m in re.finditer(motif_2, str(promoter.seq))] line = f"{promoter_id}\t{gene_symbol}\t{gene_type}\t{len(motif1_positions)}\t{len(motif2_positions)}\t{motif1_positions}\t{motif2_positions}\n" f.write(line) if __name__ == "__main__": fasta_file = "promoter_sequences_3000_3000.fasta" output_file = "motif_counts_positions.txt" find_motif_frequency_and_distribution(fasta_file, output_file) -
prepare three files from motif_counts_positions.txt and gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_NHDF.xlsx.
library(readxl) #sed -i 's/[][]//g' motif_counts_positions.txt # generated in STEP 5 motif_counts_positions <- read.table("motif_counts_positions.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) # Read the gene names from the Excel files df1 <- read_excel("gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_NHDF.xlsx") # generated in STEP 2 df2 <- read_excel("gene_with_peaks_in_promoter_K331A.xlsx") # Create a new data frame for rows in 'data' where the PromoterID is in NHDF_LT's Closest Gene --> total 1706 genes gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_peak <- motif_counts_positions[motif_counts_positions$PromoterID %in% unique(df1$`Gene Name`), ] gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- sapply(gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, toString) gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions <- sapply(gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions, toString) write.table(gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_peak, file="motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) #sed -i 's/Symbol: //g' motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt #sed -i 's/Type: //g' motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt #sed -i 's/"//g' motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt data1 <- read.table("motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data1$Motif_GCCYC_Count <- as.numeric(data1$Motif_GCCYC_Count) data1$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions), ",") data1$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data1$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions), ",") # Create data1 frames for each motif data1_motif1 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data1$PromoterID, data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count), Motif = "Motif GRGGC", Position = unlist(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions)) data1_motif2 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data1$PromoterID, data1$Motif_GCCYC_Count), Motif = "Motif GCCYC", Position = unlist(data1$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions)) data1_positions <- rbind(data1_motif1, data1_motif2) # Get positions as numeric values, excluding NAs data1_motif1_positions <- as.numeric(data1_positions$Position[data1_positions$Motif == "Motif GRGGC"]) data1_motif2_positions <- as.numeric(data1_positions$Position[data1_positions$Motif == "Motif GCCYC"]) # Create another data frame for the remaining rows --> total 60997 genes gene_and_its_motifs_without_NHDF_LT_peak <- motif_counts_positions[!motif_counts_positions$PromoterID %in% unique(df1$`Gene Name`), ] gene_and_its_motifs_without_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- sapply(gene_and_its_motifs_without_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, toString) gene_and_its_motifs_without_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions <- sapply(gene_and_its_motifs_without_NHDF_LT_peak$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions, toString) write.table(gene_and_its_motifs_without_NHDF_LT_peak, file="motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) #sed -i 's/Symbol: //g' motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt #sed -i 's/Type: //g' motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt #sed -i 's/"//g' motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt data2 <- read.table("motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data2$Motif_GCCYC_Count <- as.numeric(data2$Motif_GCCYC_Count) data2$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions), ",") data2$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data2$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions), ",") # Create data2 frames for each motif data2_motif1 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data2$PromoterID, data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count), Motif = "Motif GRGGC", Position = unlist(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions)) data2_motif2 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data2$PromoterID, data2$Motif_GCCYC_Count), Motif = "Motif GCCYC", Position = unlist(data2$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions)) data2_positions <- rbind(data2_motif1, data2_motif2) # Get positions as numeric values, excluding NAs data2_motif1_positions <- as.numeric(data2_positions$Position[data2_positions$Motif == "Motif GRGGC"]) data2_motif2_positions <- as.numeric(data2_positions$Position[data2_positions$Motif == "Motif GCCYC"]) # Create a new data frame for rows in 'data' where the PromoterID is in NHDF_LT_K331A's Closest Gene --> total 310 genes gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_K331A_peak <- motif_counts_positions[motif_counts_positions$PromoterID %in% unique(df2$`Gene Name`), ] gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_K331A_peak$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- sapply(gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_K331A_peak$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, toString) gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_K331A_peak$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions <- sapply(gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_K331A_peak$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions, toString) write.table(gene_and_its_motifs_with_NHDF_LT_K331A_peak, file="motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) #sed -i 's/Symbol: //g' motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters.txt #sed -i 's/Type: //g' motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters.txt #sed -i 's/"//g' motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters.txt data3 <- read.table("motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data3$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data3$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data3$Motif_GCCYC_Count <- as.numeric(data3$Motif_GCCYC_Count) data3$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data3$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions), ",") data3$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data3$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions), ",") # Create data3 frames for each motif data3_motif1 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data3$PromoterID, data3$Motif_GRGGC_Count), Motif = "Motif GRGGC", Position = unlist(data3$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions)) data3_motif2 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data3$PromoterID, data3$Motif_GCCYC_Count), Motif = "Motif GCCYC", Position = unlist(data3$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions)) data3_positions <- rbind(data3_motif1, data3_motif2) # Get positions as numeric values, excluding NAs data3_motif1_positions <- as.numeric(data3_positions$Position[data3_positions$Motif == "Motif GRGGC"]) data3_motif2_positions <- as.numeric(data3_positions$Position[data3_positions$Motif == "Motif GCCYC"]) -
Plot Histogram of counts and density of positions
# Adjust the number of breaks (nbins) to control the width of histograms x_limit <- max(max(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count), max(data1$Motif_GCCYC_Count), max(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count), max(data2$Motif_GCCYC_Count), max(data3$Motif_GRGGC_Count), max(data3$Motif_GCCYC_Count)) y_limit1 <- 300 y_limit2 <- 12000 y_limit3 <- 60 # Set up the layout for the plots png("Histogram_of_GRGGC_Motifs.png", width = 1600, height = 800) par(mfrow = c(1, 3)) hist(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Motif Counts in NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit1), breaks = 20, cex.main = 2) hist(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Motif Counts in NOT_NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit2), breaks = 30, cex.main = 2) hist(data3$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Motif Counts in NHDF_LT_K331A promoters", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit3), breaks = 10, cex.main = 2) mtext("Histograms of GRGGC Motifs", outer = TRUE, line = -5, cex = 1.5) dev.off() png("Histogram_of_GCCYC_Motifs.png", width = 1600, height = 800) par(mfrow = c(1, 3)) hist(data1$Motif_GCCYC_Count, main = "Motif Counts in NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit1), breaks = 20, cex.main = 2) hist(data2$Motif_GCCYC_Count, main = "Motif Counts in NOT_NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit2), breaks = 30, cex.main = 2) hist(data3$Motif_GCCYC_Count, main = "Motif Counts in NHDF_LT_K331A promoters", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit3), breaks = 10, cex.main = 2) mtext("Histograms of GCCYC Motifs", outer = TRUE, line = -5, cex = 1.5) dev.off() # Set the ylim value ylim <- c(0.0000, 0.0003) png("Density_of_GRGGC_Motifs.png", width = 1600, height = 800) par(mfrow = c(1, 3)) plot(density(data1_motif1_positions, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Motif Density in NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim, cex.main = 2) plot(density(data2_motif1_positions, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Motif Density in NOT_NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim, cex.main = 2) plot(density(data3_motif1_positions, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Motif Density in NHDF_LT_K331A promoters", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim, cex.main = 2) #mtext("Density of GRGGC Motifs", outer = TRUE, line = -5, cex = 1.5) dev.off() png("Density_of_GCCYC_Motifs.png", width = 1600, height = 800) par(mfrow = c(1, 3)) plot(density(data1_motif2_positions, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Motif Density in NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim, cex.main = 2) plot(density(data2_motif2_positions, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Motif Density in NOT_NHDF_LT promoters", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim, cex.main = 2) plot(density(data3_motif2_positions, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Motif Density in NHDF_LT_K331A promoters", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim, cex.main = 2) #mtext("Density of GCCYC Motifs", outer = TRUE, line = -5, cex = 1.5) dev.off() -
Statistical tests
How to perform a statistical test from density plots? There is in the center positions a much higher possibility than background? This means, in a condition, the peaks occurs more often in the central positions? How to perform a statistical test to see if they are significant?
If you are interested in testing whether the density of peaks in the central positions is significantly different from the background, a suitable statistical test might be a permutation test, or perhaps a Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test. The KS test, in particular, is a non-parametric test that compares two continuous one-dimensional probability distributions.
Here is an example of how you might do this using the KS test in R:
# Suppose `data1_motif1_positions` and `data2_motif2_positions` are your two datasets ks.test(data1_motif1_positions, data2_motif1_positions) #D = 0.034868, p-value < 2.2e-16 ks.test(data1_motif1_positions, data3_motif1_positions) #D = 0.048238, p-value = 4.959e-11 ks.test(data2_motif1_positions, data3_motif1_positions) #D = 0.016348, p-value = 0.07909 ks.test(data1_motif2_positions, data2_motif2_positions) #D = 0.022212, p-value = 4.441e-16 ks.test(data1_motif2_positions, data3_motif2_positions) #D = 0.038822, p-value = 4.049e-07 ks.test(data2_motif2_positions, data3_motif2_positions) #D = 0.018951, p-value = 0.02927 pvalues <- c(2.2e-16, 4.959e-11, 0.07909) bonferroni <- p.adjust(pvalues, method = "bonferroni") #"bonferroni", "BH", "holm" print(bonferroni) #6.6000e-16 1.4877e-10 2.3727e-01 pvalues <- c(4.441e-16, 4.049e-07, 0.02927) bonferroni <- p.adjust(pvalues, method = "bonferroni") print(bonferroni) #1.3323e-15 1.2147e-06 8.7810e-02The ks.test function will return a test statistic and a p-value. The null hypothesis of the KS test is that the two samples are drawn from the same distribution. Therefore, a small p-value (typically, p < 0.05) would lead you to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is a significant difference between the two distributions.
Note that the KS test, like all statistical tests, has assumptions and limitations. It is sensitive to differences in both location and shape of the empirical cumulative distribution functions of the two samples. It also assumes that the samples are independent and identically distributed, which may or may not be appropriate depending on your specific data and research question. Therefore, the test results should be interpreted in the context of these assumptions.
Keep in mind that while this test can indicate whether the densities are different, it does not specify where these differences occur (i.e., in the tails, the center, etc.). If you are specifically interested in the center, you may want to define what you mean by “center” and perform a test (e.g., t-test or KS test) on that specific subset of your data.
A bidirectional promoter is a DNA sequence located between two genes, each of which is transcribed from this shared promoter region but in opposite directions. These type of promoters are particularly common in viruses, especially in those with compact genomes, such as many DNA viruses, where genomic space is at a premium. In viruses, bidirectional promoters can help regulate the simultaneous expression of two genes, which can be critical for the viral lifecycle. Some examples of viruses using bidirectional promoters include Adenovirus, Herpes simplex virus, and the Epstein-Barr virus. For example, in the Epstein-Barr virus, the C promoter (Cp) is a bidirectional promoter that regulates the expression of the EBNA (Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen) genes. These genes are essential for the establishment of latent infection.
-
assign each promoter to a prefined class according to Motifs_Count and Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs
library(dplyr) data <- read.table("motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data$Motif_GCCYC_Count <- as.numeric(data$Motif_GCCYC_Count) # Add a column for the sum of Motif_GRGGC_Count and Motif_GCCYC_Count data <- data %>% mutate(Motifs_Count = Motif_GRGGC_Count + Motif_GCCYC_Count) # Calculate absolute average Motif_GRGGC distance to TSS data$Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC <- sapply(strsplit(data$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, ", "), function(x) round(mean(as.numeric(x), na.rm = TRUE))) # Calculate absolute average Motif_GCCYC distance to TSS data$Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC <- sapply(strsplit(data$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions, ", "), function(x) round(mean(as.numeric(x), na.rm = TRUE))) # Revised function to calculate the mean of two strings of comma-separated numbers mean_of_strings <- function(str1, str2) { # Convert strings of numbers to numeric vectors vec1 <- as.numeric(strsplit(str1, split = ",")[[1]]) vec2 <- as.numeric(strsplit(str2, split = ",")[[1]]) # Handle cases where vec1 or vec2 is NULL (i.e., when str1 or str2 is an empty string) if (is.null(vec1)) { vec1 <- numeric(0) } if (is.null(vec2)) { vec2 <- numeric(0) } # Compute the mean of the two vectors return(round(mean(c(vec1, vec2), na.rm = TRUE))) } # Apply the function to each row of the dataframe data$Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs <- mapply(mean_of_strings, data$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, data$Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions) # Assign classes based on the given rules data <- data %>% mutate( Class_based_Motif_GRGGC = case_when( Motif_GRGGC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 500 ~ "Class 1", Motif_GRGGC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 2", Motif_GRGGC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 1000 ~ "Class 3", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 500 ~ "Class 4", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 5", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 1000 ~ "Class 6", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 500 ~ "Class 7", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 8", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 1000 ~ "Class 9" ) ) data <- data %>% mutate( Class_based_Motif_GCCYC = case_when( Motif_GCCYC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) <= 500 ~ "Class 1", Motif_GCCYC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 2", Motif_GCCYC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) > 1000 ~ "Class 3", Motif_GCCYC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GCCYC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) <= 500 ~ "Class 4", Motif_GCCYC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GCCYC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 5", Motif_GCCYC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GCCYC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) > 1000 ~ "Class 6", Motif_GCCYC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GCCYC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) <= 500 ~ "Class 7", Motif_GCCYC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GCCYC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 8", Motif_GCCYC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GCCYC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC) > 1000 ~ "Class 9" ) ) data <- data %>% mutate( Class_based_Motifs = case_when( Motifs_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 500 ~ "Class 1", Motifs_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 1000 ~ "Class 2", Motifs_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 1000 ~ "Class 3", Motifs_Count >= 50 & Motifs_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 500 ~ "Class 4", Motifs_Count >= 50 & Motifs_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 1000 ~ "Class 5", Motifs_Count >= 50 & Motifs_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 1000 ~ "Class 6", Motifs_Count >= 100 & Motifs_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 500 ~ "Class 7", Motifs_Count >= 100 & Motifs_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 1000 ~ "Class 8", Motifs_Count >= 100 & Motifs_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 1000 ~ "Class 9" ) ) # Define the desired column order desired_columns <- c("PromoterID","Gene_Symbol","Gene_Type","Motif_GRGGC_Count","Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions","Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC","Class_based_Motif_GRGGC", "Motif_GCCYC_Count","Motif_GCCYC_Center_Positions","Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYC","Class_based_Motif_GCCYC", "Motifs_Count","Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs","Class_based_Motifs") # Reorder the columns data <- select(data, all_of(desired_columns)) #sed -i 's/Motifs/Motifs_GRGGC+GCCYC/g' motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak_Category.txt write.table(data, file="motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters_with_Category.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) #~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters_with_Category.txt -d$'\t' -o motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters_with_Category.xls; #~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters_with_Category.txt -d$'\t' -o motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters_with_Category.xls; #~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters_with_Category.txt -d$'\t' -o motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters_with_Category.xls; -
calculate the average positions and counts aggregated by PromoterID from the data data3_positions.
library(dplyr) data1_motif2 <- data1_motif2 %>% mutate(Position = as.numeric(Position)) avg_positions <- data1_motif2 %>% group_by(PromoterID) %>% summarise(avg_position = mean(Position, na.rm = TRUE)) print(avg_positions) average_of_avg_positions <- mean(avg_positions$avg_position, na.rm = TRUE) print(average_of_avg_positions) #67.82571 #21.56232 library(dplyr) data2_motif2 <- data2_motif2 %>% mutate(Position = as.numeric(Position)) avg_positions <- data2_motif2 %>% group_by(PromoterID) %>% summarise(avg_position = mean(Position, na.rm = TRUE)) print(avg_positions) average_of_avg_positions <- mean(avg_positions$avg_position, na.rm = TRUE) print(average_of_avg_positions) #20.62934 #13.99134 library(dplyr) data3_motif2 <- data3_motif2 %>% mutate(Position = as.numeric(Position)) avg_positions <- data3_motif2 %>% group_by(PromoterID) %>% summarise(avg_position = mean(Position, na.rm = TRUE)) print(avg_positions) average_of_avg_positions <- mean(avg_positions$avg_position, na.rm = TRUE) print(average_of_avg_positions) #15.3197 #-44.15695 library(dplyr) avg_counts <- data3_motif2 %>% group_by(PromoterID) %>% summarise(count = n()) %>% summarise(avg_count = mean(count)) print(avg_counts) #22.6 #18.8 #19.6 #22.2 #18.5 #19.1 -
Analysis Summary of “GRGGC” and “CYCCG” Motifs in Promoters. I summarized the process of how I analyzed the ‘GRGGC’ and ‘CYCCG’ motifs in promoters. In this analysis, our primary focus was to study the distribution of these two specific motifs.
-
The first stage of the analysis was to extract all promoter sequences. A range of 3000 nt upstream to 3000 nt downstream of the Transcription Start Sites (TSS) was selected for this purpose. In total, we were able to identify 62703 promoters, each spanning a length of 6000 nt.
-
We classified these 62703 promoters into three distinct sets:
- ‘NHDF_LT’: Comprises promoters with at least one NHDF LT peak. This set contains a total of 1706 promoters.
- ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’: Consists of promoters without any NHDF LT peaks, totaling 60997 promoters.
- ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’: Contains promoters with NHDF LT K331A peaks, amounting to 310 promoters.
-
Subsequently, we screened the extracted promoter sequences from these three promoter sets for occurrences of the “GRGGC” and “CYCCG” motifs. The results are in three separate files: motifs_on_NHDF_LT_promoters_with_Category.xls, motifs_on_NOT_NHDF_LT_promoters_with_Category.xls.zip, and motifs_on_NHDF_LT_K331A_promoters_with_Category.xls.
-
The next step was to calculate the average counts of both motifs across the three promoter datasets. Interestingly, the average counts revealed that the ‘NHDF_LT’ set had slightly higher counts for both “GRGGC” and “CYCCG” motifs as compared to the ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ and ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ sets. The specific averages were as follows:
- GRGGC in ‘NHDF_LT’ promoters: 22.6
- GRGGC in ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ promoters: 18.8
- GRGGC in ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ promoters: 19.6
- CYCCG in ‘NHDF_LT’ promoters: 22.2
- CYCCG in ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ promoters: 18.5
- CYCCG in ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ promoters: 19.1
-
In order to gain deeper insights into the distribution of motifs within the promoters, we generated density plots for all the motifs across the three datasets. A density plot visualizes the distribution of motifs across the promoter regions.
Our analysis of the density plots revealed that the motifs within the ‘NHDF_LT’ promoter set are more concentrated near the Transcription Start Sites (TSS) compared to the other sets.
In the file titled ‘Density_of_GRGGC_Motifs.png’, three statistical tests were conducted
- The adjusted p-value between ‘NHDF_LT’ (left) and ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ (middle) was found to be 2.2e-16, indicating statistical significance.
- The adjusted p-value between ‘NHDF_LT’ (left) and ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ (right) was 1.4877e-10, also denoting statistical significance.
- The adjusted p-value between ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ (middle) and ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ (right) was 0.237, which is not statistically significant.
In a similar manner, three statistical tests were performed for the ‘Density_of_GCCYC_Motifs.png’ file:
- The adjusted p-value between ‘NHDF_LT’ (left) and ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ (middle) was 1.3323e-15, which is statistically significant.
- The adjusted p-value between ‘NHDF_LT’ (left) and ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ (right) was 1.2147e-06, indicating statistical significance.
- The adjusted p-value between ‘NOT_NHDF_LT’ (middle) and ‘NHDF_LT_K331A’ (right) was 0.088, which is not statistically significant.
-
Peak and Motif analyses in Promoters
-
./1_generate_promoter_sequences.py gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db
-
./2_find_motifs_in_promoters.py
-
generate peaks_and_motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.xls
peaks_and_motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.xls
#--3.1. generate peak_tss_distances.csv and peak_tss_distances.png python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_NHDF_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_HEK293_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_PFSK-1_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_K331A_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db /ref/Homo_sapiens/UCSC/hg38/Sequence/WholeGenomeFasta/genome.fa #--3.2. split data into two dataframe, one is in which PromoterID occurres in filtered_peaks$Closest.Gene..Ensemble.ID., another is the remaining #sed -i 's/[][]//g' motif_counts_positions.txt data <- read.table("motif_counts_positions.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) # Read the data peaks <- read.table("peak_tss_distances.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) # Filter the rows filtered_peaks <- subset(peaks, abs(`Distance.to.TSS`) <= 3000) # Print the filtered peaks write.table(filtered_peaks, file="filtered_peak_tss_distances.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) # Create a new data frame for rows in 'data' where the PromoterID is in filtered_peaks's Closest Gene (Ensemble ID) data_in_filtered <- data[data$PromoterID %in% filtered_peaks$Closest.Gene..Ensemble.ID., ] data_in_filtered$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- sapply(data_in_filtered$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, toString) data_in_filtered$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions <- sapply(data_in_filtered$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions, toString) write.table(data_in_filtered, file="motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) # Create another data frame for the remaining rows data_not_in_filtered <- data[!data$PromoterID %in% filtered_peaks$Closest.Gene..Ensemble.ID., ] data_not_in_filtered$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- sapply(data_not_in_filtered$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, toString) data_not_in_filtered$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions <- sapply(data_not_in_filtered$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions, toString) write.table(data_not_in_filtered, file="motifs_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) #780 vs 19262 #1707 vs ca. 60000 #sed -i 's/Symbol: //g' motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt #sed -i 's/Type: //g' motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt #sed -i 's/Symbol: //g' motifs_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.txt #sed -i 's/Type: //g' motifs_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.txt #sed -i 's/"//g' motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt #sed -i 's/"//g' motifs_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.txt #--3.3. prepare data for motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt data1 <- read.table("motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data1$Motif_GCCYR_Count <- as.numeric(data1$Motif_GCCYR_Count) data1$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions), ",") data1$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data1$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions), ",") # Create data1 frames for each motif data1_motif1 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data1$PromoterID, data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count), Motif = "Motif GRGGC", Position = unlist(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions)) data1_motif2 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data1$PromoterID, data1$Motif_GCCYR_Count), Motif = "Motif GCCYR", Position = unlist(data1$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions)) # Combine motif data1 frames data1_positions <- rbind(data1_motif1, data1_motif2) # Get positions as numeric values, excluding NAs motif1_positions_with_LT_peak <- as.numeric(data1_positions$Position[data1_positions$Motif == "Motif GRGGC"]) motif2_positions_with_LT_peak <- as.numeric(data1_positions$Position[data1_positions$Motif == "Motif GCCYR"]) #--3.4. prepare data for motifs_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.txt data2 <- read.table("motifs_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data2$Motif_GCCYR_Count <- as.numeric(data2$Motif_GCCYR_Count) data2$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions), ",") data2$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions <- strsplit(as.character(data2$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions), ",") # Create data2 frames for each motif data2_motif1 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data2$PromoterID, data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count), Motif = "Motif GRGGC", Position = unlist(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions)) data2_motif2 <- data.frame(PromoterID = rep(data2$PromoterID, data2$Motif_GCCYR_Count), Motif = "Motif GCCYR", Position = unlist(data2$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions)) # Combine motif data2 frames data2_positions <- rbind(data2_motif1, data2_motif2) # Get positions as numeric values, excluding NAs motif1_positions_without_LT_peak <- as.numeric(data2_positions$Position[data2_positions$Motif == "Motif GRGGC"]) motif2_positions_without_LT_peak <- as.numeric(data2_positions$Position[data2_positions$Motif == "Motif GCCYR"]) #--3.5. Plot Histogram of counts and density of positions # Define a common x-axis limit for all plots x_limit <- max(max(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count), max(data1$Motif_GCCYR_Count), max(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count), max(data2$Motif_GCCYR_Count)) # Adjust the number of breaks (nbins) to control the width of histograms nbins <- 30 y_limit1 <- 300 y_limit2 <- 12000 # Plot Histogram of counts with the same scale for x-axis png("Histogram_of_Motif_GRGGC_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) hist(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Histogram of Motif GRGGC in promoters with LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit1), breaks = 20) dev.off() png("Histogram_of_Motif_GRGGC_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) hist(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Histogram of Motif GRGGC in promoters without LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit2), breaks = nbins) dev.off() png("Histogram_of_Motif_GCCYR_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) hist(data1$Motif_GCCYR_Count, main = "Histogram of Motif GCCYR in promoters with LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit1), breaks = nbins) dev.off() png("Histogram_of_Motif_GCCYR_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) hist(data2$Motif_GCCYR_Count, main = "Histogram of Motif GCCYR in promoters without LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit2), breaks = nbins) dev.off() # Set up the layout for the plots png("Histogram_of_Motifs.png", width = 1000, height = 1000) par(mfrow = c(2, 2)) hist(data1$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Motif GRGGC Counts with LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit1), breaks = 20) hist(data2$Motif_GRGGC_Count, main = "Motif GRGGC Counts without LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit2), breaks = nbins) hist(data1$Motif_GCCYR_Count, main = "Motif GCCYR Counts with LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit1), breaks = nbins) hist(data2$Motif_GCCYR_Count, main = "Motif GCCYR Counts without LT peak", xlab = "Counts", xlim = c(0, x_limit), ylim = c(0, y_limit2), breaks = nbins) dev.off() # Set the ylim value ylim <- c(0.0001, 0.0003) png("Density_of_Motif_GRGGC_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) plot(density(motif1_positions_with_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main="Density of GRGGC in promoters with LT peak", xlab="Position", ylim = ylim) dev.off() png("Density_of_Motif_GRGGC_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) plot(density(motif1_positions_without_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main="Density of GRGGC in promoters without LT peak", xlab="Position", ylim = ylim) dev.off() png("Density_of_Motif_GCCYR_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) plot(density(motif2_positions_with_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main="Density of GCCYR in promoters with LT peak", xlab="Position", ylim = ylim) dev.off() png("Density_of_Motif_GCCYR_in_promoters_without_LT_peak.png", width=800, height=800) plot(density(motif2_positions_without_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main="Density of GCCYR in promoters without LT peak", xlab="Position", ylim = ylim) dev.off() png("Density_of_Motifs.png", width = 1000, height = 1000) par(mfrow = c(2, 2)) plot(density(motif1_positions_with_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Density of GRGGC in promoters with LT peak", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim) plot(density(motif1_positions_without_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Density of GRGGC in promoters without LT peak", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim) plot(density(motif2_positions_with_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Density of GCCYR in promoters with LT peak", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim) plot(density(motif2_positions_without_LT_peak, na.rm = TRUE), main = "Density of GCCYR in promoters without LT peak", xlab = "Position", ylim = ylim) dev.off() #--3.6. assign each promoter to a prefined class according to Motifs_Count and Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs library(dplyr) data <- read.table("motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt", sep="\t", header=TRUE, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) data$Motif_GRGGC_Count <- as.numeric(data$Motif_GRGGC_Count) data$Motif_GCCYR_Count <- as.numeric(data$Motif_GCCYR_Count) # Add a column for the sum of Motif_GRGGC_Count and Motif_GCCYR_Count data <- data %>% mutate(Motifs_Count = Motif_GRGGC_Count + Motif_GCCYR_Count) # Calculate absolute average Motif_GRGGC distance to TSS data$Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC <- sapply(strsplit(data$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, ", "), function(x) round(mean(as.numeric(x), na.rm = TRUE))) # Calculate absolute average Motif_GCCYR distance to TSS data$Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR <- sapply(strsplit(data$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions, ", "), function(x) round(mean(as.numeric(x), na.rm = TRUE))) # Revised function to calculate the mean of two strings of comma-separated numbers mean_of_strings <- function(str1, str2) { # Convert strings of numbers to numeric vectors vec1 <- as.numeric(strsplit(str1, split = ",")[[1]]) vec2 <- as.numeric(strsplit(str2, split = ",")[[1]]) # Handle cases where vec1 or vec2 is NULL (i.e., when str1 or str2 is an empty string) if (is.null(vec1)) { vec1 <- numeric(0) } if (is.null(vec2)) { vec2 <- numeric(0) } # Compute the mean of the two vectors return(round(mean(c(vec1, vec2), na.rm = TRUE))) } # Apply the function to each row of the dataframe data$Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs <- mapply(mean_of_strings, data$Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions, data$Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions) # Assign classes based on the given rules data <- data %>% mutate( Class_based_Motif_GRGGC = case_when( Motif_GRGGC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 500 ~ "Class 1", Motif_GRGGC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 2", Motif_GRGGC_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 1000 ~ "Class 3", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 500 ~ "Class 4", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 5", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 50 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 1000 ~ "Class 6", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 500 ~ "Class 7", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) <= 1000 ~ "Class 8", Motif_GRGGC_Count >= 100 & Motif_GRGGC_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC) > 1000 ~ "Class 9" ) ) data <- data %>% mutate( Class_based_Motif_GCCYR = case_when( Motif_GCCYR_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) <= 500 ~ "Class 1", Motif_GCCYR_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) <= 1000 ~ "Class 2", Motif_GCCYR_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) > 1000 ~ "Class 3", Motif_GCCYR_Count >= 50 & Motif_GCCYR_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) <= 500 ~ "Class 4", Motif_GCCYR_Count >= 50 & Motif_GCCYR_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) <= 1000 ~ "Class 5", Motif_GCCYR_Count >= 50 & Motif_GCCYR_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) > 1000 ~ "Class 6", Motif_GCCYR_Count >= 100 & Motif_GCCYR_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) <= 500 ~ "Class 7", Motif_GCCYR_Count >= 100 & Motif_GCCYR_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) <= 1000 ~ "Class 8", Motif_GCCYR_Count >= 100 & Motif_GCCYR_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR) > 1000 ~ "Class 9" ) ) data <- data %>% mutate( Class_based_Motifs = case_when( Motifs_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 500 ~ "Class 1", Motifs_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 1000 ~ "Class 2", Motifs_Count < 50 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 1000 ~ "Class 3", Motifs_Count >= 50 & Motifs_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 500 ~ "Class 4", Motifs_Count >= 50 & Motifs_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 1000 ~ "Class 5", Motifs_Count >= 50 & Motifs_Count < 100 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 1000 ~ "Class 6", Motifs_Count >= 100 & Motifs_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 500 ~ "Class 7", Motifs_Count >= 100 & Motifs_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 500 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) <= 1000 ~ "Class 8", Motifs_Count >= 100 & Motifs_Count < 150 & abs(Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs) > 1000 ~ "Class 9" ) ) # Define the desired column order desired_columns <- c("PromoterID","Gene_Symbol","Gene_Type","Motif_GRGGC_Count","Motif_GRGGC_Center_Positions","Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GRGGC","Class_based_Motif_GRGGC", "Motif_GCCYR_Count","Motif_GCCYR_Center_Positions","Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motif_GCCYR","Class_based_Motif_GCCYR", "Motifs_Count","Avg_Distance_To_TSS_of_Motifs","Class_based_Motifs") # Reorder the columns data <- select(data, all_of(desired_columns)) #sed -i 's/Motifs/Motifs_GRGGC+GCCYR/g' motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak_Category.txt write.table(data, file="motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak_Category.txt", sep="\t", row.names = FALSE) #--3.7. add peak information into motif table ./add_peaks_to_motifs.py #~/Tools/csv2xls-0.4/csv_to_xls.py _peaks_and_motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.txt peak_tss_distances.txt -d$'\t' -o peaks_and_motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak.xls; #rename the name of sheet1 to "peaks_and_motifs_in_promoters_with_LT_peak" and "all_LT_peaks_NHDF"
-
plot_peaks.py (updated code)
-
plot_peaks.py (updated code)
#python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_NHDF_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db #mv peak_tss_distances.xlsx peak_tss_distances_NHDF.xlsx #mv peak_tss_distances.txt peak_tss_distances_NHDF.txt #mv peak_distribution.csv peak_distribution_NHDF.csv #mv peak_distribution.png peak_distribution_NHDF.png #python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_HEK293_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db #mv peak_tss_distances.xlsx peak_tss_distances_HEK293.xlsx #mv peak_tss_distances.txt peak_tss_distances_HEK293.txt #mv peak_distribution.csv peak_distribution_HEK293.csv #mv peak_distribution.png peak_distribution_HEK293.png #python3 plot_peaks.py peaks_PFSK-1_.bed /home/jhuang/REFs/gencode.v43.annotation.gtf.db #mv peak_tss_distances.xlsx peak_tss_distances_PFSK-1.xlsx #mv peak_tss_distances.txt peak_tss_distances_PFSK-1.txt #mv peak_distribution.csv peak_distribution_PFSK-1.csv #mv peak_distribution.png peak_distribution_PFSK-1.png import pprint import argparse import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd import gffutils import numpy as np def plot_peak_distribution(peaks_file, gencode_db): db = gffutils.FeatureDB(gencode_db, keep_order=True) peaks = pd.read_table(peaks_file, header=None) peaks.columns = ['chrom', 'start', 'end', 'name', 'score'] tss_positions = [] tss_genes = [] for gene in db.features_of_type('gene'): if gene.strand == '+': tss_positions.append(gene.start) else: tss_positions.append(gene.end) tss_genes.append(gene) peak_tss_distances = [] peak_names = [] closest_genes = [] closest_gene_names = [] closest_strands = [] closest_gene_types = [] # New list for gene_type for _, peak in peaks.iterrows(): peak_center = (peak['start'] + peak['end']) // 2 closest_tss_index = np.argmin([abs(tss - peak_center) for tss in tss_positions]) distance_to_tss = peak_center - tss_positions[closest_tss_index] peak_tss_distances.append(distance_to_tss) peak_names.append(peak['name']) closest_genes.append(tss_genes[closest_tss_index].id) if 'gene_name' in tss_genes[closest_tss_index].attributes: closest_gene_name = tss_genes[closest_tss_index].attributes['gene_name'][0] else: closest_gene_name = 'N/A' # Set a default value if 'gene_name' attribute is not present closest_gene_names.append(closest_gene_name) closest_strands.append(tss_genes[closest_tss_index].strand) if 'gene_type' in tss_genes[closest_tss_index].attributes: closest_gene_type = tss_genes[closest_tss_index].attributes['gene_type'][0] else: closest_gene_type = 'N/A' # Set a default value if 'gene_type' attribute is not present closest_gene_types.append(closest_gene_type) df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Peak Name': peak_names, 'Distance to TSS': peak_tss_distances, 'Closest Gene (Ensemble ID)': closest_genes, 'Closest Gene (Gene name)': closest_gene_names, 'Gene Strand': closest_strands, 'Gene Type': closest_gene_types # Add new column for gene_type }) df.to_excel('peak_tss_distances.xlsx', index=False) df.to_csv('peak_tss_distances.txt', sep='\t', index=False) # Save as tab-separated text file bins_no=600 #1000 for nHDF, 600 for HEK293 and PFSK-1 counts, bin_edges = np.histogram(peak_tss_distances, bins=bins_no) bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2 hist_df = pd.DataFrame({'Bin Center': bin_centers, 'Count': counts}) hist_df.to_csv('peak_distribution.csv', index=False) total_peaks = hist_df['Count'].sum() with open('peak_distribution.csv', 'a') as f: f.write(f'\nTotal number of peaks: {total_peaks}') # Set the figure background to be transparent plt.gcf().set_facecolor('none') plt.gcf().patch.set_alpha(0.0) plt.hist(peak_tss_distances, bins=bins_no) plt.xlabel('Distance to TSS', fontsize=17) plt.ylabel('Number of peaks', fontsize=17) plt.title('') #plt.title('Distribution of peaks around TSS', fontsize=12) # Set tick label font sizes plt.xticks(fontsize=14) plt.yticks(fontsize=14) # Adjust the space on the left of the figure plt.gcf().subplots_adjust(left=0.15) # Set x-axis range plt.xlim(-8000, 8000) plt.savefig('peak_distribution.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight') plt.show() if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Plot peak distribution around TSS.') parser.add_argument('peaks_file', type=str, help='Path to the peaks.bed file') parser.add_argument('gencode_db', type=str, help='Path to the gencode.v43.annotation.db file') args = parser.parse_args() plot_peak_distribution(args.peaks_file, args.gencode_db)
Regulating Gene Expression in Diploid Organisms with Different Haplotypes
If two haplotypes in a diploid organism are different, then the genome sequences for those haplotypes are also different. These genetic differences can indeed impact gene expression, and there are various mechanisms in place to regulate and coordinate the expression of genes from both haplotypes. This regulation helps ensure that the organism functions properly despite having two different sets of genetic information.
Here are some key mechanisms involved in regulating gene expression from different haplotypes:
-
Allelic Specific Expression (ASE): In many cases, both alleles (one from each haplotype) of a gene can be expressed, but the extent of expression may differ between the two alleles. This phenomenon is known as allelic-specific expression. It can be influenced by factors such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, and the binding of transcription factors.
-
Epigenetic Modifications: Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, play a crucial role in gene regulation. Differences in epigenetic marks between the two haplotypes can lead to differences in gene expression. For example, if one haplotype has more methylated DNA in a particular gene promoter region, that gene may be less active on that haplotype.
-
Imprinting: Some genes are imprinted, which means that one allele is preferentially expressed over the other, depending on its parental origin. This imprinting is established during gametogenesis and can lead to differential expression between the two haplotypes.
-
Regulatory Elements: The presence of specific regulatory elements, such as enhancers and silencers, can also influence gene expression. Differences in the sequences of these regulatory elements between haplotypes can lead to differential gene expression.
-
Transcription Factors: Transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate gene expression. Differences in transcription factor binding sites between haplotypes can affect how genes are turned on or off.
-
Post-Transcriptional Regulation: After transcription, RNA molecules are subject to post-transcriptional regulation, including alternative splicing, RNA editing, and microRNA-mediated regulation. Differences in these processes can further modulate gene expression from different haplotypes.
-
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors and signaling pathways can also influence gene expression. The response to external stimuli may vary between haplotypes due to differences in gene regulation.
Overall, the regulation of gene expression from two different haplotypes is a complex interplay of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. This regulation helps maintain the balance of gene expression required for normal cellular and organismal function, even when there are genetic differences between the two haplotypes.
如果一个二倍体生物的两个单倍型不同,那么这两个单倍型的基因组序列也是不同的。这些遗传差异确实会影响基因表达,有各种机制来调节和协调来自两个单倍型的基因表达。这种调控有助于确保在拥有两套不同遗传信息的情况下,生物体能正常运作。
以下是调节来自不同单倍型的基因表达的一些关键机制:
-
等位特异性表达(ASE):在许多情况下,一个基因的两个等位基因(分别来自两个单倍型)都可以被表达,但两个等位基因的表达程度可能不同。这种现象被称为等位特异性表达。它可以受到DNA甲基化、组蛋白修饰和转录因子结合等因素的影响。
-
表观遗传修饰:表观遗传修饰,如DNA甲基化和组蛋白修饰,在基因调控中起着关键作用。两个单倍型之间的表观标记差异可能导致基因表达差异。例如,如果一个单倍型在某个基因启动子区域中有更多的甲基化DNA,那么该基因在该单倍型上可能不太活跃。
-
印迹:一些基因具有印迹,这意味着其中一个等位基因会优先表达,这取决于它的亲本来源。这种印迹是在生殖细胞形成期间建立的,可以导致两个单倍型之间的差异表达。
-
调控元件:特定调控元件(如增强子和抑制子)的存在也可以影响基因表达。两个单倍型之间的调控元件序列差异可能导致基因差异表达。
-
转录因子:转录因子是能够结合到特定DNA序列并调控基因表达的蛋白质。两个单倍型之间的转录因子结合位点差异可以影响基因的启动或关闭。
-
转录后调控:在转录后,RNA分子会经历转录后调控,包括可选剪接、RNA编辑和microRNA介导的调控。这些过程的差异可以进一步调节来自不同单倍型的基因表达。
-
环境因素:环境因素和信号通路也可以影响基因表达。对外部刺激的反应可能因为基因调控的差异而有所不同。
总的来说,调节两个不同单倍型基因表达的机制是基因、表观遗传和环境因素之间复杂的相互作用。这种调控有助于维持细胞和生物体正常功能所需的基因表达平衡,即使两个单倍型之间存在遗传差异。