Single-Molecule Binding/Bleaching Detection Pipeline for Data_Vero_Kymographs
“What is confirmed is hexamer and double-hexamer binding to DNA, whereas monomer/dimer binding to DNA is not confirmed.”
Overview
This workflow robustly detects and quantifies molecular binding and bleaching events from single-molecule fluorescence trajectories. It employs Hidden Markov Model (HMM) analysis to convert noisy intensity data into interpretable discrete state transitions, using a combination of MATLAB/Octave and Python scripts.
Step 1: ICON HMM Fitting per Track
- Runs
icon_from_track_csv.m, loading each track’s photon count data, fitting a HMM (via the ICON algorithm), and saving results (icon_analysis_track_XX.mat). - Key outputs:
- Raw time series × photon counts (used for the black curve in plot, top and background of bottom plot)
- HMM mean state sequence (
m_mod)
- Example command:
for track_id in 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14; do
octave icon_post_equal_levels.m icon_analysis_track_${track_id}.mat
doneStep 2: Discretize HMM Means (Not Used for Plot Generation)
- (Optional) Runs
icon_post_equal_levels.mto generateequal_levels_track_XX.mat, which contains a stepwise, discretized version of the HMM fit. - This step is designed for diagnostic parameter tuning (finding L_best), but the plotting script does not use these files for figure generation.
- 后处理成“等间距台阶 + bleaching step” (这些文件主要用来“告诉你 L 选多少比较合适”(namely L_best),而不是直接给 Python 画图用).
for track_id in 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14; do octave icon_post_equal_levels.m icon_analysis_track_${track_id}.mat done # 生成 equal_levels_track_100.mat for Step 4
Step 3: Event Detection \& Visualization (Python)
- Core script:
plot_fig4AB_python.py - Loads
icon_analysis_track_XX_matlab.matproduced by Step 1. - Black plot (top and gray in lower panel): Raw photon count data.
- Red plot (lower panel): Stepwise HMM fit — generated by mapping the HMM mean trajectory to L (e.g. 10) equally spaced photon count levels (
L_best). - Event detection:
- Blue triangles: Up-step events (binding)
- Black triangles: Down-step events (bleaching)
- Uses in-script logic to detect transitions meeting user-set thresholds:
min_levels_bind=3, min_levels_bleach=2, dwell_min=0.2s, baseline_state_max=5
- Produces both plots and machine-readable event tables (CSV, Excel)
- Sample commands:
mamba activate kymo_plots
for track_id in 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 100; do
python plot_fig4AB_python.py ${track_id} 10 3 2 0.2 5
doneStep 4: (For Future) Aggregation
icon_multimer_histogram.mis prepared for future use to aggregate results from many tracks (e.g., make multimer/stoichiometry histograms).- This step is not used for the current plots.
octave icon_multimer_histogram.m
# for subset use:
octave icon_multimer_histogram.m "equal_levels_track_1*.mat"
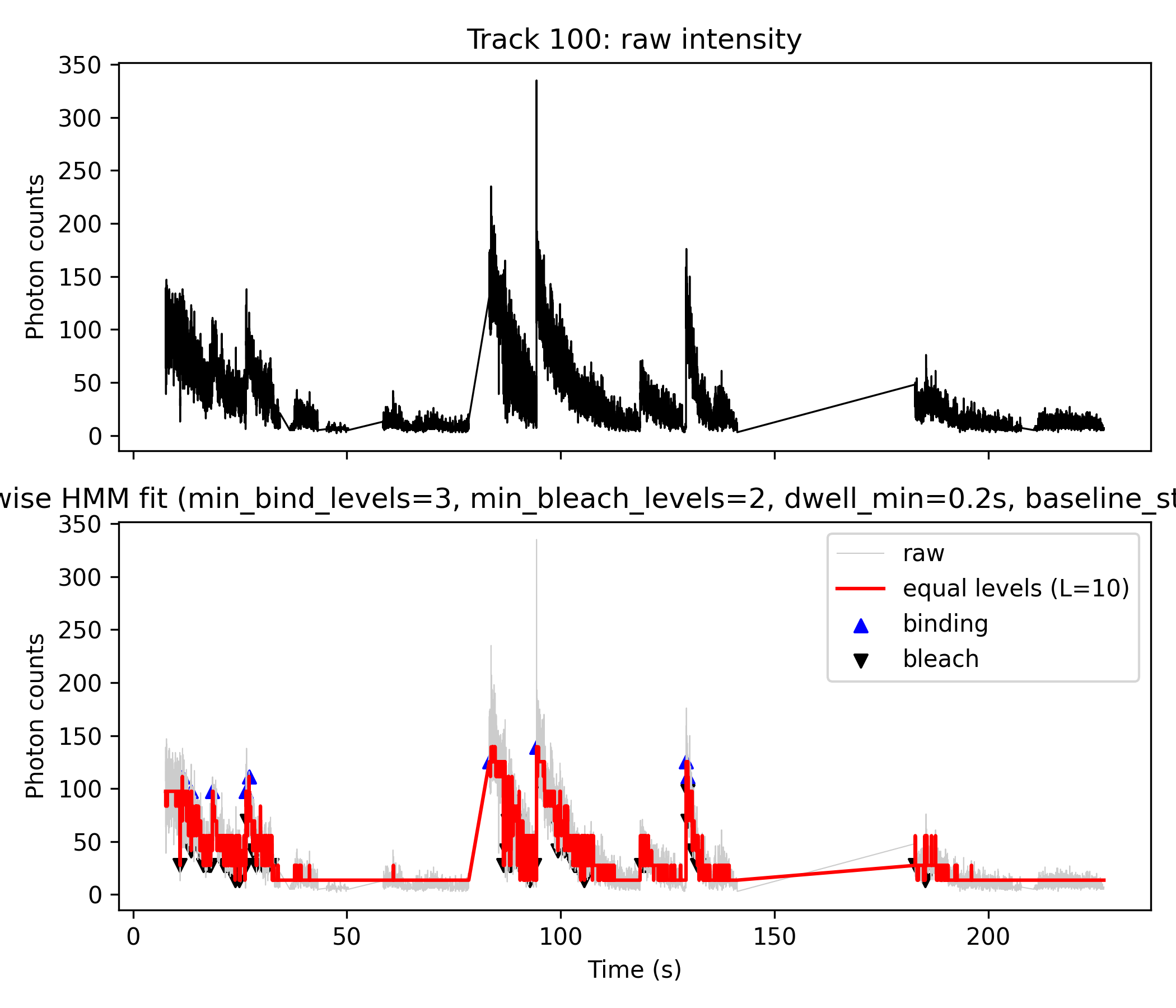
#→ 得到 multimer_histogram.png, 就是你的 Fig. 4C-like 图.Figure Explanation (e.g. Track 14 and Track 100)
- Top panel (black line): Raw photon counts (
z).- Direct output from Step 1 HMM analysis; visualizes the original noisy fluorescence trace.
- Bottom panel:
- Gray line: Raw photon counts for direct comparison.
- Red line: Step-wise fit produced by discretizing the HMM mean (
m_mod) from Step 1 directly inside the python script. - Blue “▲”: Detected binding (upward) events.
- Black “▼”: Detected bleaching (downward) events.
- Event Table: Both “binding” and “bleach” events are exported with details: time, photon count, state transition, and dwell time.
Note:
- For these figures, only Step 1 and Step 3 are used.
- Step 2 is for diagnostic/discretization, but in our current pipeline,
L_bestwas given directly with 10, was not calculated from Step 2, therefore Step 2 was not used. - Step 4 is left for future population summaries.
Key Script Function Descriptions
1. icon_from_track_csv.m (Octave/MATLAB)
- Loads a csv photon count time sequence for a single molecule track.
- Infers hidden states and mean trajectory with ICON/HMM.
- Saves all variables for python to use.
2. plot_fig4AB_python.py (Python)
- Loads
.matresults: time (t), photons (z), and HMM means (m_mod). - Discretizes the mean trajectory into L equal steps, maps continuous states to nearest discrete, and fits photon counts by linear regression for step heights.
- Detects step transitions corresponding to binding or bleaching based on user parameters (size thresholds, dwell filters).
- Plots raw data + stepwise fit, annotates events, and saves tables.
(Script excerpt, see full file for details):
def assign_to_levels(m_mod, levels):
# Map every m_mod value to the nearest discrete level
...
def detect_binding_bleach_from_state(...):
# Identify up/down steps using given jump sizes and baseline cutoff
...
def filter_short_episodes_by_dwell(...):
# Filter events with insufficient dwell time
...
...
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Parse command line args, load .mat, process and plotComplete Scripts
See attached files for full script code:
icon_from_track_csv.mplot_fig4AB_python.pyicon_post_equal_levels.m(diagnostic, not used for current figures)icon_multimer_histogram.m(future)
Example Event Table Output
The python script automatically produces a CSV/Excel file summarizing:
- Event type (“binding” or “bleach”)
- Time (seconds)
- Photon count (at event)
- States before/after the event
- Dwell time (for binding)
In summary:
- Figures output from
plot_fig4AB_python.pydirectly visualize both binding and bleaching events as blue (▲) and black (▼) markers, using logic based on HMM analysis and transition detection within the Python code, without any direct dependence on Step 2 “equal_levels” files. This approach is both robust and reproducible for detailed single-molecule state analysis. [^1][^2]
icon_from_track_csv.m
clear all;
%% icon_from_track_csv.m
%% 用 ICON HMM 分析你自己的 track_intensity CSV 数据
%%
%% 用法(命令行):
%% octave icon_from_track_csv.m your_track_intensity_file.csv [track_id]
%%
%% - your_track_intensity_file.csv:
%% 3 列分号分隔:
%% # track index;time (seconds);track intensity (photon counts)
%% - track_id(可选):
%% 要分析的 track_index 数值,例如 0、2、10、100 等
%% 如果不给,则自动:
%% - 若存在 track 100,则用 100
%% - 否则用第一个 track
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 0. 处理命令行参数
%%--------------------------------------------
arg_list = argv();
if numel(arg_list) < 1
error("Usage: octave icon_from_track_csv.m
<track_intensity_csv> [track_id]");
end
input_file = arg_list{1};
track_id_arg = NaN;
if numel(arg_list) >= 2
track_id_arg = str2double(arg_list{2});
end
fprintf("Input CSV : %s\n", input_file);
if ~isnan(track_id_arg)
fprintf("Requested track_id: %g\n", track_id_arg);
end
%% 链接 ICON sampler 的源码
%addpath('sampler_SRC');
% 尝试加载 statistics 包(gamrnd 在这里)
try
pkg load statistics;
catch
warning("Could not load 'statistics' package. Please install it via 'pkg install -forge statistics'.");
end
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 1. 读入 3 列 CSV: track_index;time;counts
%%--------------------------------------------
fid = fopen(input_file, 'r');
if fid < 0
error("Cannot open file: %s", input_file);
end
% 第一行是注释头 "# track index;time (seconds);track intensity (photon counts)"
header_line = fgetl(fid); %#ok
<NASGU>
% 后面每行: track_index;time_sec;intensity
data = textscan(fid, "%f%f%f", "Delimiter", ";");
fclose(fid);
track_idx = data{1};
time_sec = data{2};
counts = data{3};
% 按 track 和时间排序,保证序列有序
[~, order] = sortrows([track_idx, time_sec], [1, 2]);
track_idx = track_idx(order);
time_sec = time_sec(order);
counts = counts(order);
tracks = unique(track_idx);
fprintf("Found %d tracks: ", numel(tracks));
fprintf("%g ", tracks);
fprintf("\n");
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 2. 选择要分析的 track
%%--------------------------------------------
if ~isnan(track_id_arg)
tr = track_id_arg;
else
% 如果存在 track 100,则优先选 100(你自己定义的 accumulated 轨迹)
if any(tracks == 100)
tr = 100;
else
tr = tracks(1); % 否则就选第一个
end
end
if ~any(tracks == tr)
error("Requested track_id = %g not found in file.", tr);
end
fprintf("Using track_id = %g for ICON analysis.\n", tr);
sel = (track_idx == tr);
t = time_sec(sel);
z = counts(sel);
% 按时间排序(理论上已经排过一次,这里再保险)
[ t, order_t ] = sort(t);
z = z(order_t);
z = z(:); % 列向量
N = numel(z);
fprintf("Track %g has %d time points.\n", tr, N);
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 3. 设置 ICON 参数(与原始脚本一致)
%%--------------------------------------------
% 浓度(Dirichlet 相关超参数)
opts.a = 1; % Transitions (alpha)
opts.g = 1; % Base (gamma)
% 超参数 Q
opts.Q(1) = mean(z); % mean of means (lambda)
opts.Q(2) = 1 / std(z)^2; % Precision of means (rho)
opts.Q(3) = 0.1; % Shape of precisions (beta)
opts.Q(4) = 0.00001; % Scale of precisions (omega)
opts.M = 10; % Nodes in the interpolation
% 采样器参数
opts.dr_sk = 1; % Stride: 每多少步保存一次 sample
opts.K_init = 50; % 初始 photon levels 数量(ICON 会自动收缩)
% 输出标志
flag_stat = true; % 在命令行里打印进度
flag_anim = false; % 是否弹出动画(Octave 下可以改成 false 更稳定)
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 4. 运行 ICON 采样器
%%--------------------------------------------
R = 1000; % 样本数,可按需要调整
fprintf("Running ICON sampler on track %g ...\n", tr);
chain = chainer_main( z, R, [], opts, flag_stat, flag_anim );
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 5. 导出 samples 方便后处理
%%--------------------------------------------
fr = 0.25; % burn-in 比例(前 25%% 样本丢掉)
dr = 2; % sample stride(每隔多少个样本导出一个)
out_prefix = sprintf('samples_track_%g', tr);
chainer_export(chain, fr, dr, out_prefix, 'mat');
fprintf("Samples exported to %s.mat\n", out_prefix);
%%--------------------------------------------
%% 6. 基本后验分析:state trajectory / transitions / drift
%%--------------------------------------------
% 离散化 state space (在 [0,1] 上划分 25 个 bin)
m_min = 0;
m_max = 1;
m_num = 25;
% (1) 状态轨迹(归一化):m_mod
[m_mod, m_red] = chainer_analyze_means(chain, fr, dr, m_min, m_max, m_num, z);
% (2) 转移概率
[m_edges, p_mean, d_dist] = chainer_analyze_transitions( ...
chain, fr, dr, m_min, m_max, m_num, true);
% (3) 漂移轨迹
[y_mean, y_std] = chainer_analyze_drift(chain, fr, dr, z);
% 1) Load the original Octave .mat file
%load('icon_analysis_track_100.mat');
% 2) Re-save in MATLAB-compatible v5/v7 format, with new name
%save('-mat', 'icon_analysis_track_100_matlab.mat');
%% 存到一个 mat 文件里,方便之后画图
%icon_mat = sprintf('icon_analysis_track_%g.mat', tr);
%save(icon_mat, 't', 'z', 'm_mod', 'm_red', 'm_edges', 'p_mean', ...
% 'd_dist', 'y_mean', 'y_std');
% 原来的 Octave 版本(可留可不留)
mat_out = sprintf("icon_analysis_track_%d.mat", tr);
save(mat_out, "m_mod", "m_red", "m_edges", "p_mean", "d_dist", ...
"y_mean", "y_std", "t", "z");
% 额外保存一个专门给 Python / SciPy 用的 MATLAB-compatible 版本
mat_out_matlab = sprintf("icon_analysis_track_%d_matlab.mat", tr);
save('-mat', mat_out_matlab, "m_mod", "m_red", "m_edges", "p_mean", "d_dist", ...
"y_mean", "y_std", "t", "z");
fprintf("ICON analysis saved to %s\n", icon_mat);
fprintf("Done.\n");icon_post_equal_levels.m
% icon_post_equal_levels.m (script version)
%
% 用法(终端):
% octave icon_post_equal_levels.m icon_analysis_track_XXX.mat
%
% 对 ICON 分析结果 (icon_analysis_track_XXX.mat) 做等间距 photon level 后处理
arg_list = argv();
if numel(arg_list) < 1
error("Usage: octave icon_post_equal_levels.m icon_analysis_track_XXX.mat");
end
mat_file = arg_list{1};
fprintf("Loading ICON analysis file: %s\n", mat_file);
S = load(mat_file);
if ~isfield(S, 'm_mod') || ~isfield(S, 't') || ~isfield(S, 'z')
error("File %s must contain variables: t, z, m_mod.", mat_file);
end
t = S.t(:);
z = S.z(:);
m_mod = S.m_mod(:);
N = numel(m_mod);
if numel(t) ~= N || numel(z) ~= N
error("t, z, m_mod must have the same length.");
end
% 从文件名里解析 track_id(如果有)
[~, name, ~] = fileparts(mat_file);
track_id = NaN;
tokens = regexp(name, 'icon_analysis_track_([0-9]+)', 'tokens');
if ~isempty(tokens)
track_id = str2double(tokens{1}{1});
fprintf("Detected track_id = %g from file name.\n", track_id);
else
fprintf("Could not parse track_id from file name, set to NaN.\n");
end
%--------------------------------------------
% 1. 在 m_mod 的范围上搜索等间距 level 数 L
%--------------------------------------------
m_min = min(m_mod);
m_max = max(m_mod);
fprintf("m_mod range: [%.4f, %.4f]\n", m_min, m_max);
L_min = 2;
L_max = 12; % 可以按需要改大一些
best_score = Inf;
L_best = L_min;
fprintf("Scanning candidate level numbers L = %d .. %d ...\n", L_min, L_max);
for L = L_min:L_max
levels = linspace(m_min, m_max, L);
% 把每个 m_mod(t) 映射到最近的 level:state_temp ∈ {1..L}
state_temp = assign_to_levels(m_mod, levels);
% 用这些 level 生成 step-wise 轨迹
m_step_temp = levels(state_temp);
% 计算拟合误差 SSE(在归一化空间)
residual = m_mod - m_step_temp;
sse = sum(residual.^2);
% 类 BIC 评分:误差 + 惩罚 L
score = N * log(sse / N + eps) + L * log(N);
fprintf(" L = %2d -> SSE = %.4g, score = %.4g\n", L, sse, score);
if score < best_score
best_score = score;
L_best = L;
end
end
fprintf("Best L (number of equally spaced levels) = %d\n", L_best);
%--------------------------------------------
% 2. 用最优 L_best 构建最终的等间距 level & state
%--------------------------------------------
levels_norm = linspace(m_min, m_max, L_best);
state = assign_to_levels(m_mod, levels_norm); % 1..L_best
m_step = levels_norm(state); % 归一化台阶轨迹
%--------------------------------------------
% 3. 将归一化台阶轨迹线性映射回 photon counts
% z ≈ a * m_step + b (最小二乘)
%--------------------------------------------
A = [m_step(:), ones(N,1)];
theta = A \ z; % 最小二乘拟合 [a; b]
a = theta(1);
b = theta(2);
z_step = A * theta; % 拟合出来的 photon counts 台阶轨迹
fprintf("Fitted z ≈ a * m_step + b with a = %.4f, b = %.4f\n", a, b);
%--------------------------------------------
% 4. 检测 bleaching 步:state 下降的时刻
%--------------------------------------------
%s_prev = state(1:end-1);
%s_next = state(2:end);
%
%bleach_idx = find(s_next < s_prev) + 1;
%bleach_times = t(bleach_idx);
%
%fprintf("Found %d bleaching step(s).\n", numel(bleach_idx));
%--------------------------------------------
% Detect upward (binding) and downward (bleach) steps
%--------------------------------------------
s_prev = state(1:end-1);
s_next = state(2:end);
% raw step indices
bind_idx_raw = find(s_next > s_prev) + 1; % upward jumps
bleach_idx_raw = find(s_next < s_prev) + 1; % downward jumps
% Optional: threshold by intensity change to ignore tiny noisy steps
dz = z_step(2:end) - z_step(1:end-1);
min_jump = 30; % <-- choose something ~ one level step or larger
keep_bind = dz > min_jump;
keep_bleach = dz < -min_jump;
bind_idx = bind_idx_raw(keep_bind(bind_idx_raw-1));
bleach_idx = bleach_idx_raw(keep_bleach(bleach_idx_raw-1));
bind_times = t(bind_idx);
bleach_times = t(bleach_idx);
fprintf("Found %d binding and %d bleaching steps (with threshold %.1f).\n", ...
numel(bind_idx), numel(bleach_idx), min_jump);
%--------------------------------------------
% 5. 保存结果
%--------------------------------------------
out_name = sprintf('equal_levels_track_%s.mat', ...
ternary(isnan(track_id), 'X', num2str(track_id)));
fprintf("Saving equal-level analysis to %s\n", out_name);
% Save them in the .mat file
%save(out_name, ...
% 't', 'z', 'm_mod', ...
% 'L_best', 'levels_norm', ...
% 'state', 'm_step', 'z_step', ...
% 'bleach_idx', 'bleach_times', ...
% 'track_id');
save(out_name, ...
't', 'z', 'm_mod', ...
'L_best', 'levels_norm', ...
'state', 'm_step', 'z_step', ...
'bind_idx', 'bind_times', ...
'bleach_idx', 'bleach_times', ...
'track_id');
fprintf("Done.\n");plot_fig4AB_python.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
plot_fig4AB_python.py
Usage:
python plot_fig4AB_python.py
<track_id> [L_best] [min_levels_bind] [min_levels_bleach] [dwell_min] [baseline_state_max]
Arguments
---------
<track_id> : int
e.g. 10 → uses icon_analysis_track_10_matlab.mat
[L_best] : int, optional
Number of equally spaced levels to use for the step-wise fit
in Fig. 4B. If omitted, default = 3.
[min_levels_bind] : int, optional
Minimum number of state levels for an upward jump to count as a
binding event. Default = 3.
[min_levels_bleach] : int, optional
Minimum number of state levels for a downward jump to count as a
bleaching step. Default = 1.
[dwell_min] : float, optional
Minimum allowed dwell time between a binding event and the NEXT
bleaching event. If Δt = t_bleach - t_bind < dwell_min, then:
- that binding is removed
- the paired bleaching event is also removed
Default = 0 (no dwell-based filtering).
[baseline_state_max] : int, optional
Highest state index (0-based) that is still considered "baseline /
unbound" before a binding jump.
Binding condition becomes:
dstate >= min_levels_bind AND state_before <= baseline_state_max
If omitted → no baseline constraint (any state can be a start).
Input file
----------
icon_analysis_track_
<track_id>_matlab.mat
Expected variables inside the .mat file:
t : time vector (1D, seconds)
z : photon counts (1D)
m_mod : ICON mean trajectory (1D), same length as t and z
Outputs
-------
1) Figure:
fig4AB_track_
<track_id>_L<L_best>.png
2) Event tables:
binding_bleach_events_track_
<track_id>_L<L_best>.csv
binding_bleach_events_track_
<track_id>_L<L_best>.xlsx (if pandas available)
"""
import sys
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.io import loadmat
# Try to import pandas for Excel output
try:
import pandas as pd
HAS_PANDAS = True
except ImportError:
HAS_PANDAS = False
print("[WARN] pandas not available: Excel output (.xlsx) will be skipped.")
def assign_to_levels(m_mod, levels):
"""
Map each point in m_mod to the nearest level.
Parameters
----------
m_mod : array-like, shape (N,)
Normalized ICON mean trajectory.
levels : array-like, shape (L,)
Candidate level values.
Returns
-------
state : ndarray, shape (N,)
Integer state indices in {0, 1, ..., L-1}.
"""
m_mod = np.asarray(m_mod).ravel()
levels = np.asarray(levels).ravel()
diff = np.abs(m_mod[:, None] - levels[None, :]) # (N, L)
state = np.argmin(diff, axis=1) # 0..L-1
return state
def detect_binding_bleach_from_state(
z_step,
t,
state,
levels,
min_levels_bind=3,
min_levels_bleach=1,
baseline_state_max=None,
):
"""
Detect binding (big upward state jumps) and bleaching (downward jumps)
using the discrete state sequence.
- Binding: large upward jump (>= min_levels_bind) starting from a
"baseline" state (state_before <= baseline_state_max) if that
parameter is given.
- Bleaching: downward jump (<= -min_levels_bleach)
Parameters
----------
z_step : array-like, shape (N,)
Step-wise photon counts.
t : array-like, shape (N,)
Time vector (seconds).
state : array-like, shape (N,)
Integer states 0..L-1 from assign_to_levels().
levels : array-like, shape (L,)
Level values (in m_mod space, not directly photon counts).
min_levels_bind : int
Minimum number of levels for an upward jump to be
considered a binding event.
min_levels_bleach : int
Minimum number of levels for a downward jump to be
considered a bleaching event.
baseline_state_max : int or None
Highest state index considered "baseline" before binding.
If None, any state can be the start of a binding jump.
Returns
-------
bind_idx, bleach_idx : np.ndarray of indices
bind_times, bleach_times : np.ndarray of times (seconds)
bind_values, bleach_values : np.ndarray of photon counts at those events
bind_state_before, bind_state_after : np.ndarray of integer states
bleach_state_before, bleach_state_after : np.ndarray of integer states
"""
z_step = np.asarray(z_step).ravel()
t = np.asarray(t).ravel()
state = np.asarray(state).ravel()
levels = np.asarray(levels).ravel()
N = len(t)
dstate = np.diff(state) # length N-1
idx = np.arange(N - 1)
# ----- Binding: big upward jump, optionally from baseline only -----
bind_mask = (dstate >= min_levels_bind)
if baseline_state_max is not None:
bind_mask &= (state[idx] <= baseline_state_max)
bind_idx = idx[bind_mask] + 1
# ----- Bleaching: downward jump -----
bleach_mask = (dstate <= -min_levels_bleach)
bleach_idx = idx[bleach_mask] + 1
bind_times = t[bind_idx]
bleach_times = t[bleach_idx]
bind_values = z_step[bind_idx]
bleach_values = z_step[bleach_idx]
bind_state_before = state[bind_idx - 1]
bind_state_after = state[bind_idx]
bleach_state_before = state[bleach_idx - 1]
bleach_state_after = state[bleach_idx]
return (
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
)
def filter_short_episodes_by_dwell(
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
dwell_min,
):
"""
Remove short binding episodes based on dwell time and also remove
the paired bleaching step.
Rule:
For each binding, find the first bleaching with t_bleach > t_bind.
If Δt = t_bleach - t_bind < dwell_min, then:
- remove this binding
- remove this bleaching
All other bleaching events remain.
Returns
-------
(filtered binding arrays, dwell_times) + filtered bleaching arrays
"""
if dwell_min <= 0 or len(bind_idx) == 0 or len(bleach_idx) == 0:
# no filtering requested or missing events
dwell_times = np.full(len(bind_idx), np.nan)
for i in range(len(bind_idx)):
future = np.where(bleach_times > bind_times[i])[0]
if len(future) > 0:
dwell_times[i] = bleach_times[future[0]] - bind_times[i]
return (
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
dwell_times,
)
bind_idx = np.asarray(bind_idx)
bleach_idx = np.asarray(bleach_idx)
bind_times = np.asarray(bind_times)
bleach_times = np.asarray(bleach_times)
bind_values = np.asarray(bind_values)
bleach_values = np.asarray(bleach_values)
bind_state_before = np.asarray(bind_state_before)
bind_state_after = np.asarray(bind_state_after)
bleach_state_before = np.asarray(bleach_state_before)
bleach_state_after = np.asarray(bleach_state_after)
keep_bind = np.ones(len(bind_idx), dtype=bool)
keep_bleach = np.ones(len(bleach_idx), dtype=bool)
dwell_times = np.full(len(bind_idx), np.nan)
removed_bind = 0
removed_bleach = 0
for i in range(len(bind_idx)):
t_b = bind_times[i]
future = np.where(bleach_times > t_b)[0]
if len(future) == 0:
# no bleaching afterwards → dwell undefined, keep binding
dwell_times[i] = np.nan
continue
j = future[0]
dt = bleach_times[j] - t_b
dwell_times[i] = dt
if dt < dwell_min:
# remove this binding and its paired bleaching
keep_bind[i] = False
if keep_bleach[j]:
keep_bleach[j] = False
removed_bleach += 1
removed_bind += 1
print(
f"[INFO] Dwell-based filter: removed {removed_bind} binding(s) and "
f"{removed_bleach} paired bleaching step(s) with Δt < {dwell_min} s; "
f"{np.sum(keep_bind)} binding(s) and {np.sum(keep_bleach)} bleaching step(s) kept."
)
# Apply masks
bind_idx = bind_idx[keep_bind]
bind_times = bind_times[keep_bind]
bind_values = bind_values[keep_bind]
bind_state_before = bind_state_before[keep_bind]
bind_state_after = bind_state_after[keep_bind]
dwell_times = dwell_times[keep_bind]
bleach_idx = bleach_idx[keep_bleach]
bleach_times = bleach_times[keep_bleach]
bleach_values = bleach_values[keep_bleach]
bleach_state_before = bleach_state_before[keep_bleach]
bleach_state_after = bleach_state_after[keep_bleach]
return (
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
dwell_times,
)
def plot_fig4AB(
track_id,
L_best=None,
min_levels_bind=3,
min_levels_bleach=1,
dwell_min=0.0,
baseline_state_max=None,
):
# --------------------------
# 1. Load ICON analysis file
# --------------------------
mat_file = f"icon_analysis_track_{track_id}_matlab.mat"
print(f"Loading {mat_file}")
if not os.path.exists(mat_file):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"{mat_file} does not exist in current directory.")
data = loadmat(mat_file)
def extract_vector(name):
if name not in data:
raise KeyError(f"Variable '{name}' not found in {mat_file}")
v = data[name]
return np.squeeze(v)
t = extract_vector("t")
z = extract_vector("z")
m_mod = extract_vector("m_mod")
if not (len(t) == len(z) == len(m_mod)):
raise ValueError("t, z, and m_mod must have the same length.")
N = len(t)
print(f"Track {track_id}: N = {N} points")
# --------------------------
# 2. Choose L (number of levels)
# --------------------------
if L_best is None:
L_best = 3 # fallback default
print(f"No L_best provided, using default L_best = {L_best}")
else:
print(f"Using user-specified L_best = {L_best}")
m_min = np.min(m_mod)
m_max = np.max(m_mod)
levels = np.linspace(m_min, m_max, L_best)
print(f"m_mod range: [{m_min:.4f}, {m_max:.4f}]")
print(f"Equally spaced levels ({L_best}): {levels}")
# --------------------------
# 3. Build step-wise trajectory from m_mod
# --------------------------
state = assign_to_levels(m_mod, levels) # 0..L_best-1
m_step = levels[state]
# Map back to photon counts via linear fit z ≈ a*m_step + b
A = np.column_stack([m_step, np.ones(N)])
theta, *_ = np.linalg.lstsq(A, z, rcond=None)
a, b = theta
z_step = A @ theta
print(f"Fitted z ≈ a * m_step + b with a = {a:.4f}, b = {b:.4f}")
# --------------------------
# 4. Detect binding / bleaching events (state-based)
# --------------------------
(
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
) = detect_binding_bleach_from_state(
z_step,
t,
state,
levels,
min_levels_bind=min_levels_bind,
min_levels_bleach=min_levels_bleach,
baseline_state_max=baseline_state_max,
)
base_msg = (
f"baseline_state_max={baseline_state_max}"
if baseline_state_max is not None
else "baseline_state_max=None (no baseline restriction)"
)
print(
f"Initial detection: {len(bind_idx)} binding and {len(bleach_idx)} bleaching "
f"events (min_levels_bind={min_levels_bind}, "
f"min_levels_bleach={min_levels_bleach}, {base_msg})."
)
# --------------------------
# 5. Apply dwell-time filter to binding + paired bleach
# --------------------------
(
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
dwell_times,
) = filter_short_episodes_by_dwell(
bind_idx,
bleach_idx,
bind_times,
bleach_times,
bind_values,
bleach_values,
bind_state_before,
bind_state_after,
bleach_state_before,
bleach_state_after,
dwell_min=dwell_min,
)
print(
f"After dwell filter (dwell_min={dwell_min}s): "
f"{len(bind_idx)} binding and {len(bleach_idx)} bleaching events remain."
)
# --------------------------
# 6. Build event table & save CSV / Excel
# --------------------------
rows = []
# Binding events
for i in range(len(bind_idx)):
idx = int(bind_idx[i])
rows.append({
"event_type": "binding",
"sample_index": idx,
"time_seconds": float(bind_times[i]),
"photon_count": float(bind_values[i]),
"state_before": int(bind_state_before[i]),
"state_after": int(bind_state_after[i]),
"level_before_norm": float(levels[bind_state_before[i]]),
"level_after_norm": float(levels[bind_state_after[i]]),
"dwell_time": float(dwell_times[i]) if not np.isnan(dwell_times[i]) else "",
})
# Bleaching events
for i in range(len(bleach_idx)):
idx = int(bleach_idx[i])
rows.append({
"event_type": "bleach",
"sample_index": idx,
"time_seconds": float(bleach_times[i]),
"photon_count": float(bleach_values[i]),
"state_before": int(bleach_state_before[i]),
"state_after": int(bleach_state_after[i]),
"level_before_norm": float(levels[bleach_state_before[i]]),
"level_after_norm": float(levels[bleach_state_after[i]]),
"dwell_time": "",
})
# Sort by time
rows = sorted(rows, key=lambda r: r["time_seconds"])
# Write CSV
csv_name = f"binding_bleach_events_track_{track_id}_L{L_best}.csv"
import csv
with open(csv_name, "w", newline="") as f:
writer = csv.DictWriter(
f,
fieldnames=[
"event_type",
"sample_index",
"time_seconds",
"photon_count",
"state_before",
"state_after",
"level_before_norm",
"level_after_norm",
"dwell_time",
],
)
writer.writeheader()
for r in rows:
writer.writerow(r)
print(f"Saved event table to {csv_name}")
# Write Excel (if pandas available)
if HAS_PANDAS:
df = pd.DataFrame(rows)
xlsx_name = f"binding_bleach_events_track_{track_id}_L{L_best}.xlsx"
df.to_excel(xlsx_name, index=False)
print(f"Saved event table to {xlsx_name}")
else:
print("[INFO] pandas not installed → skipped Excel (.xlsx) output.")
# --------------------------
# 7. Make a figure similar to Fig. 4A + 4B
# --------------------------
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(7, 6), sharex=True)
# ---- Fig. 4A-like: raw intensity vs time ----
ax1 = axes[0]
ax1.plot(t, z, color="black", linewidth=0.8)
ax1.set_ylabel("Photon counts")
ax1.set_title(f"Track {track_id}: raw intensity") #(Fig. 4A-like)
# ---- Fig. 4B-like: step-wise HMM fit vs time ----
ax2 = axes[1]
ax2.plot(t, z, color="0.8", linewidth=0.5, label="raw")
ax2.plot(t, z_step, color="red", linewidth=1.5,
label=f"equal levels (L={L_best})")
# Mark binding (up-steps) and bleaching (down-steps) AFTER filtering
if len(bind_idx) > 0:
ax2.scatter(
bind_times,
bind_values,
marker="^",
color="blue",
s=30,
label="binding",
)
if len(bleach_idx) > 0:
ax2.scatter(
bleach_times,
bleach_values,
marker="v",
color="black",
s=30,
label="bleach",
)
ax2.set_xlabel("Time (s)")
ax2.set_ylabel("Photon counts")
ax2.set_title(
f"Step-wise HMM fit (" #Fig. 4B-like,
f"min_bind_levels={min_levels_bind}, "
f"min_bleach_levels={min_levels_bleach}, "
f"dwell_min={dwell_min}s, "
f"baseline_state_max={baseline_state_max})"
)
ax2.legend(loc="best")
fig.tight_layout()
out_png = f"fig4AB_track_{track_id}_L{L_best}.png"
fig.savefig(out_png, dpi=300)
plt.close(fig)
print(f"Saved figure to {out_png}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("Usage: python plot_fig4AB_python.py
<track_id> [L_best] [min_levels_bind] [min_levels_bleach] [dwell_min] [baseline_state_max]")
sys.exit(1)
track_id = int(sys.argv[1])
# Defaults
L_best = None
min_levels_bind = 3
min_levels_bleach = 1
dwell_min = 0.0
baseline_state_max = None
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
L_best = int(sys.argv[2])
if len(sys.argv) >= 4:
min_levels_bind = int(sys.argv[3])
if len(sys.argv) >= 5:
min_levels_bleach = int(sys.argv[4])
if len(sys.argv) >= 6:
dwell_min = float(sys.argv[5])
if len(sys.argv) >= 7:
baseline_state_max = int(sys.argv[6])
plot_fig4AB(
track_id,
L_best=L_best,
min_levels_bind=min_levels_bind,
min_levels_bleach=min_levels_bleach,
dwell_min=dwell_min,
baseline_state_max=baseline_state_max,
)icon_multimer_histogram.m
% icon_multimer_histogram.m
%
% 用法(终端):
% octave icon_multimer_histogram.m [pattern]
%
% 默认 pattern = "equal_levels_track_*.mat"
%
% 要求每个 mat 文件里至少有:
% state : 等间距 level 的索引 (1..L_best)
% t : 时间向量
% z : 原始 photon counts
% track_id : (可选) 轨迹编号,用于打印信息
%
% 输出:
% - 在命令行打印每条轨迹估计出的 multimer 数目
% - 生成 Fig. 4C 风格直方图:
% multimer_histogram.png
arg_list = argv();
if numel(arg_list) >= 1
pattern = arg_list{1};
else
pattern = "equal_levels_track_*.mat";
end
fprintf("Searching files with pattern: %s\n", pattern);
files = dir(pattern);
if isempty(files)
error("No files matched pattern: %s", pattern);
end
multimers = []; % 保存每条轨迹的 multimer size
track_ids = []; % 保存对应的 track_id(若存在)
fprintf("Found %d files.\n", numel(files));
for i = 1:numel(files)
fname = files(i).name;
fprintf("\nLoading %s ...\n", fname);
S = load(fname);
if ~isfield(S, "state") || ~isfield(S, "t")
warning(" File %s does not contain 'state' or 't'. Skipped.", fname);
continue;
end
state = S.state(:);
t = S.t(:);
N = numel(state);
if N < 5
warning(" File %s has too few points (N=%d). Skipped.", fname, N);
continue;
end
% 解析 track_id(如果有)
tr_id = NaN;
if isfield(S, "track_id")
tr_id = S.track_id;
else
% 尝试从文件名里解析
tokens = regexp(fname, 'equal_levels_track_([0-9]+)', 'tokens');
if ~isempty(tokens)
tr_id = str2double(tokens{1}{1});
end
end
% 取前 10%% 和后 10%% 时间段的 state 中位数
n_head = max(1, round(0.1 * N));
n_tail = max(1, round(0.1 * N));
head_idx = 1:n_head;
tail_idx = (N - n_tail + 1):N;
initial_state = round(median(state(head_idx)));
final_state = round(median(state(tail_idx)));
multimer_size = initial_state - final_state;
if multimer_size <= 0
fprintf(" Track %g: initial_state=%d, final_state=%d -> multimer_size=%d (ignored)\n", ...
tr_id, initial_state, final_state, multimer_size);
continue;
end
fprintf(" Track %g: initial_state=%d, final_state=%d -> multimer_size=%d\n", ...
tr_id, initial_state, final_state, multimer_size);
multimers(end+1,1) = multimer_size;
track_ids(end+1,1) = tr_id;
end
if isempty(multimers)
error("No valid multimer sizes estimated. Check your data or thresholds.");
end
% 像论文那样,可以选择去掉 monomer/dimer
fprintf("\nTotal %d events (including monomer/dimer).\n", numel(multimers));
% 可选:过滤掉 ≤2 的(monomer / dimer)
mask = multimers > 2;
multimers_filtered = multimers(mask);
fprintf("After removing monomer/dimer (<=2): %d events.\n", numel(multimers_filtered));
if isempty(multimers_filtered)
error("No events left after filtering monomer/dimer. Try including them.");
end
% 计算直方图
max_mult = max(multimers_filtered);
edges = 0.5:(max_mult + 0.5);
[counts, edges_out] = histcounts(multimers_filtered, edges);
centers = 1:max_mult;
% 画 Fig. 4C 风格的柱状图
figure;
bar(centers, counts, 'FaceColor', [0.2 0.6 0.8]); % 颜色随便,Octave 会忽略
xlabel('Number of mN-LT per origin (multimer size)');
ylabel('Frequency');
title('Distribution of multimer sizes (Fig. 4C-like)');
xlim([0.5, max_mult + 0.5]);
% 在每个柱子上标一下计数
hold on;
for k = 1:max_mult
if counts(k) > 0
text(centers(k), counts(k) + 0.1, sprintf('%d', counts(k)), ...
'HorizontalAlignment', 'center');
end
end
hold off;
print('-dpng', 'multimer_histogram.png');
fprintf("\n[INFO] Multimer histogram saved to multimer_histogram.png\n");