-
Generate protein fasta
python3 getProteinSequences_1.py > Proximity_labelling.fasta python3 getProteinSequences_2.py > ALFA_pulldown.fasta python3 getProteinSequences_3.py > schnittmenge.fasta -
Using eggnog_env to generate the intial annotations
mamba activate eggnog_env emapper.py -i Proximity_labelling.fasta -o eggnog_out_Proximity_labelling --cpu 60 #--resume emapper.py -i ALFA_pulldown.fasta -o eggnog_out_ALFA_pulldown --cpu 60 emapper.py -i schnittmenge.fasta -o eggnog_out_schnittmenge --cpu 60 -
Using BLAST2GO to generate GO terms and EC terms
-
Using R to merge the two files blast2goannot.annot2 and eggnog_out.emapper.annotations.txt
#mamba activate r_env # PREPARING go_terms and ec_terms: annot_* file: cut -f1-2 -d$'\t' blast2go_annot.annot2 > blast2go_annot.annot2_ # PREPARING cp eggnog_out.emapper.annotations eggnog_out.emapper.annotations.txt. Note that the first last 3 lines starting with "#" should be removed; '#query' to query # Load required libraries library(openxlsx) # For Excel file handling library(dplyr) # For data manipulation library(clusterProfiler) # For KEGG and GO enrichment analysis #library(org.Hs.eg.db) # Replace with appropriate organism database #BiocManager::install("GO.db") #BiocManager::install("AnnotationDbi") library(GO.db) library(AnnotationDbi) # Step 1: Load the blast2go annotation file with a check for missing columns annot_df <- read.table("/home/jhuang/b2gWorkspace_schnittmenge/blast2go_annot.annot2_", header = FALSE, sep = "\t", stringsAsFactors = FALSE, fill = TRUE) # If the structure is inconsistent, we can make sure there are exactly 3 columns: colnames(annot_df) <- c("GeneID", "Term") # Step 2: Filter and aggregate GO and EC terms as before go_terms <- annot_df %>% filter(grepl("^GO:", Term)) %>% group_by(GeneID) %>% summarize(GOs = paste(Term, collapse = ","), .groups = "drop") ec_terms <- annot_df %>% filter(grepl("^EC:", Term)) %>% group_by(GeneID) %>% summarize(EC = paste(Term, collapse = ","), .groups = "drop") eggnog_data <- read.delim("~/DATA/Data_Michelle_ProteinClustering/eggnog_out_schnittmenge.emapper.annotations.txt", header = TRUE, sep = "\t") # Perform the left joins and rename columns eggnog_data_updated <- eggnog_data %>% left_join(go_terms, by = "GeneID") %>% left_join(ec_terms, by = "GeneID") #%>% select(-EC.x, -GOs.x) #%>% rename(EC = EC.y, GOs = GOs.y) # Create a new workbook wb <- createWorkbook() # Add the complete dataset as the first sheet (with annotations) addWorksheet(wb, "Complete_Data") writeData(wb, "Complete_Data", eggnog_data_updated) # Save the workbook to a file saveWorkbook(wb, "Gene_with_Annotations_schnittmenge.xlsx", overwrite = TRUE) #Manually DELETE GOs.x and EC.x and rename GOs.y to GOs, EC.y to EC. -
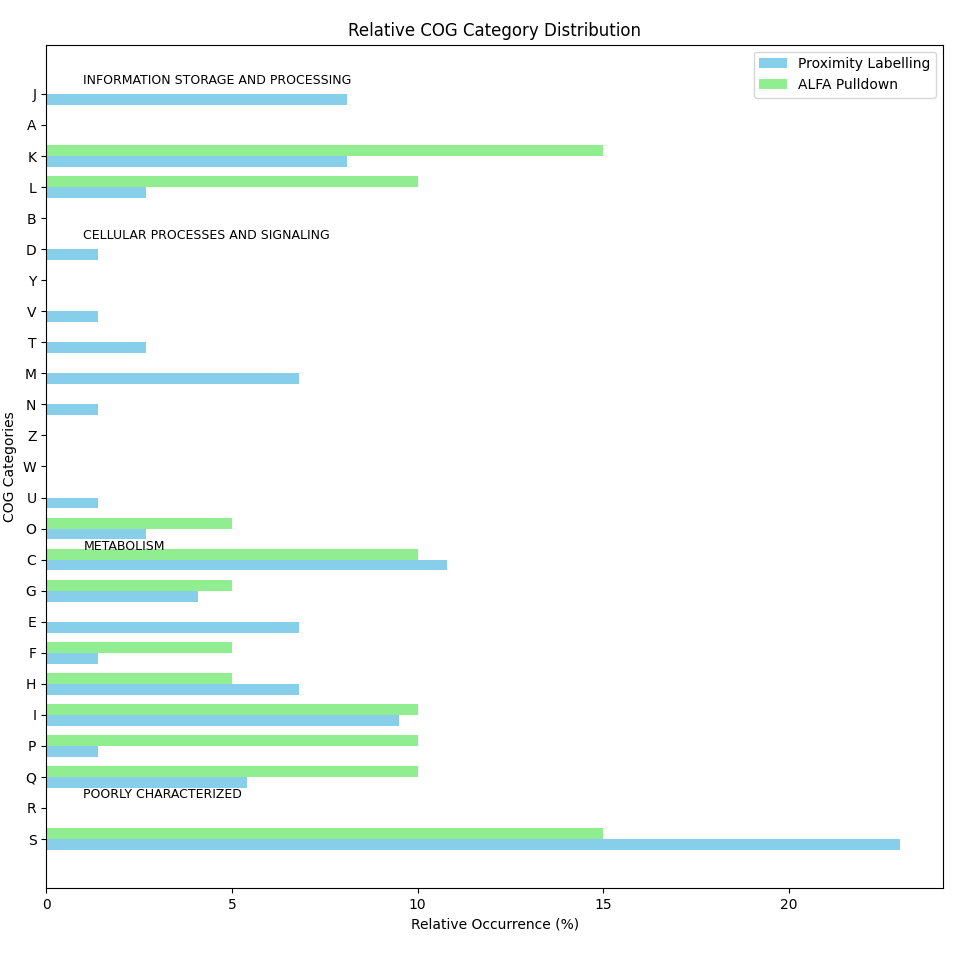
Draw group bar plot for relative occurrence
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd import numpy as np # COG annotations for the two gene sets proximity_labelling = [ 'D', 'S', 'K', 'S', 'T', 'S', 'S', 'F', 'E', 'J', 'G', 'C', 'C', 'S', 'I', 'L', 'I', 'S', 'S', 'G', 'O', 'H', 'IQ', 'L', 'C', 'H', 'C', 'NU', 'O', 'C', 'M', 'S', 'IQ', 'G', 'S', 'M', 'M', '-', 'M', 'S', 'J', 'S', 'IQ', 'K', 'E', 'J', 'K', 'E', 'J', 'S', 'K', 'E', 'S', 'J', 'S', 'V', 'C', 'I', 'K', 'IQ', 'M', 'S', 'T', 'P', 'C', 'J', 'S', 'E', 'C', 'K', 'H', 'S', 'H', 'H' ] alfa_pulldown = [ 'K', 'S', 'P', 'K', 'C', 'K', 'I', 'O', '-', 'F', 'C', 'P', 'HQ', '-', 'L', 'L', 'S', 'G', 'IQ', 'S' ] # Define all possible COG categories (including the combinations) all_cog_categories_ = ['J','A', 'K', 'L', 'B', 'D', 'Y', 'V', 'T', 'M', 'N', 'Z', 'W', 'U', 'O', 'C','G', 'E', 'F', 'H', 'I', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S'] all_cog_categories = all_cog_categories_[::-1] # Define functional groups for COG categories functional_groups = { "INFORMATION STORAGE AND PROCESSING": ['J', 'A', 'K', 'L', 'B'], "CELLULAR PROCESSES AND SIGNALING": ['D', 'Y', 'V', 'T', 'M', 'N', 'Z', 'W', 'U', 'O'], "METABOLISM": ['C', 'G', 'E', 'F', 'H', 'I', 'P', 'Q'], "POORLY CHARACTERIZED": ['R', 'S'] } # Function to count occurrences of each COG category in a gene set, handling combinations def count_cog_categories(gene_set): counts = {cog: gene_set.count(cog) for cog in all_cog_categories} # Treat combinations (e.g., IQ, HQ, NU) as belonging to both respective categories combination_categories = { 'IQ': ['I', 'Q'], 'HQ': ['H', 'Q'], 'NU': ['N', 'U'] } for comb, categories in combination_categories.items(): comb_count = gene_set.count(comb) for category in categories: counts[category] += comb_count counts[comb] = 0 # Remove the combination itself as it is distributed return counts # Count COG categories for each gene set proximity_counts = count_cog_categories(proximity_labelling) alfa_counts = count_cog_categories(alfa_pulldown) # Calculate relative occurrence (percentage) of each COG category for both gene sets total_proximity = len(proximity_labelling) total_alfa = len(alfa_pulldown) # Calculate percentages for each COG category in both gene sets proximity_percentage = {cog: count / total_proximity * 100 for cog, count in proximity_counts.items()} alfa_percentage = {cog: count / total_alfa * 100 for cog, count in alfa_counts.items()} # Create a DataFrame to store the percentages for both gene sets df_percentage = pd.DataFrame({ 'Proximity Labelling (%)': [proximity_percentage.get(cog, 0) for cog in all_cog_categories], 'ALFA Pulldown (%)': [alfa_percentage.get(cog, 0) for cog in all_cog_categories] }, index=all_cog_categories) ## Reverse the order of the COG categories #df_percentage = df_percentage[::-1] # Round the values to 1 decimal place df_percentage = df_percentage.round(1) # Save the relative occurrence data in a text file file_path = "COG_relative_occurrence.txt" df_percentage.to_csv(file_path, sep='\t', header=True, index=True) # Save the relative occurrence data in an Excel file file_path = "COG_relative_occurrence.xlsx" df_percentage.to_excel(file_path, header=True, index=True) # Display file path where the data was saved print(f"Relative occurrence data has been saved to {file_path}") # -------------------- # Horizontal Grouped Bar Plot # -------------------- # Plot a horizontal grouped bar chart fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8)) # Create the positions for each group of bars bar_height = 0.35 index = np.arange(len(df_percentage)) # Plot bars for both gene sets bar1 = ax.barh(index, df_percentage['Proximity Labelling (%)'], bar_height, label='Proximity Labelling', color='skyblue') bar2 = ax.barh(index + bar_height, df_percentage['ALFA Pulldown (%)'], bar_height, label='ALFA Pulldown', color='lightgreen') # Customize the plot ax.set_ylabel('COG Categories') ax.set_xlabel('Relative Occurrence (%)') ax.set_title('Relative COG Category Distribution') ax.set_yticks(index + bar_height / 2) ax.set_yticklabels(all_cog_categories) # Annotate functional groups #, fontweight='bold' for group, categories in functional_groups.items(): # Find indices of the categories in this group group_indices = [all_cog_categories.index(cog) for cog in categories] # Add a label for the functional group ax.annotate(group, xy=(1, group_indices[0] + 0.5), xycoords='data', fontsize=9, color='black') # Add legend ax.legend() # Show the plot plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
Functional Clustering of Genes Based on COG Terms Using Eggnog and Blast2GO
Leave a reply