Category Archives: Articles
FASTQ / raw sequencing datasets overview (T. and F.)
1) Per-dataset sample inventory (compact lists)
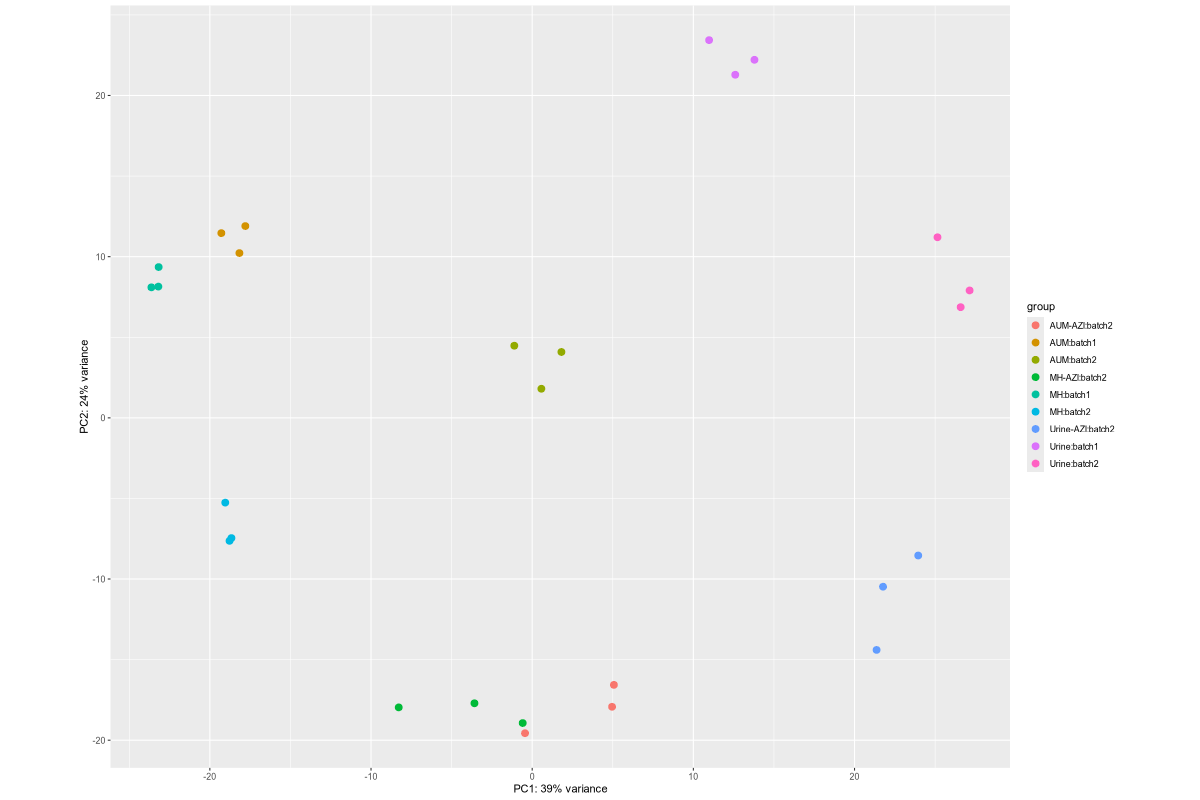
1. Data_Tam_RNAseq_2024_AUM_MHB_Urine_on_ATCC19606
X101SC24105589-Z01-J001:AUM-1..3,MHB-1..3,Urine-1..3(all PE)X101SC25062155-Z01-J002:AUM-1..3,AUM-AZI-1..3,MH-1..3,MH-AZI-1..3,Urine-1..3,Urine-AZI-1..3(all PE)
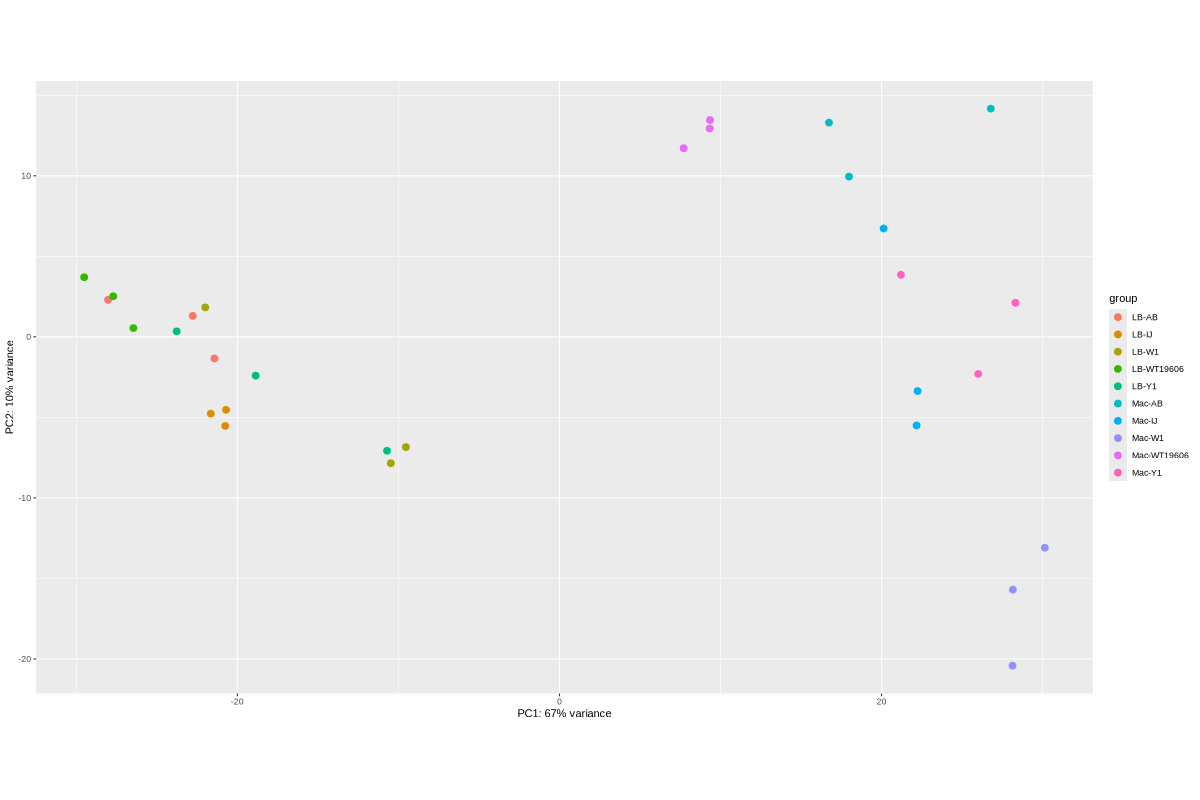
2. Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_LB-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_vs_Mac-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_on_ATCC19606
- LB:
LB-AB-1..3,LB-IJ-(1,2,4),LB-W1-1..3,LB-WT19606-2..4,LB-Y1-2..4 - Mac:
Mac-AB-1..3,Mac-IJ-(1,2,4),Mac-W1-1..3,Mac-WT19606-2..4,Mac-Y1-2..4
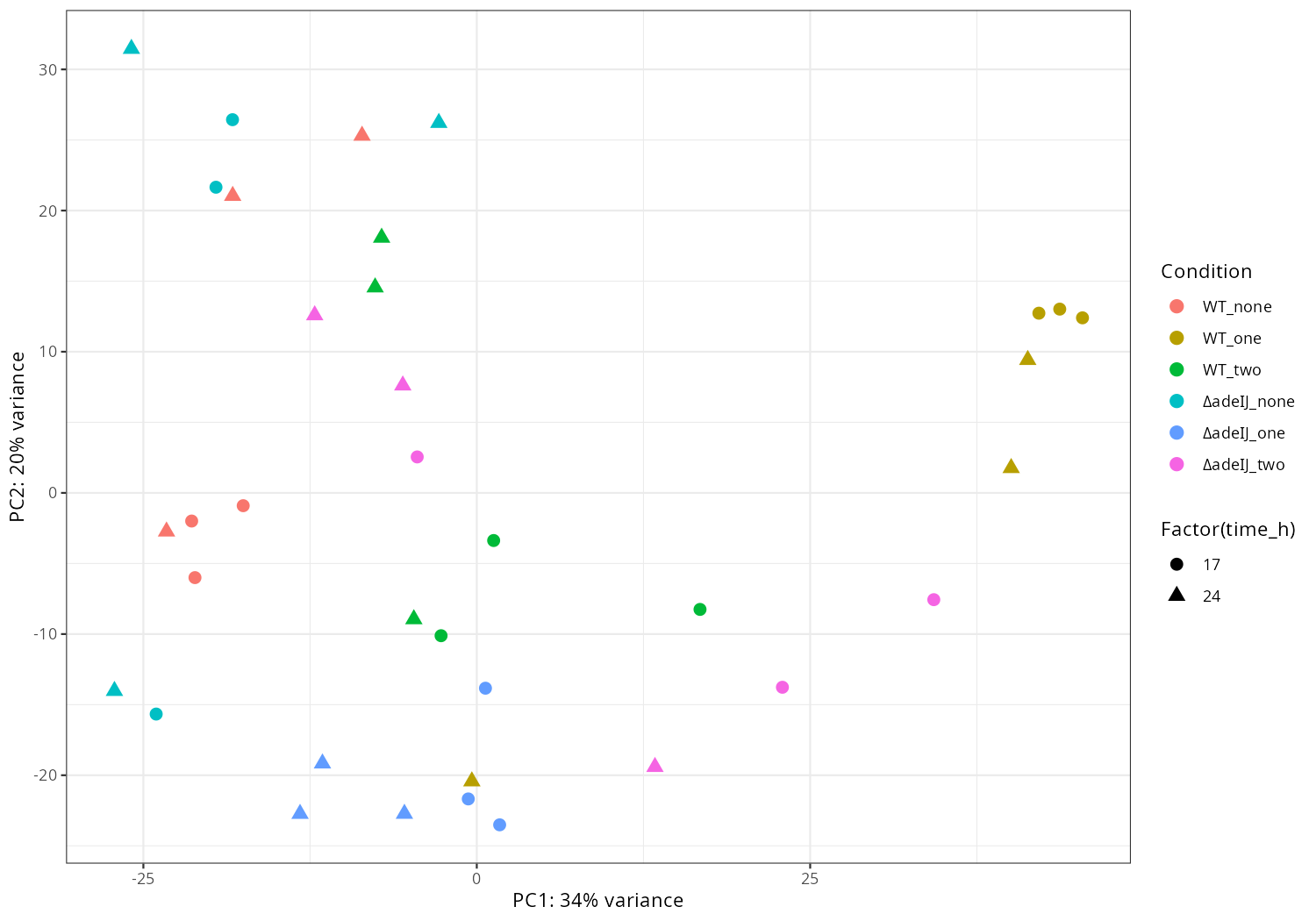
3. Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_subMIC_exposure_on_ATCC19606
Each with reps -1..-3 (all PE):
0_5ΔIJ-17,0_5ΔIJ-24preWT-17,preWT-24preΔIJ-17,preΔIJ-24WT0_5-17,WT0_5-24WT-17,WT-24ΔIJ-17,ΔIJ-24
4. Data_Tam_DNAseq_2023_lab_strains
- A6WT – Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC19606
- A10CraA – Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC19606
- A12AYE – Acinetobacter baumannii AYE
- A1917978 – Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC17978
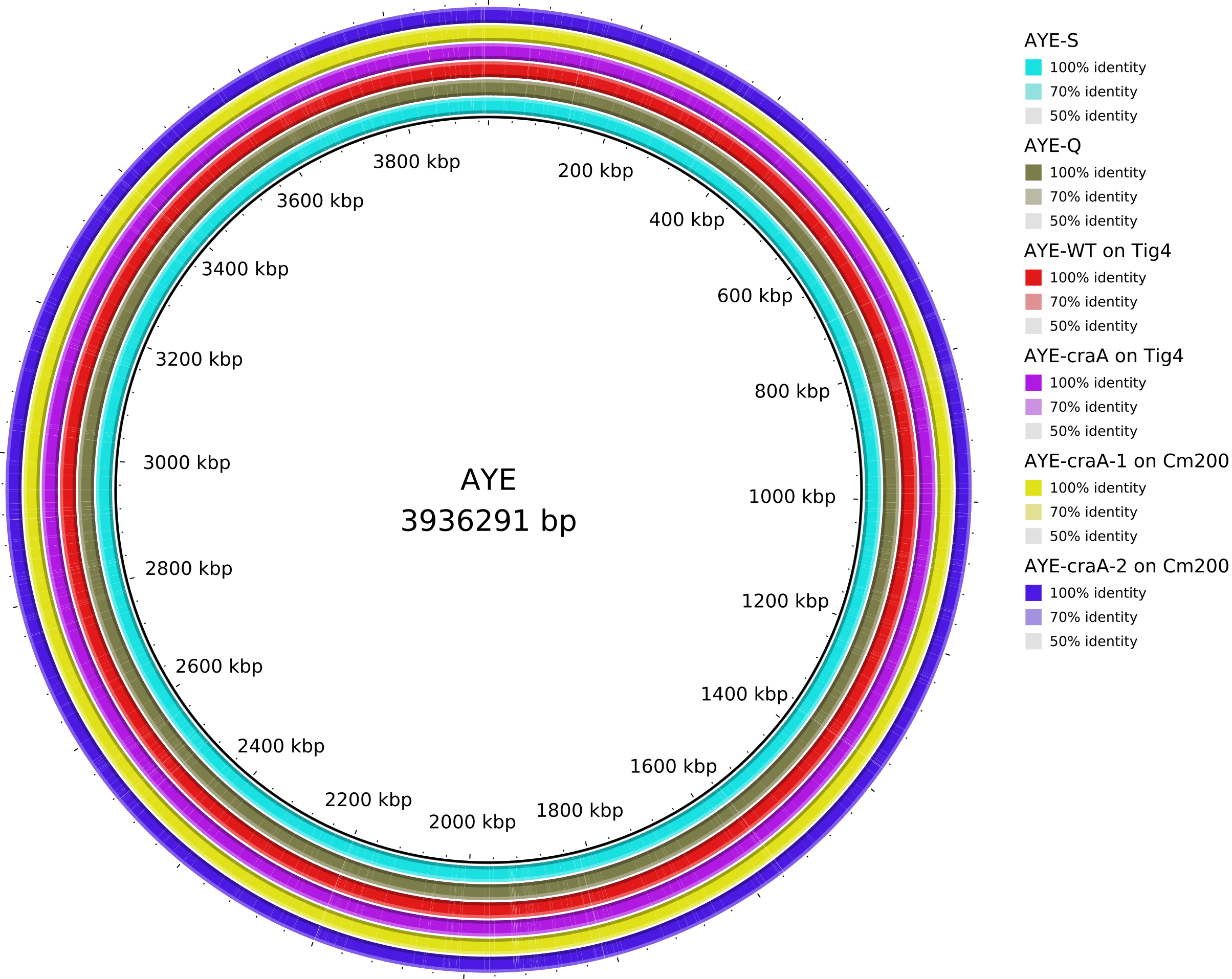
5. Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_AYE-WT_Q_S_craA-Tig4_craA-1-Cm200_craA-2-Cm200
AYE-Q,AYE-S,AYE-WTonTig4,AYE-craAonTig4,AYE-craA-1onCm200,AYE-craA-2onCm200,clinical(all PE)
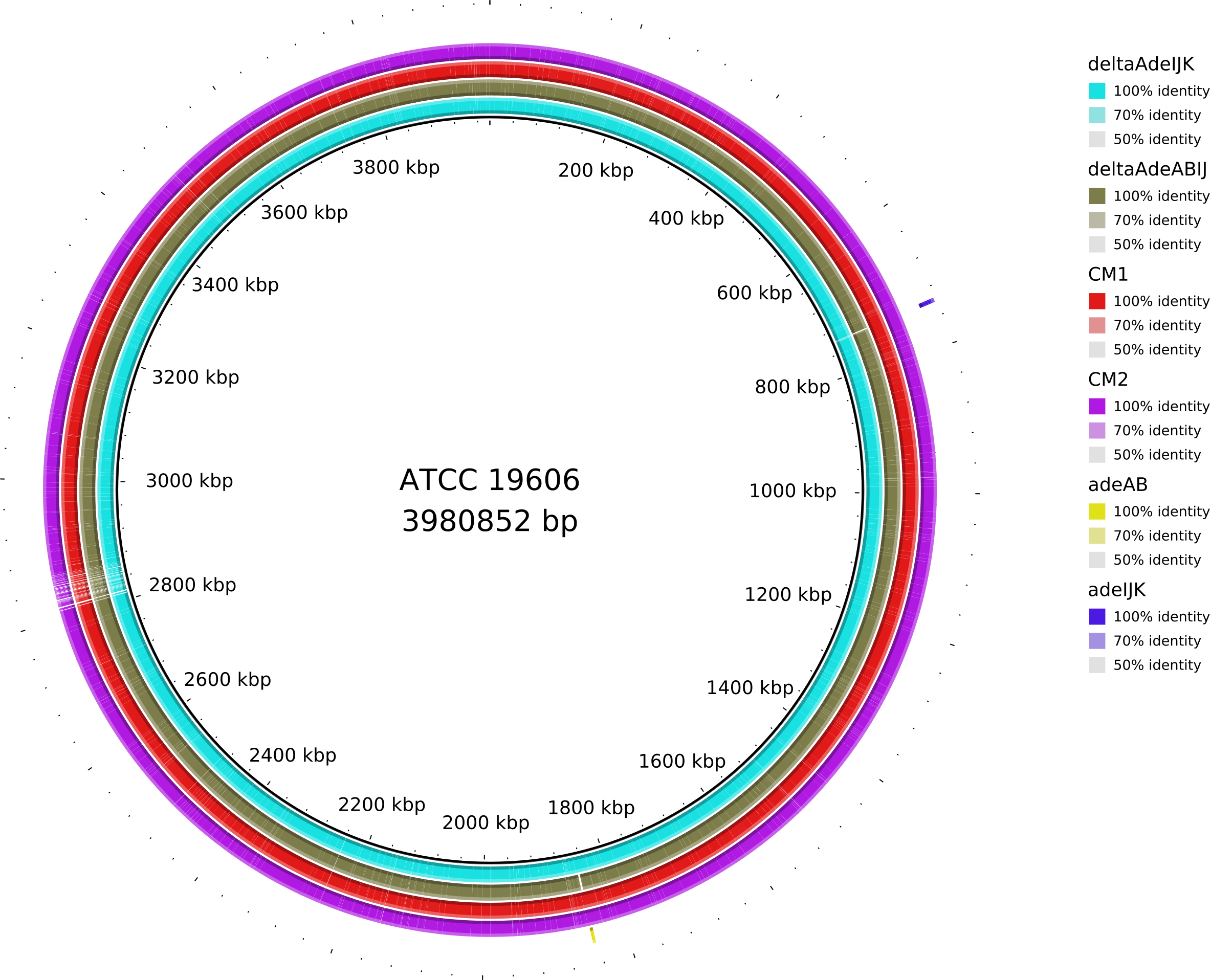
6. Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_E.hormaechei-adeABadeIJ_adeIJK_CM1_CM2_on_ATCC19606
adeABadeIJ,adeIJK,CM1,CM2,HF(all PE)
7. Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_ATCC19606-Y1Y2Y3Y4W1W2W3W4
- Illumina PE:
△adeIJ,Tig1,Tig2,W,W2,W3,W4,Y,Y2,Y3,Y4 -
Nanopore (
*_fastq_pass.tar):W1(3 tar files),W2(1),W3(2),W4(1)Y1(3),Y2(1),Y3(1),Y4(1)
8. Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_19606deltaIJfluE
All PE; grouped by background:
19606△ABfluE:cef-1,cipro-2,dori-2,nitro-3,pip-1,polyB-3,tet-119606△IJfluE:cef-4,cipro-3,dori-1,nitro-3,pip-4,polyB-419606wtfluE:cef-1,cipro-2,dori-1,nitro-1,pip-4,polyB-4,tet-2
9. Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_Acinetobacter_harbinensis
An6(PE)
10. Data_Tam_Metagenomics_2026
A1,A1a,A2,B1,B2(PE)
11. Data_Foong_RNAseq_2021_ATCC19606_Cm (mapping list provided)
- Batch1:
WT_1,WT_2B,C_1B,C_2,J_1,J_2 - Batch2:
Control,WT_1B,WT_2B,WT_3B,Cra_1,Cra_2,Cra_3,IJ_1B,IJ_2B,IJ_3 - Batch3:
adIJ_1,adIJ_2,crA2,crA_ab_1,crA_ab_2,crA_ab_3,adAB_1,adAB_2,adAB_ab1,adAB_ab2,adAB_ab3
12. Data_Foong_DNAseq_2025_AYE_Dark_vs_Light
Dark,Light(PE)
2) Dataset-level summary (quick lookup)
| Dataset folder | Year | Data type | Platform / format | Run / project IDs present | Samples (n) | Files (n) | Sample groups / notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Data_Tam_RNAseq_2024_AUM_MHB_Urine_on_ATCC19606/ |
2024 | RNA-seq | Illumina PE (*_1.fq.gz, *_2.fq.gz) |
X101SC24105589-Z01-J001, X101SC25062155-Z01-J002 |
27 | 54 | J001: AUM/MHB/Urine (each 1–3). J002: AUM, AUM-AZI, MH, MH-AZI, Urine, Urine-AZI (each 1–3). |
Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_LB-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_vs_Mac-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_on_ATCC19606/ |
2025 | RNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC25015922-Z02-J002 |
30 | 60 | LB vs Mac sets; conditions AB, IJ, W1, Y1, WT19606 with listed replicates (mostly 1–3 or 2–4; IJ uses 1,2,4). |
Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_subMIC_exposure_on_ATCC19606/ |
2025 | RNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC25062155-Z01-J001 |
36 | 72 | 12 condition blocks × 3 reps: preWT, preΔIJ, WT, ΔIJ, WT0_5, 0_5ΔIJ at timepoints 17 and 24. |
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_ATCC19606-Y1Y2Y3Y4W1W2W3W4/ |
2025 | DNA-seq | Illumina PE + Nanopore (*_fastq_pass.tar) |
Illumina: X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/J002; Nanopore: X101SC25080408-Z01-J001 |
11 (Illumina) + 13 tar archives | 22 + 13 | Illumina: △adeIJ, Tig1, Tig2, W, W2–W4, Y, Y2–Y4. Nanopore: W1(3), W2(1), W3(2), W4(1), Y1(3), Y2(1), Y3(1), Y4(1) tar files. |
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_AYE-WT_Q_S_craA-Tig4_craA-1-Cm200_craA-2-Cm200/ |
2025 | DNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC25015922-Z01-J001 |
7 | 14 | AYE variants: AYE-Q, AYE-S, AYE-WTonTig4, AYE-craAonTig4, AYE-craA-1onCm200, AYE-craA-2onCm200, plus clinical. |
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_E.hormaechei-adeABadeIJ_adeIJK_CM1_CM2 |
2025 | DNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC24115801-Z01-J001 |
5 | 10 | adeABadeIJ, adeIJK, CM1, CM2, HF. |
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_19606deltaIJfluE/ |
2026 | DNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC25116512-Z01-J003 |
20 | 40 | Three backgrounds: 19606△ABfluE* (7), 19606△IJfluE* (6), 19606wtfluE* (7) across drug tags (cef/cipro/dori/nitro/pip/polyB/tet) with replicate suffixes. |
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_Acinetobacter_harbinensis/ |
2026 | DNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC25116512-Z01-J002 |
1 | 2 | An6 (paired-end). |
Data_Tam_Metagenomics_2026/ |
2026 | Metagenomics | Illumina PE | X101SC25123808-Z01-J001 |
5 | 10 | A1, A1a, A2, B1, B2. |
Data_Foong_RNAseq_2021_ATCC19606_Cm/ |
2021 | RNA-seq | Illumina PE (symlink/mapping list shown) | (paths point to raw_data_batch1/2/3) |
27 | 54 | Batch1: WT/craA/adeIJ (each 2 reps). Batch2: Control + WT.abx + craA.abx + adeIJ.abx (various reps). Batch3: adeIJ, craA, craA.abx, adeAB, adeAB.abx (various reps). |
Data_Foong_DNAseq_2025_AYE_Dark_vs_Light/ |
2025 | DNA-seq | Illumina PE | X101SC25116512-Z01-J001 |
2 | 4 | Dark, Light. |
3) Complete list
Data_Tam_RNAseq_2024_AUM_MHB_Urine_on_ATCC19606/
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AUM-1/AUM-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AUM-1/AUM-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AUM-2/AUM-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AUM-2/AUM-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AUM-3/AUM-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AUM-3/AUM-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/MHB-1/MHB-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/MHB-1/MHB-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/MHB-2/MHB-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/MHB-2/MHB-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/MHB-3/MHB-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/MHB-3/MHB-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Urine-1/Urine-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Urine-1/Urine-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Urine-2/Urine-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Urine-2/Urine-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Urine-3/Urine-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24105589-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Urine-3/Urine-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-1/AUM-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-1/AUM-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-2/AUM-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-2/AUM-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-3/AUM-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-3/AUM-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-AZI-1/AUM-AZI-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-AZI-1/AUM-AZI-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-AZI-2/AUM-AZI-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-AZI-2/AUM-AZI-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-AZI-3/AUM-AZI-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/AUM-AZI-3/AUM-AZI-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-1/MH-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-1/MH-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-2/MH-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-2/MH-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-3/MH-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-3/MH-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-AZI-1/MH-AZI-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-AZI-1/MH-AZI-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-AZI-2/MH-AZI-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-AZI-2/MH-AZI-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-AZI-3/MH-AZI-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/MH-AZI-3/MH-AZI-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-1/Urine-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-1/Urine-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-2/Urine-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-2/Urine-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-3/Urine-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-3/Urine-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-AZI-1/Urine-AZI-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-AZI-1/Urine-AZI-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-AZI-2/Urine-AZI-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-AZI-2/Urine-AZI-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-AZI-3/Urine-AZI-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Urine-AZI-3/Urine-AZI-3_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_LB-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_vs_Mac-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_on_ATCC19606/
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-AB-1/LB-AB-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-AB-1/LB-AB-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-AB-2/LB-AB-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-AB-2/LB-AB-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-AB-3/LB-AB-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-AB-3/LB-AB-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-IJ-1/LB-IJ-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-IJ-1/LB-IJ-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-IJ-2/LB-IJ-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-IJ-2/LB-IJ-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-IJ-4/LB-IJ-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-IJ-4/LB-IJ-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-W1-1/LB-W1-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-W1-1/LB-W1-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-W1-2/LB-W1-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-W1-2/LB-W1-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-W1-3/LB-W1-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-W1-3/LB-W1-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-WT19606-2/LB-WT19606-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-WT19606-2/LB-WT19606-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-WT19606-3/LB-WT19606-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-WT19606-3/LB-WT19606-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-WT19606-4/LB-WT19606-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-WT19606-4/LB-WT19606-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-Y1-2/LB-Y1-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-Y1-2/LB-Y1-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-Y1-3/LB-Y1-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-Y1-3/LB-Y1-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-Y1-4/LB-Y1-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/LB-Y1-4/LB-Y1-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-AB-1/Mac-AB-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-AB-1/Mac-AB-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-AB-2/Mac-AB-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-AB-2/Mac-AB-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-AB-3/Mac-AB-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-AB-3/Mac-AB-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-IJ-1/Mac-IJ-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-IJ-1/Mac-IJ-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-IJ-2/Mac-IJ-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-IJ-2/Mac-IJ-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-IJ-4/Mac-IJ-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-IJ-4/Mac-IJ-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-W1-1/Mac-W1-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-W1-1/Mac-W1-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-W1-2/Mac-W1-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-W1-2/Mac-W1-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-W1-3/Mac-W1-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-W1-3/Mac-W1-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-WT19606-2/Mac-WT19606-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-WT19606-2/Mac-WT19606-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-WT19606-3/Mac-WT19606-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-WT19606-3/Mac-WT19606-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-WT19606-4/Mac-WT19606-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-WT19606-4/Mac-WT19606-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-Y1-2/Mac-Y1-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-Y1-2/Mac-Y1-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-Y1-3/Mac-Y1-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-Y1-3/Mac-Y1-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-Y1-4/Mac-Y1-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z02-J002/01.RawData/Mac-Y1-4/Mac-Y1-4_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_subMIC_exposure_on_ATCC19606/
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-17-1/0_5ΔIJ-17-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-17-1/0_5ΔIJ-17-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-17-2/0_5ΔIJ-17-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-17-2/0_5ΔIJ-17-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-17-3/0_5ΔIJ-17-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-17-3/0_5ΔIJ-17-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-24-1/0_5ΔIJ-24-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-24-1/0_5ΔIJ-24-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-24-2/0_5ΔIJ-24-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-24-2/0_5ΔIJ-24-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-24-3/0_5ΔIJ-24-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/0_5ΔIJ-24-3/0_5ΔIJ-24-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-17-1/preWT-17-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-17-1/preWT-17-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-17-2/preWT-17-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-17-2/preWT-17-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-17-3/preWT-17-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-17-3/preWT-17-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-24-1/preWT-24-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-24-1/preWT-24-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-24-2/preWT-24-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-24-2/preWT-24-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-24-3/preWT-24-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preWT-24-3/preWT-24-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-17-1/preΔIJ-17-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-17-1/preΔIJ-17-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-17-2/preΔIJ-17-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-17-2/preΔIJ-17-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-17-3/preΔIJ-17-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-17-3/preΔIJ-17-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-24-1/preΔIJ-24-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-24-1/preΔIJ-24-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-24-2/preΔIJ-24-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-24-2/preΔIJ-24-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-24-3/preΔIJ-24-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/preΔIJ-24-3/preΔIJ-24-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-17-1/WT0_5-17-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-17-1/WT0_5-17-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-17-2/WT0_5-17-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-17-2/WT0_5-17-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-17-3/WT0_5-17-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-17-3/WT0_5-17-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-24-1/WT0_5-24-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-24-1/WT0_5-24-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-24-2/WT0_5-24-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-24-2/WT0_5-24-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-24-3/WT0_5-24-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT0_5-24-3/WT0_5-24-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-17-1/WT-17-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-17-1/WT-17-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-17-2/WT-17-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-17-2/WT-17-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-17-3/WT-17-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-17-3/WT-17-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-24-1/WT-24-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-24-1/WT-24-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-24-2/WT-24-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-24-2/WT-24-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-24-3/WT-24-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/WT-24-3/WT-24-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-17-1/ΔIJ-17-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-17-1/ΔIJ-17-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-17-2/ΔIJ-17-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-17-2/ΔIJ-17-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-17-3/ΔIJ-17-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-17-3/ΔIJ-17-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-24-1/ΔIJ-24-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-24-1/ΔIJ-24-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-24-2/ΔIJ-24-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-24-2/ΔIJ-24-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-24-3/ΔIJ-24-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25062155-Z01-J001/01.RawData/ΔIJ-24-3/ΔIJ-24-3_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_ATCC19606-Y1Y2Y3Y4W1W2W3W4/
Illumina short-sequencing:
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/△adeIJ/△adeIJ_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/△adeIJ/△adeIJ_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Tig1/Tig1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Tig1/Tig1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Tig2/Tig2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Tig2/Tig2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/W/W_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/W/W_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/W2/W2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/W2/W2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/W3/W3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/W3/W3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/W4/W4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/W4/W4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Y/Y_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Y/Y_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Y2/Y2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Y2/Y2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Y3/Y3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Y3/Y3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Y4/Y4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24065637-Z01-J002/01.RawData/Y4/Y4_2.fq.gz
Nanopore long-sequencing:
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W1/0710_2F_PBG50143_74807b09/W1_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W1/0629_2H_PBG55359_f19e323f/W1_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W1/0631_2C_PBG05153_55abe88b/W1_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W2/0620_2C_PBG17000_6bfd0048/W2_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W3/0710_2F_PBG50143_74807b09/W3_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W3/0629_2H_PBG55359_f19e323f/W3_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/W4/0620_2C_PBG17000_6bfd0048/W4_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Y1/0655_3B_PBE70655_6bbd09a4/Y1_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Y1/0620_2C_PBG17000_6bfd0048/Y1_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Y1/0631_2C_PBG05153_55abe88b/Y1_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Y2/0620_2C_PBG17000_6bfd0048/Y2_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Y3/0620_2C_PBG17000_6bfd0048/Y3_fastq_pass.tar
./X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Release-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001-20251009/Data-X101SC25080408-Z01-J001/Y4/0620_2C_PBG17000_6bfd0048/Y4_fastq_pass.tar
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_AYE-WT_Q_S_craA-Tig4_craA-1-Cm200_craA-2-Cm200/
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-craA-1onCm200/AYE-craA-1onCm200_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-craA-1onCm200/AYE-craA-1onCm200_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-craA-2onCm200/AYE-craA-2onCm200_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-craA-2onCm200/AYE-craA-2onCm200_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-craAonTig4/AYE-craAonTig4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-craAonTig4/AYE-craAonTig4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-Q/AYE-Q_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-Q/AYE-Q_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-S/AYE-S_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-S/AYE-S_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-WTonTig4/AYE-WTonTig4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/AYE-WTonTig4/AYE-WTonTig4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/clinical/clinical_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25015922-Z01-J001/01.RawData/clinical/clinical_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_E.hormaechei-adeABadeIJ_adeIJK_CM1_CM2
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/adeABadeIJ/adeABadeIJ_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/adeABadeIJ/adeABadeIJ_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/adeIJK/adeIJK_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/adeIJK/adeIJK_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/CM1/CM1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/CM1/CM1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/CM2/CM2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/CM2/CM2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/HF/HF_1.fq.gz
./X101SC24115801-Z01-J001/01.RawData/HF/HF_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_19606deltaIJfluE/
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEcef-1/19606△ABfluEcef-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEcef-1/19606△ABfluEcef-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEcipro-2/19606△ABfluEcipro-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEcipro-2/19606△ABfluEcipro-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEdori-2/19606△ABfluEdori-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEdori-2/19606△ABfluEdori-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEnitro-3/19606△ABfluEnitro-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEnitro-3/19606△ABfluEnitro-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEpip-1/19606△ABfluEpip-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEpip-1/19606△ABfluEpip-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEpolyB-3/19606△ABfluEpolyB-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEpolyB-3/19606△ABfluEpolyB-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEtet-1/19606△ABfluEtet-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△ABfluEtet-1/19606△ABfluEtet-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEcef-4/19606△IJfluEcef-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEcef-4/19606△IJfluEcef-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEcipro-3/19606△IJfluEcipro-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEcipro-3/19606△IJfluEcipro-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEdori-1/19606△IJfluEdori-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEdori-1/19606△IJfluEdori-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEnitro-3/19606△IJfluEnitro-3_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEnitro-3/19606△IJfluEnitro-3_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEpip-4/19606△IJfluEpip-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEpip-4/19606△IJfluEpip-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEpolyB-4/19606△IJfluEpolyB-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606△IJfluEpolyB-4/19606△IJfluEpolyB-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEcef-1/19606wtfluEcef-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEcef-1/19606wtfluEcef-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEcipro-2/19606wtfluEcipro-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEcipro-2/19606wtfluEcipro-2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEdori-1/19606wtfluEdori-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEdori-1/19606wtfluEdori-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEnitro-1/19606wtfluEnitro-1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEnitro-1/19606wtfluEnitro-1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEpip-4/19606wtfluEpip-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEpip-4/19606wtfluEpip-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEpolyB-4/19606wtfluEpolyB-4_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEpolyB-4/19606wtfluEpolyB-4_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEtet-2/19606wtfluEtet-2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J003/01.RawData/19606wtfluEtet-2/19606wtfluEtet-2_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_Acinetobacter_harbinensis/
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_2.fq.gz
Data_Tam_Metagenomics_2026/
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/A1/A1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/A1/A1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/A1a/A1a_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/A1a/A1a_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/A2/A2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/A2/A2_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/B1/B1_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/B1/B1_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/B2/B2_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25123808-Z01-J001/01.RawData/B2/B2_2.fq.gz
Data_Foong_RNAseq_2021_ATCC19606_Cm/
wt_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/WT_1_1.fq.gz
wt_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/WT_1_2.fq.gz
wt_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/WT_2B_1.fq.gz
wt_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/WT_2B_2.fq.gz
craA_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/C_1B_1.fq.gz
craA_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/C_1B_2.fq.gz
craA_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/C_2_1.fq.gz
craA_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/C_2_2.fq.gz
adeIJ_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/J_1_1.fq.gz
adeIJ_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/J_1_2.fq.gz
adeIJ_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/J_2_1.fq.gz
adeIJ_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch1/J_2_2.fq.gz
wt_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Control_1.fq.gz
wt_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Control_2.fq.gz
wt.abx_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/WT_1B_1.fq.gz
wt.abx_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/WT_1B_2.fq.gz
wt.abx_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/WT_2B_1.fq.gz
wt.abx_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/WT_2B_2.fq.gz
wt.abx_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/WT_3B_1.fq.gz
wt.abx_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/WT_3B_2.fq.gz
craA.abx_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Cra_1_1.fq.gz
craA.abx_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Cra_1_2.fq.gz
craA.abx_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Cra_2_1.fq.gz
craA.abx_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Cra_2_2.fq.gz
craA.abx_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Cra_3_1.fq.gz
craA.abx_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/Cra_3_2.fq.gz
adeIJ.abx_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/IJ_1B_1.fq.gz
adeIJ.abx_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/IJ_1B_2.fq.gz
adeIJ.abx_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/IJ_2B_1.fq.gz
adeIJ.abx_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/IJ_2B_2.fq.gz
adeIJ.abx_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/IJ_3_1.fq.gz
adeIJ.abx_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch2/IJ_3_2.fq.gz
adeIJ_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adIJ_1_1.fq.gz
adeIJ_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adIJ_1_2.fq.gz
adeIJ_r4_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adIJ_2_1.fq.gz
adeIJ_r4_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adIJ_2_2.fq.gz
craA_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA2_1.fq.gz
craA_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA2_2.fq.gz
craA.abx_r4_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA_ab_1_1.fq.gz
craA.abx_r4_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA_ab_1_2.fq.gz
craA.abx_r5_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA_ab_2_1.fq.gz
craA.abx_r5_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA_ab_2_2.fq.gz
craA.abx_r6_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA_ab_3_1.fq.gz
craA.abx_r6_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/crA_ab_3_2.fq.gz
adeAB_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_1_1.fq.gz
adeAB_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_1_2.fq.gz
adeAB_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_2_1.fq.gz
adeAB_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_2_2.fq.gz
adeAB.abx_r1_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_ab1_1.fq.gz
adeAB.abx_r1_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_ab1_2.fq.gz
adeAB.abx_r2_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_ab2_1.fq.gz
adeAB.abx_r2_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_ab2_2.fq.gz
adeAB.abx_r3_R1.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_ab3_1.fq.gz
adeAB.abx_r3_R2.fq.gz -> ../raw_data_batch3/adAB_ab3_2.fq.gz
Data_Foong_DNAseq_2025_AYE_Dark_vs_Light/
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Dark/Dark_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Dark/Dark_2.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Light/Light_1.fq.gz
./X101SC25116512-Z01-J001/01.RawData/Light/Light_2.fq.gzDirectory Listings Summary (Disk Directories)
/media/jhuang/INTENSO
(empty; data now on
~/DATA_Intenso)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | (empty) |
~/DATA
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Ute_MKL1 |
| 2 | Data_Ute_RNA_4_2022-11_test |
| 3 | Data_Ute_RNA_3 |
| 4 | Data_Susanne_Carotis_RNASeq_PUBLISHING |
| 5 | Data_Jiline_Yersinia_SNP |
| 6 | Data_Tam_ABAYE_RS05070_on_A_calcoaceticus_baumannii_complex_DUPLICATED_DEL |
| 7 | Data_Nicole_CRC1648 |
| 8 | Mouse_HS3ST1_12373_out |
| 9 | Mouse_HS3ST1_12175_out |
| 10 | Data_Biobakery |
| 11 | Data_Xiaobo_10x_2 |
| 12 | Data_Xiaobo_10x_3 |
| 13 | Talk_Nicole_CRC1648 |
| 14 | Talks_Bioinformatics_Meeting |
| 15 | Talks_resources |
| 16 | Data_Susanne_MPox_DAMIAN |
| 17 | Data_host_transcriptional_response |
| 18 | Talks_including_DEEP-DV |
| 19 | DOKTORARBEIT |
| 20 | Data_Susanne_MPox |
| 21 | Data_Jiline_Transposon |
| 22 | Data_Jiline_Transposon2 |
| 23 | Data_Matlab |
| 24 | deepseek-ai |
| 25 | Stick_Mi_DEL |
| 26 | TODO_shares |
| 27 | Data_Ute_RNA_4 |
| 28 | Data_Liu_PCA_plot |
| 29 | README_run_viral-ngs_inside_Docker |
| 30 | README_compare_genomes |
| 31 | mapped.bam |
| 32 | Data_Serpapi |
| 33 | Data_Ute_RNA_1_2 |
| 34 | Data_Marc_RNAseq_2024 |
| 35 | Data_Nicole_CaptureProbeSequencing |
| 36 | LOG_mapping |
| 37 | Data_Huang_Human_herpesvirus_3 |
| 38 | Data_Nicole_DAMIAN_Post-processing_Pathoprobe_FluB_Links |
| 39 | Access_to_Win7 |
| 40 | Data_DAMIAN_Post-processing_Flavivirus_and_FSME_and_Haemophilus |
| 41 | Data_Luise_Sepi_STKN |
| 42 | Data_Patricia_Sepi_7samples |
| 43 | Data_Soeren_2025_PUBLISHING |
| 44 | Data_Ben_RNAseq_2025 |
| 45 | Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_AYE-WT_Q_S_craA-Tig4_craA-1-Cm200_craA-2-Cm200 |
| 46 | Data_Patricia_Transposon |
| 47 | Data_Patricia_Transposon_2025 |
| 48 | Colocation_Space |
| 49 | Data_Tam_Methylation_2025_empty |
| 50 | 2025-11-03_eVB-Schreiben_12-57.pdf |
| 51 | DEGs_Group1_A1-A3+A8-A10_vs_Group2_B10-B16.png |
| 52 | README.pdf |
| 53 | Data_Hannes_JCM00612 |
| 54 | 167_redundant_DEL |
| 55 | Lehre_Bioinformatik |
| 56 | Data_Ben_Boruta_Analysis |
| 57 | Data_Childrensclinic_16S_2025_DEL |
| 58 | Data_Ben_Mycobacterium_pseudoscrofulaceum |
| 59 | Foong_RNA_mSystems_Huang_Changed.txt |
| 60 | Data_Pietro_Scatturo_and_Charlotte_Uetrecht_16S_2025 |
| 61 | Data_JuliaBerger_RNASeq_SARS-CoV-2 |
| 62 | Data_PaulBongarts_S.epidermidis_HDRNA |
| 63 | Data_Ute |
| 64 | Data_Foong_DNAseq_2025_AYE_Dark_vs_Light_TODO |
| 65 | Data_Foong_RNAseq_2021_ATCC19606_Cm |
| 66 | Data_Tam_Funding |
| 67 | Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_LB-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_vs_Mac-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_on_ATCC19606 |
| 68 | Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_subMIC_exposure_on_ATCC19606 |
| 69 | Data_Tam.txt |
| 70 | Data_Tam_RNAseq_2024_AUM_MHB_Urine_on_ATCC19606 |
| 71 | Data_Tam_Metagenomics_2026 |
| 72 | Data_Michelle |
| 73 | Data_Nicole_16S_2025_Childrensclinic |
| 74 | Data_Sophie_HDV_Sequences |
| 75 | Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_19606deltaIJfluE |
| 76 | README_nf-core |
| 77 | Data_Vero_Kymographs |
| 78 | Access_to_Win10 |
| 79 | Data_Patricia_AMRFinderPlus_2025 |
| 80 | Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_Unknown-adeABadeIJ_adeIJK_CM1_CM2 |
| 81 | Data_Damian |
| 82 | Data_Karoline_16S |
| 83 | Data_JuliaFuchs_RNAseq_2025 |
| 84 | Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_ATCC19606-Y1Y2Y3Y4W1W2W3W4_TODO |
| 85 | Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_Acinetobacter_harbinensis |
| 86 | Data_Benjamin_DNAseq_2026_GE11174 |
| 87 | Data_Susanne_spatialRNA_2022.9.1_backup |
| 88 | Data_Susanne_spatialRNA |
~/DATA_A
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Damian_NEW_CREATED |
| 2 | Data_R_bubbleplots |
| 3 | Data_Ute_TRANSFERED_DEL |
| 4 | Paper_Target_capture_sequencing_MHH_PUBLISHED |
| 5 | Data_Nicole8_Lamprecht_new_PUBLISHED |
| 6 | Data_Samira_RNAseq |
~/DATA_B
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_DAMIAN_endocarditis_encephalitis |
| 2 | Data_Denise_sT_PUBLISHING |
| 3 | Data_Fran2_16S_func |
| 4 | Data_Holger_5179-R1_vs_5179 |
| 5 | Antraege_ |
| 6 | Data_16S_Nicole_210222 |
| 7 | Data_Adam_Influenza_A_virus |
| 8 | Data_Anna_Efaecium_assembly |
| 9 | Data_Bactopia |
| 10 | Data_Ben_RNAseq |
| 11 | Data_Johannes_PIV3 |
| 12 | Data_Luise_Epidome_longitudinal_nose |
| 13 | Data_Manja_Hannes_Probedesign |
| 14 | Data_Marc_AD_PUBLISHING |
| 15 | Data_Marc_RNA-seq_Saureus_Review |
| 16 | Data_Nicole_16S |
| 17 | Data_Nicole_cfDNA_pathogens |
| 18 | Data_Ring_and_CSF_PegivirusC_DAMIAN |
| 19 | Data_Song_Microarray |
| 20 | Data_Susanne_Omnikron |
| 21 | Data_Viro |
| 22 | Doktorarbeit |
| 23 | Poster_Rohde_20230724 |
| 24 | Data_Django |
| 25 | Data_Holger_S.epidermidis_1585_5179_HD05 |
| 26 | Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids_Virus |
| 27 | Data_Holger_MT880870_MT880872_Annotation |
| 28 | Data_Soeren_RNA-seq_2022 |
| 29 | Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids_Merged |
| 30 | Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics |
| 31 | Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids |
| 32 | Data_Susanne_Carotis_MS |
~/DATA_C
(names only; as listed)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2022-10-27_IRI_manuscript_v03_JH.docx |
| 2 | 16304905.fasta |
| 3 | ’16S data manuscript_NF.docx’ |
| 4 | 180820_2_supp_4265595_sw6zjk.docx |
| 5 | 180820_2_supp_4265596_sw6zjk.docx |
| 6 | 1a_vs_3.csv |
| 7 | ‘2.05.01.05-A01 Urlaubsantrag-Shuting-beantragt.pdf’ |
| 8 | 2014SawickaBBA.pdf |
| 9 | 20160509Manuscript_NDM_OXA_mitKomm.doc |
| 10 | 220607_Agenda_monthly_meeting.pdf |
| 11 | ‘20221129 Table mutations.docx’ |
| 12 | 230602_NB501882_0428_AHKG53BGXT.zip |
| 13 | 362383173.rar |
| 14 | 562.9459.1.fa |
| 15 | 562.9459.1_rc.fa |
| 16 | ASA3P.pdf |
| 17 | All_indels_annotated_vHR.xlsx |
| 18 | ‘Amplikon_indeces_Susanne +groups.xlsx’ |
| 19 | Amplikon_indeces_Susanne.xlsx |
| 20 | GAMOLA2 |
| 21 | Data_Susanne_Carotis_spatialRNA_PUBLISHING (dead link) |
| 22 | Data_Paul_Staphylococcus_epidermidis |
| 23 | Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg_PICRUSt |
| 24 | Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg |
| 25 | Data_Nicola_Gagliani |
| 26 | Data_methylome_MMc |
| 27 | Data_Jingang |
| 28 | Data_Indra_RNASeq_GSM2262901 |
| 29 | Data_Holger_VRE |
| 30 | Data_Holger_Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_SNP |
| 31 | Data_Hannes_ChIPSeq |
| 32 | Data_Emilia_MeDIP |
| 33 | Data_ChristophFR_HepE_published |
| 34 | Data_Christopher_MeDIP_MMc_published |
| 35 | Data_Anna_Kieler_Sepi_Staemme |
| 36 | Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_final |
| 37 | Data_Anastasia_RNASeq_PUBLISHING |
| 38 | Aufnahmeantrag_komplett_10_2022.pdf |
| 39 | Astrovirus.pdf |
| 40 | COMMANDS |
| 41 | Bacterial_pipelines.txt |
| 42 | COMPSRA_uke_DEL.jar |
| 43 | ChIPSeq_pipeline_desc.docx |
| 44 | ChIPSeq_pipeline_desc.pdf |
| 45 | Comparative_genomic_analysis_of_eight_novel_haloal.pdf |
| 46 | CvO_Klassenliste_7_3.pdf |
| 47 | ‘Copy of pool_b1_CGATGT_300.xlsx’ |
| 48 | Fran_16S_Exp8-17-21-27.txt |
| 49 | HPI_DRIVE |
| 50 | HEV_aligned.fasta |
| 51 | INTENSO_DIR |
| 52 | HPI_samples_for_NGS_29.09.22.xlsx |
| 53 | Hotmail_to_Gmail |
| 54 | Indra_Thesis_161020.pdf |
| 55 | ‘LT K331A.gbk’ |
| 56 | LOG_p954_stat |
| 57 | LOG |
| 58 | Manuscript_10_02_2021.docx |
| 59 | Metagenomics_Tools_and_Insights.pdf |
| 60 | ‘Miseq Amplikon LAuf April.xlsx’ |
| 61 | NGS.tar.gz |
| 62 | Nachweis_Bakterien_Viren_im_Hochdurchsatz.pdf |
| 63 | Nicole8_Lamprecht_logs |
| 64 | Nanopore.handouts.pdf |
| 65 | ‘Norovirus paper Susanne 191105.docx’ |
| 66 | PhyloRNAalifold.pdf |
| 67 | README_R |
| 68 | README_RNAHiSwitch_DEL |
| 69 | RNA-NGS_Analysis_modul3_NanoStringNorm.zip |
| 70 | RNAConSLOptV1.2.tar.gz |
| 71 | ‘RSV GFP5 including 3`UTR.docx’ |
| 72 | SNPs_on_pangenome.txt |
| 73 | SERVER |
| 74 | R_tutorials-master.zip |
| 75 | Rawdata_Readme.pdf |
| 76 | SUB10826945_record_preview.txt |
| 77 | S_staphylococcus_annotated_diff_expr.xls |
| 78 | Snakefile_list |
| 79 | Source_Classification_Code.rds |
| 80 | Supplementary_Table_S3.xlsx |
| 81 | Untitled.ipynb |
| 82 | UniproUGENE_UserManual.pdf |
| 83 | Untitled1.ipynb |
| 84 | Untitled2.ipynb |
| 85 | Untitled3.ipynb |
| 86 | WAC6h_vs_WAP6h_down.txt |
| 87 | damian_nodbs |
| 88 | WAC6h_vs_WAP6h_up.txt |
| 89 | ‘add. Figures Hamburg_UKE.pptx’ |
| 90 | all_gene_counts_with_annotation.xlsx |
| 91 | app_flask.py |
| 92 | bengal-bay-0.1.json |
| 93 | bengal3_ac3.yml |
| 94 | call_shell_from_Ruby.png |
| 95 | bengal3ac3.yml |
| 96 | empty.fasta |
| 97 | coefficients_csaw_vs_diffreps.xlsx |
| 98 | exchange.txt |
| 99 | exdata-data-NEI_data.zip |
| 100 | genes_wac6_wap6.xls |
| 101 | go1.13.linux-amd64.tar.gz.1 |
| 102 | hev_p2-p5.fa |
| 103 | map_corrected_backup.txt |
| 104 | install_nginx_on_hamm |
| 105 | hg19.rmsk.bed |
| 106 | metadata-9563675-processed-ok.tsv |
| 107 | mkg_sprechstundenflyer_ver1b_dezember_2019.pdf |
| 108 | multiqc_config.yaml |
| 109 | p11326_OMIKRON3398_corsurv.gb |
| 110 | p11326_OMIKRON3398_corsurv.gb_converted.fna |
| 111 | parseGenbank_reformat.py |
| 112 | pangenome-snakemake-master.zip |
| 113 | ‘phylo tree draft.pdf’ |
| 114 | qiime_params.txt |
| 115 | pool_b1_CGATGT_300.zip |
| 116 | qiime_params_backup.txt |
| 117 | qiime_params_s16_s18.txt |
| 118 | snakePipes |
| 119 | results_description.html |
| 120 | rnaalihishapes.tar.gz |
| 121 | rnaseq_length_bias.pdf |
| 122 | 3932-Leber |
| 123 | BioPython |
| 124 | Biopython |
| 125 | DEEP-DV |
| 126 | DOKTORARBEIT |
| 127 | Data_16S_Arck_vaginal_stool |
| 128 | Data_16S_BS052 |
| 129 | Data_16S_Birgit |
| 130 | Data_16S_Christner |
| 131 | Data_16S_Leonie |
| 132 | Data_16S_PatientA-G_CSF |
| 133 | Data_16S_Schaltenberg |
| 134 | Data_16S_benchmark |
| 135 | Data_16S_benchmark2 |
| 136 | Data_16S_gcdh_BKV |
| 137 | Data_Alex1_Amplicon |
| 138 | Data_Alex1_SNP |
| 139 | Data_Analysis_for_Life_Science |
| 140 | Data_Anna13_vanA-Element |
| 141 | Data_Anna14_PACBIO_methylation |
| 142 | Data_Anna_C.acnes2_old_DEL |
| 143 | Data_Anna_MT880872_update |
| 144 | Data_Anna_gap_filling_agrC |
| 145 | Data_Baechlein_Hepacivirus_2018 |
| 146 | Data_Bornavirus |
| 147 | Data_CSF |
| 148 | Data_Christine_cz19-178-rothirsch-bovines-hepacivirus |
| 149 | Data_Daniela_adenovirus_WGS |
| 150 | Data_Emilia_MeDIP_DEL |
| 151 | Data_Francesco2021_16S |
| 152 | Data_Francesco2021_16S_re |
| 153 | Data_Gunnar_MS |
| 154 | Data_Hannes_RNASeq |
| 155 | Data_Holger_Efaecium_variants_PUBLISHED |
| 156 | Data_Holger_VRE_DEL |
| 157 | Data_Icebear_Damian |
| 158 | Data_Indra3_H3K4_p2_DEL |
| 159 | Data_Indra6_RNASeq_ChipSeq_Integration_DEL |
| 160 | Data_Indra_Figures |
| 161 | Data_KatjaGiersch_new_HDV |
| 162 | Data_MHH_Encephalitits_DAMIAN |
| 163 | Data_Manja_RPAChIPSeq_public |
| 164 | Data_Manuel_WGS_Yersinia |
| 165 | Data_Manuel_WGS_Yersinia2_DEL |
| 166 | Data_Manuel_WGS_Yersinia_DEL |
| 167 | Data_Marcus_tracrRNA_structures |
| 168 | Data_Mausmaki_Damian |
| 169 | Data_Nicole1_Tropheryma_whipplei |
| 170 | Data_Nicole5 |
| 171 | Data_Nicole5_77-92 |
| 172 | Data_PaulBecher_Rotavirus |
| 173 | Data_Pietschmann_HCV_Amplicon_bigFile |
| 174 | Data_Piscine_Orthoreovirus_3_in_Brown_Trout |
| 175 | Data_Proteomics |
| 176 | Data_RNABioinformatics |
| 177 | Data_RNAKinetics |
| 178 | Data_R_courses |
| 179 | Data_SARS-CoV-2 |
| 180 | Data_SARS-CoV-2_Genome_Announcement_PUBLISHED |
| 181 | Data_Seite |
| 182 | Data_Song_aggregate_sum |
| 183 | Data_Susanne_Amplicon_RdRp_orf1_2_re |
| 184 | Data_Tabea_RNASeq |
| 185 | Data_Thaiss1_Microarray_new |
| 186 | Data_Tintelnot_16S |
| 187 | Data_Wuenee_Plots |
| 188 | Data_Yang_Poster |
| 189 | Data_jupnote |
| 190 | Data_parainfluenza |
| 191 | Data_snakemake_recipe |
| 192 | Data_temp |
| 193 | Data_viGEN |
| 194 | Genomic_Data_Science |
| 195 | Learn_UGENE |
| 196 | MMcPaper |
| 197 | Manuscript_Epigenetics_Macrophage_Yersinia |
| 198 | Manuscript_RNAHiSwitch |
| 199 | MeDIP_Emilia_copy_DEL |
| 200 | Method_biopython |
| 201 | NGS |
| 202 | Okazaki-Seq_Processing |
| 203 | RNA-NGS_Analysis_modul3_NanoStringNorm |
| 204 | RNAConSLOptV1.2 |
| 205 | RNAHeliCes |
| 206 | RNA_li_HeliCes |
| 207 | RNAliHeliCes |
| 208 | RNAliHeliCes_Relatedshapes_modified |
| 209 | R_refcard |
| 210 | R_DataCamp |
| 211 | R_cats_package |
| 212 | R_tutorials-master |
| 213 | SnakeChunks |
| 214 | align_4l_on_FJ705359 |
| 215 | align_4p_on_FJ705359 |
| 216 | assembly |
| 217 | bacto |
| 218 | bam2fastq_mapping_again |
| 219 | chipster |
| 220 | damian_GUI |
| 221 | enhancer-snakemake-demo |
| 222 | hg19_gene_annotations |
| 223 | interlab_comparison_DEL |
| 224 | my_flask |
| 225 | papers |
| 226 | pangenome-snakemake_zhaoc1 |
| 227 | pyflow-epilogos |
| 228 | raw_data_rnaseq_Indra |
| 229 | test_raw_data_dnaseq |
| 230 | test_raw_data_rnaseq |
| 231 | to_Francesco |
| 232 | ukepipe |
| 233 | ukepipe_nf |
| 234 | var_www_DjangoApp_mysite2_2023-05 |
| 235 | roentgenpass.pdf |
| 236 | salmon_tx2gene_GRCh38.tsv |
| 237 | salmon_tx2gene_chrHsv1.tsv |
| 238 | ‘sample IDs_Lamprecht.xlsx’ |
| 239 | summarySCC_PM25.rds |
| 240 | untitled.py |
| 241 | tutorial-rnaseq.pdf |
| 242 | x.log |
| 243 | webapp.tar.gz |
| 244 | temp |
| 245 | temp2 |
| 246 | Data_Susanne_Amplicon_haplotype_analyses_RdRp_orf1_2_re |
| 247 | Data_Susanne_WGS_unbiased |
~/DATA_D
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Soeren_RNA-seq_2023_PUBLISHING |
| 2 | Data_Ute |
| 3 | Data_Marc_RNA-seq_Sepidermidis |
| 4 | Data_Patricia_Transposon |
| 5 | Books_DA_for_Life |
| 6 | Data_Sven |
| 7 | Datasize_calculation_based_on_coverage.txt |
| 8 | Data_Paul_HD46_1-wt_resequencing |
| 9 | Data_Sanam_DAMIAN |
| 10 | Data_Tam_variant_calling |
| 11 | Data_Samira_Manuscripts |
| 12 | Data_Silvia_VoltRon_Debug |
| 13 | Data_Pietschmann_229ECoronavirus_Mutations_2024 |
| 14 | Data_Pietschmann_229ECoronavirus_Mutations_2025 |
| 15 | Data_Birthe_Svenja_RSV_Probe3_PUBLISHING |
~/DATA_E
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | j_huang_until_201904 |
| 2 | Data_2019_April |
| 3 | Data_2019_May |
| 4 | Data_2019_June |
| 5 | Data_2019_July |
| 6 | Data_2019_August |
| 7 | Data_2019_September |
| 8 | Data_Song_RNASeq_PUBLISHED |
| 9 | Data_Laura_MP_RNASeq |
| 10 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_Swantje2 |
| 11 | Data_Becher_Damian_Picornavirus_BovHepV |
| 12 | bacteria_refseq.zip |
| 13 | bacteria_refseq |
| 14 | Data_Rotavirus |
| 15 | Data_Xiaobo_10x |
| 16 | Data_Becher_Damian_Picornavirus_BovHepV_INCOMPLETE_DEL |
~/DATA_Intenso
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | HOME_FREIBURG_DEL |
| 2 | 150810_M03701_0019_000000000-AFJFK |
| 3 | Data_Thaiss2_Microarray |
| 4 | VirtualBox_VMs_DEL |
| 5 | ‘VirtualBox VMs_DEL’ |
| 6 | ‘VirtualBox VMs2_DEL’ |
| 7 | websites |
| 8 | DATA |
| 9 | Data_Laura |
| 10 | Data_Laura_2 |
| 11 | Data_Laura_3 |
| 12 | galaxy_tools |
| 13 | Downloads2 |
| 14 | Downloads |
| 15 | mom-baby_com_cn |
| 16 | ‘VirtualBox VMs2’ |
| 17 | VirtualBox_VMs |
| 18 | CLC_Data |
| 19 | Work_Dir2 |
| 20 | Work_Dir2_SGE |
| 21 | Data_SPANDx1_Kpneumoniae_vs_Assembly1 |
| 22 | MauveOutput |
| 23 | Fastqs |
| 24 | Data_Anna3_VRE_Ausbruch |
| 25 | Work_Dir_mock_broad_mockinput |
| 26 | Work_Dir_dM_broad_mockinput |
| 27 | Data_Anna8_RNASeq_static_shake_deprecated |
| 28 | PENDRIVE_cont |
| 29 | Work_Dir_WAP_broad_mockinput |
| 30 | Work_Dir_WAC_broad_mockinput |
| 31 | Work_Dir_dP_broad_mockinput |
| 32 | Data_Nicole10_16S_interlab |
| 33 | PAPERS |
| 34 | TB |
| 35 | Data_Anna4_SNP |
| 36 | Data_Carolin1_16S |
| 37 | ChipSeq_Raw_Data3_171009_NB501882_0024_AHNGTYBGX3 |
| 38 | m_aepfelbacher_DEL.zip |
| 39 | Data_Anna7_RNASeq_Cytoscape |
| 40 | Data_Nicole9_Hund_Katze_Mega |
| 41 | Data_Anna2_CO6114 |
| 42 | Data_Nicole3_TH17_orig |
| 43 | Data_Nicole1_Tropheryma_whipplei |
| 44 | results_K27 |
| 45 | ‘VirtualBox VMs’ |
| 46 | Data_Anna6_RNASeq |
| 47 | Data_Anna1_1585_RNAseq |
| 48 | Data_Thaiss1_Microarray |
| 49 | Data_Nicole7_Anelloviruses_Polyomavirus |
| 50 | Data_Nina1_Nicole5_1-76 |
| 51 | Data_Nina1_merged |
| 52 | Data_Nicole8_Lamprecht |
| 53 | Data_Anna5_SNP |
| 54 | chipseq |
| 55 | Downloads_DEL |
| 56 | Data_Gagliani2_enriched_16S |
| 57 | Data_Gagliani1_18S_16S |
| 58 | m_aepfelbacher |
| 59 | Data_Susanne_WGS_3amplicons |
/media/jhuang/Titisee
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Anna4_SNP |
| 2 | Data_Anna5_SNP_rsync_error |
| 3 | TRASH |
| 4 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_4_SNP_calling_PE_DEL |
| 5 | Data_Nina1_Nicole7 |
| 6 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_4_SNP_calling_SE_DEL |
| 7 | 180119_M03701_0115_000000000-BFG46.zip |
| 8 | Data_Nicole10_16S_interlab_PUBLISHED |
| 9 | Anna11_assemblies |
| 10 | Anna11_trees |
| 11 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_new_orig_fastqs |
| 12 | Data_Anna9_OXA-48_or_OXA-181 |
| 13 | bengal_results_v1_2018 |
| 14 | DO.pdf |
| 15 | damian_DEL |
| 16 | MAGpy_db |
| 17 | UGENE_v1_32_data_cistrome |
| 18 | UGENE_v1_32_data_ngs_classification |
| 19 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_Swantje |
| 20 | Data_Nico_Gagliani |
| 21 | GAMOLA2_prototyp |
| 22 | Thomas_methylation_EPIC_DO |
| 23 | Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg |
| 24 | Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg_PICRUSt |
| 25 | HOME_FREIBURG |
| 26 | Data_Francesco_16S |
| 27 | 3rd_party |
| 28 | ConsPred_prokaryotic_genome_annotation |
| 29 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 30 | damian_v201016 |
| 31 | Data_Holger_VRE |
| 32 | Data_Holger_Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_SNP |
| 33 | Eigene_Ordner_HR |
| 34 | GAMOLA2 |
| 35 | Data_Anastasia_RNASeq |
| 36 | Data_Amir_PUBLISHED |
| 37 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
| 38 | Data_Xiaobo_10x_3 |
| 39 | Data_Tam_DNAseq_2023_Comparative_ATCC19606_AYE_ATCC17978 |
| 40 | Data_Holger_S.epidermidis_short |
| 41 | TEMP |
| 42 | Data_Holger_S.epidermidis_long |
/media/jhuang/Elements(Denise_ChIPseq)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Denise_LTtrunc_H3K27me3_2_results_DEL |
| 2 | Data_Denise_LTtrunc_H3K4me3_2_results_DEL |
| 3 | Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_final_not_finished_DEL |
| 4 | m_aepfelbacher_DEL |
| 5 | Data_Damian |
| 6 | ST772_DEL |
| 7 | ALL_trimmed_part_DEL |
| 8 | Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol1 |
| 9 | Data_Pietschmann_HCV_Amplicon |
| 10 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_ownMethod_new |
| 11 | HD04-1.fasta |
| 12 | RNAHiSwitch_ |
| 13 | RNAHiSwitch__ |
| 14 | RNAHiSwitch___ |
| 15 | RNAHiSwitchpaper |
| 16 | RNAHiSwitch_milestone1_DELETED |
| 17 | RNAHiSwitch_paper.tar.gz |
| 18 | RNAHiSwitch_paper_DELETED |
| 19 | RNAHiSwitch_milestone1 |
| 20 | RNAHiSwitch_paper |
| 21 | Ute_RNASeq_results |
| 22 | Ute_miRNA_results_38 |
| 23 | RNAHiSwitch |
| 24 | Data_HepE_Freiburg_PUBLISHED |
| 25 | Data_INTENSO_2022-06 |
| 26 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
| 27 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 28 | Data_Anna_Mixta_hanseatica_PUBLISHED |
| 29 | coi_disclosure.docx |
| 30 | Data_Jingang |
| 31 | **Data_Susanne_16S_re_UNPUBLISHED *** |
| 32 | Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol2 |
| 33 | Data_Caroline_RNAseq_wt_timecourse |
| 34 | Data_Caroline_RNAseq_brain_organoids |
| 35 | Data_Amir_PUBLISHED_DEL |
| 36 | Data_download_virus_fam |
| 37 | Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics_COPYFAILED_DEL |
| 38 | Data_Paul_and_Marc_Epidome_batch3 |
| 39 | ifconfig_hamm.txt |
| 40 | Data_Soeren_2023_PUBLISHING |
| 41 | Data_Birthe_Svenja_RSV_Probe3_PUBLISHING |
| 42 | Data_Ute |
| 43 | **Data_Susanne_16S_UNPUBLISHED *** |
/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(HOffice)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | SeagateExpansion.ico |
| 2 | Autorun.inf |
| 3 | Start_Here_Win.exe |
| 4 | Warranty.pdf |
| 5 | Start_Here_Mac.app |
| 6 | Seagate |
| 7 | HomeOffice_DIR (Data_Anna_HAPDICS_RNASeq, From_Samsung_T5) |
| 8 | DATA_COPY_FROM_178528 (copy_and_clean.sh, logfile_jhuang.log, jhuang) |
| 9 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 10 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
/media/jhuang/Elements(Anna_C.arnes)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Swantje_HEV_using_viral-ngs |
| 2 | VIPER_static_DEL |
| 3 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_Swantje1_blood |
| 4 | Data_Nicole6_HEV_benchmark |
| 5 | Data_Denise_RNASeq_GSE79958 |
| 6 | Data_16S_Leonie_from_Nico_Gaglianis |
| 7 | Fastqs_19-21 |
| 8 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 9 | Data_Luise_Epidome_test |
| 10 | Data_Anna_C.acnes_PUBLISHED |
| 11 | Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung |
| 12 | Data_Denise_LT_K331A_RNASeq |
| 13 | Data_Luise_Epidome_batch1 |
| 14 | Data_Luise_Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_PUBLISHED |
| 15 | Data_Luise_Epidome_batch2 |
| 16 | picrust2_out_2024_2 |
| 17 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(DATA_COPY_FROM_hamburg)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Autorun.inf |
| 2 | Start_Here_Win.exe |
| 3 | Warranty.pdf |
| 4 | Start_Here_Mac.app |
| 5 | Seagate |
| 6 | DATA_COPY_TRANSFER_INCOMPLETE_DEL |
| 7 | DATA_COPY_FROM_hamburg |
/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(Seagate_1)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | RNA_seq_analysis_tools_2013 |
| 2 | Data_Laura0 |
| 3 | Data_Petra_Arck |
| 4 | Data_Martin_mycoplasma |
| 5 | chromhmm-enhancers |
| 6 | ChromHMM_Dir |
| 7 | Data_Denise_sT_H3K4me3 |
| 8 | Data_Denise_sT_H3K27me3 |
| 9 | Start_Here_Mac.app |
| 10 | Seagate |
| 11 | Data_Nicole16_parapoxvirus |
| 12 | Project_h_rohde_Susanne_WGS_unbiased_DEL.zip |
| 13 | Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol1 |
| 14 | Data_ENNGS_pathogen_detection_pipeline_comparison |
| 15 | j_huang_201904_202002 |
| 16 | Data_Laura_ChIPseq_GSE120945 |
| 17 | batch_200314_incomplete |
| 18 | m_aepfelbacher.zip |
| 19 | m_error_DEL |
| 20 | batch_200325 |
| 21 | batch_200319 |
| 22 | GAMOLA2_prototyp |
| 23 | Data_Nicola_Gagliani |
| 24 | 2017-18_raw_data |
| 25 | Data_Arck_MeDIP |
| 26 | trimmed |
| 27 | Data_Nicole_16S_Christmas_2020_2 |
| 28 | j_huang_202007_202012 |
| 29 | Data_Nicole_16S_Christmas_2020 |
| 30 | Downloads_2021-01-18_DEL |
| 31 | Data_Laura_plasmid |
| 32 | Data_Laura_16S_2_re |
| 33 | Data_Laura_16S_2 |
| 34 | Data_Laura_16S_2re |
| 35 | Data_Laura_16S_merged |
| 36 | Downloads_DEL |
| 37 | Data_Laura_16S |
| 38 | Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_final |
| 39 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
| 40 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(Seagate_2)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Nicole4_TH17 |
| 2 | Start_Here_Win.exe |
| 3 | Autorun.inf |
| 4 | Warranty.pdf |
| 5 | Start_Here_Mac.app |
| 6 | Seagate |
| 7 | Data_Denise_RNASeq_trimmed_DEL |
| 8 | HD12 |
| 9 | Qi_panGenome |
| 10 | ALL |
| 11 | fastq_HPI_bw_2019_08_and_2020_02 |
| 12 | f1_R1_link.sh |
| 13 | f1_R2_link.sh |
| 14 | rtpd_files |
| 15 | m_aepfelbacher.zip |
| 16 | Data_Nicole_16S_Hamburg_Odense_Cornell_Muenster |
| 17 | HyAsP_incomplete_genomes |
| 18 | HyAsP_normal_sampled_input |
| 19 | HyAsP_complete_genomes |
| 20 | video.zip |
| 21 | sam2bedgff.pl |
| 22 | HD04.infection.hS_vs_HD04.nose.hS_annotated_degenes.xls |
| 23 | ALL83 |
| 24 | Data_Pietschmann_RSV_Probe_PUBLISHED |
| 25 | HyAsP_normal |
| 26 | Data_Manthey_16S |
| 27 | rtpd_files_DEL |
| 28 | HyAsP_bold |
| 29 | Data_HEV |
| 30 | Seq_VRE_hybridassembly |
| 31 | Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_raw_data_shovill_prokka |
| 32 | Data_Anna_HAPDICS_WGS_ALL |
| 33 | Data_HEV_Freiburg_2020 |
| 34 | Data_Nicole_HDV_Recombination_PUBLISHED |
| 35 | s_hero2x |
| 36 | 201030_M03701_0207_000000000-J57B4.zip |
| 37 | README |
| 38 | ‘README(1)’ |
| 39 | dna2.fasta.fai |
| 40 | 91.pep |
| 41 | 91.orf |
| 42 | 91.orf.fai |
| 43 | dgaston-dec-06-2012-121211124858-phpapp01.pdf |
| 44 | tileshop.fcgi |
| 45 | ppat.1009304.s016.tif |
| 46 | sequence.txt |
| 47 | ‘sequence(1).txt’ |
| 48 | GSE128169_series_matrix.txt.gz |
| 49 | GSE128169_family.soft.gz |
| 50 | Data_Anna_HAPDICS_RNASeq |
| 51 | Data_Christopher_MeDIP_MMc_PUBLISHED |
| 52 | Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics_IMCOMPLETE_DEL |
| 53 | Data_Denise_RNASeq |
| 54 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 55 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
/media/jhuang/Elements(An14_RNAs)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Anna10_RP62A |
| 2 | Data_Nicole12_16S_Kluwe_Bunders |
| 3 | chromhmm-enhancers |
| 4 | Data_Denise_sT_Methylation |
| 5 | Data_Denise_LTtrunc_Methylation |
| 6 | Data_16S_arckNov |
| 7 | Data_Tabea_RNASeq |
| 8 | nr_gz_README |
| 9 | j_huang_raw_fq |
| 10 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 11 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
| 12 | host_refs |
| 13 | Vraw |
| 14 | **Data_Susanne_Amplicon_RdRp_orf1_2 *** |
| 15 | tmp |
| 16 | Data_RNA188_Paul_Becher |
| 17 | Data_ChIPSeq_Laura |
| 18 | Data_16S_arckNov_review_PUBLISHED |
| 19 | Data_16S_arckNov_re |
| 20 | Fastqs |
| 21 | Data_Tabea_RNASeq_submission |
| 22 | Data_Anna_Cutibacterium_acnes_DEL |
| 23 | Data_Silvia_RNASeq_SUBMISSION |
| 24 | Data_Hannes_ChIPSeq |
| 25 | Data_Anna14_RNASeq_to_be_DEL |
| 26 | Data_Pietschmann_RSV_Probe2_PUBLISHED |
| 27 | Data_Holger_Klebsiella_pneumoniae_SNP_PUBLISHING |
| 28 | Data_Anna14_RNASeq_plus_public |
/media/jhuang/Elements(Indra_HAPDICS)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Data_Anna11_Sepdermidis_DEL |
| 2 | HD15_without_10 |
| 3 | HD31 |
| 4 | HD33 |
| 5 | HD39 |
| 6 | HD43 |
| 7 | HD46 |
| 8 | HD15_with_10 |
| 9 | HD26 |
| 10 | HD59 |
| 11 | HD25 |
| 12 | HD21 |
| 13 | HD17 |
| 14 | HD04 |
| 15 | Data_Anna11_Pair1-6_P6 |
| 16 | Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_HyAsP |
| 17 | HAPDICS_hyasp_plasmids |
| 18 | Data_Anna_HAPDICS_review |
| 19 | data_overview.txt |
| 20 | align_assem_res_DEL |
| 21 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 22 | EXCHANGE_DEL |
| 23 | Data_Indra_H3K4me3_public |
| 24 | Data_Gunnar_MS |
| 25 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
| 26 | UKE_DELLWorkstation_C_Users_indbe_Desktop |
| 27 | Linux_DELLWorkstation_C_Users_indbe_VirtualBoxVMs |
| 28 | Data_Anna_HAPDICS_RNASeq_rawdata |
| 29 | Data_Indra_H3K27ac_public |
| 30 | Data_Holger_Klebsiella_pneumoniae_SNP_PUBLISHING |
| 31 | DATA_INDRA_RNASEQ |
| 32 | DATA_INDRA_CHIPSEQ |
/media/jhuang/Elements(jhuang_*)
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | ‘Install Western Digital Software for Windows.exe’ |
| 2 | ‘Install Western Digital Software for Mac.dmg’ |
| 3 | ‘System Volume Information’ |
| 4 | ‘$RECYCLE.BIN’ |
| 5 | 20250203_FS10003086_95_BTR67811-0621 |
/media/jhuang/Smarty
| # | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | lost+found |
| 2 | Blast_db |
| 3 | temporary_files_DEL |
| 4 | ALIGN_ASSEM |
| 5 | Data_Paul_Staphylococcus_epidermidis |
| 6 | Data_16S_Degenhardt_Marius_DEL |
| 7 | Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics_DEL |
| 8 | Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids_Virus |
| 9 | Data_Emilia_MeDIP |
| 10 | DjangoApp_Backup_2023-10-30 |
| 11 | ref |
| 12 | Data_Michelle_RNAseq_2025_raw_data_DEL_AFTER_UPLOAD_GEO |
Original input (as one point)
/media/jhuang/INTENSO is empty --> Now the data are on ~/DATA_Intenso
/dev/sdg1 3,7T 512K 3,7T 1% /media/jhuang/INTENSO
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA$ ls -tlrh
total 1,6M
drwxrwxrwx 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 26 2022 Data_Ute_MKL1
drwxrwxrwx 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 13 2023 Data_Ute_RNA_4_2022-11_test
drwxrwxr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 8 2023 Data_Ute_RNA_3
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 19 2023 Data_Susanne_Carotis_RNASeq_PUBLISHING
drwxr-xr-x 21 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Jiline_Yersinia_SNP
drwxrwxr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 22 2024 Data_Tam_ABAYE_RS05070_on_A_calcoaceticus_baumannii_complex_DUPLICATED_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 23 2024 Data_Nicole_CRC1648
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 6 2024 Mouse_HS3ST1_12373_out
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 6 2024 Mouse_HS3ST1_12175_out
drwxrwxr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 12 2024 Data_Biobakery
drwxrwxr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 23 2024 Data_Xiaobo_10x_2
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 23 2024 Data_Xiaobo_10x_3
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 26 2024 Talk_Nicole_CRC1648
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 26 2024 Talks_Bioinformatics_Meeting
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 12K Sep 26 2024 Talks_resources
drwxrwxr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 12K Okt 10 2024 Data_Susanne_MPox_DAMIAN
drwxrwxr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 14 2024 Data_host_transcriptional_response
drwxr-xr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 23 2024 Talks_including_DEEP-DV
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 24 2024 DOKTORARBEIT
drwxrwxr-x 18 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 11 2024 Data_Susanne_MPox
drwxrwxr-x 25 jhuang jhuang 12K Nov 11 2024 Data_Jiline_Transposon
drwxrwxr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 20K Nov 25 2024 Data_Jiline_Transposon2
drwxrwxr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 13 2024 Data_Matlab
drwxrwxr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 28 2025 deepseek-ai
drwx------ 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 5 2025 Stick_Mi_DEL
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 1,1K Feb 18 2025 TODO_shares
drwxrwxrwx 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 3 2025 Data_Ute_RNA_4
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 31 2025 Data_Liu_PCA_plot
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 43K Apr 3 2025 README_run_viral-ngs_inside_Docker
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 8,7K Apr 9 2025 README_compare_genomes
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Apr 11 2025 mapped.bam
drwxrwxr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 24 2025 Data_Serpapi
drwxrwxrwx 22 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 30 2025 Data_Ute_RNA_1_2
drwxrwxr-x 15 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 30 2025 Data_Marc_RNAseq_2024
drwxrwxr-x 45 jhuang jhuang 12K Mai 15 2025 Data_Nicole_CaptureProbeSequencing
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 657 Mai 23 2025 LOG_mapping
drwxrwxr-x 46 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 26 2025 Data_Huang_Human_herpesvirus_3
drwxrwxr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 13 2025 Data_Nicole_DAMIAN_Post-processing_Pathoprobe_FluB_Links
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 37 Jun 16 2025 Access_to_Win7 -> ./Data_Marius_16S/picrust2_out_2024_2
drwxrwxr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2025 Data_DAMIAN_Post-processing_Flavivirus_and_FSME_and_Haemophilus
drwxr-xr-x 42 jhuang jhuang 36K Jun 23 2025 Data_Luise_Sepi_STKN
drwxrwxr-x 29 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 22 2025 Data_Patricia_Sepi_7samples
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 8 2025 Data_Soeren_2025_PUBLISHING
drwxrwxr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 13 2025 Data_Ben_RNAseq_2025
drwxrwxr-x 34 jhuang jhuang 12K Sep 3 12:18 Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_AYE-WT_Q_S_craA-Tig4_craA-1-Cm200_craA-2-Cm200
drwxrwxr-x 50 jhuang jhuang 16K Okt 6 17:59 Data_Patricia_Transposon
drwxrwxr-x 23 jhuang jhuang 12K Okt 20 13:27 Data_Patricia_Transposon_2025
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 23 12:21 Colocation_Space
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 27 12:56 Data_Tam_Methylation_2025_empty
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 151K Nov 3 13:01 2025-11-03_eVB-Schreiben_12-57.pdf
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 67K Nov 5 16:59 DEGs_Group1_A1-A3+A8-A10_vs_Group2_B10-B16.png
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 687K Nov 14 09:55 README.pdf
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 24 15:43 Data_Hannes_JCM00612
drwxrwxr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 4 17:03 167_redundant_DEL
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 8 10:33 Lehre_Bioinformatik
drwxrwxr-x 27 jhuang jhuang 12K Dez 8 11:29 Data_Ben_Boruta_Analysis
drwxrwxr-x 18 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 8 17:39 Data_Childrensclinic_16S_2025_DEL
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 10 10:05 Data_Ben_Mycobacterium_pseudoscrofulaceum
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 8,9K Dez 15 12:42 Foong_RNA_mSystems_Huang_Changed.txt
drwxrwxr-x 22 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 17 13:07 Data_Pietro_Scatturo_and_Charlotte_Uetrecht_16S_2025
drwxrwxr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 18 10:45 Data_JuliaBerger_RNASeq_SARS-CoV-2
drwxrwxr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 3 17:42 Data_PaulBongarts_S.epidermidis_HDRNA
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 31 Jan 12 14:30 Data_Ute -> /media/jhuang/Elements/Data_Ute
drwxrwxr-x 12 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 12:44 Data_Foong_DNAseq_2025_AYE_Dark_vs_Light_TODO
drwxrwxrwx 22 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 12:48 Data_Foong_RNAseq_2021_ATCC19606_Cm
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 13:02 Data_Tam_Funding
drwxrwxr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 13:32 Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_LB-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_vs_Mac-AB_IJ_W1_Y1_WT_on_ATCC19606
drwxrwxr-x 12 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 13:32 Data_Tam_RNAseq_2025_subMIC_exposure_on_ATCC19606
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 1,2K Jan 16 13:34 Data_Tam.txt
drwxrwxr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 13:37 Data_Tam_RNAseq_2024_AUM_MHB_Urine_on_ATCC19606
drwxrwxr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 18:22 Data_Tam_Metagenomics_2026
drwxrwxr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 16K Jan 23 16:35 Data_Michelle
drwxrwxr-x 38 jhuang jhuang 12K Jan 28 15:20 Data_Nicole_16S_2025_Childrensclinic
drwxr-xr-x 145 jhuang jhuang 36K Jan 29 10:49 Data_Sophie_HDV_Sequences
drwxrwxr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 30 11:44 Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_19606deltaIJfluE
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 63K Jan 30 17:53 README_nf-core
drwxrwxr-x 22 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 4 10:43 Data_Vero_Kymographs
drwxrwxr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 4 14:06 Access_to_Win10
drwxrwxr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 5 11:59 Data_Patricia_AMRFinderPlus_2025
drwxrwxr-x 45 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 6 11:54 Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_Unknown-adeABadeIJ_adeIJK_CM1_CM2
drwxrwxr-x 41 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 9 15:11 Data_Damian
drwxrwxr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 13 12:48 Data_Karoline_16S
drwxrwxr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 13 18:09 Data_JuliaFuchs_RNAseq_2025
drwxrwxr-x 18 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 16 11:19 Data_Tam_DNAseq_2025_ATCC19606-Y1Y2Y3Y4W1W2W3W4_TODO
drwxrwxr-x 34 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 16 15:54 Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_Acinetobacter_harbinensis
drwxrwxr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 16 17:13 Data_Benjamin_DNAseq_2026_GE11174
drwxrwxrwx 36 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 17 15:02 Data_Susanne_spatialRNA_2022.9.1_backup
drwxrwxr-x 39 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 17 15:12 Data_Susanne_spatialRNA
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA_A$ ls -ltrh
total 24K
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Damian_NEW_CREATED
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_R_bubbleplots
drwxr-xr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Ute_TRANSFERED_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 7 2024 Paper_Target_capture_sequencing_MHH_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 20 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 8 2024 Data_Nicole8_Lamprecht_new_PUBLISHED
drwxrwxrwx 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 21 2025 Data_Samira_RNAseq
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA_B$ ls -tlrh
total 136K
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_DAMIAN_endocarditis_encephalitis
drwxr-xr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Denise_sT_PUBLISHING
drwxr-xr-x 12 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Fran2_16S_func
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Holger_5179-R1_vs_5179
drwxr-xr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Antraege_
drwxr-xr-x 18 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_Nicole_210222
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Adam_Influenza_A_virus
drwxr-xr-x 14 jhuang jhuang 12K Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna_Efaecium_assembly
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Bactopia
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Ben_RNAseq
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Johannes_PIV3
drwxr-xr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Luise_Epidome_longitudinal_nose
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Manja_Hannes_Probedesign
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Marc_AD_PUBLISHING
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Marc_RNA-seq_Saureus_Review
drwxr-xr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicole_16S
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicole_cfDNA_pathogens
drwxr-xr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Ring_and_CSF_PegivirusC_DAMIAN
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Song_Microarray
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Susanne_Omnikron
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Viro
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Doktorarbeit
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Poster_Rohde_20230724
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 12 2024 Data_Django
drwxr-xr-x 35 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 21 2024 Data_Holger_S.epidermidis_1585_5179_HD05
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 18 2024 Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids_Virus
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 21 2025 Data_Holger_MT880870_MT880872_Annotation
drwxr-xr-x 12 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 8 2025 Data_Soeren_RNA-seq_2022
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 11 2025 Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids_Merged
drwxr-xr-x 24 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 25 2025 Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 17:14 Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 17 12:11 Data_Susanne_Carotis_MS
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA_C$ ls -tlrh
total 13G
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,7M Jun 18 2024 2022-10-27_IRI_manuscript_v03_JH.docx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 7,1K Jun 18 2024 16304905.fasta
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 55K Jun 18 2024 '16S data manuscript_NF.docx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 792K Jun 18 2024 180820_2_supp_4265595_sw6zjk.docx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 17K Jun 18 2024 180820_2_supp_4265596_sw6zjk.docx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jun 18 2024 1a_vs_3.csv
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 90K Jun 18 2024 '2.05.01.05-A01 Urlaubsantrag-Shuting-beantragt.pdf'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 708K Jun 18 2024 2014SawickaBBA.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 61K Jun 18 2024 20160509Manuscript_NDM_OXA_mitKomm.doc
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 289K Jun 18 2024 220607_Agenda_monthly_meeting.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 14K Jun 18 2024 '20221129 Table mutations.docx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12G Jun 18 2024 230602_NB501882_0428_AHKG53BGXT.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 107K Jun 18 2024 362383173.rar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 128K Jun 18 2024 562.9459.1.fa
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 126K Jun 18 2024 562.9459.1_rc.fa
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,6M Jun 18 2024 ASA3P.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 21K Jun 18 2024 All_indels_annotated_vHR.xlsx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 11K Jun 18 2024 'Amplikon_indeces_Susanne +groups.xlsx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 9,6K Jun 18 2024 Amplikon_indeces_Susanne.xlsx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 68 Jun 18 2024 GAMOLA2
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 88 Jun 18 2024 Data_Susanne_Carotis_spatialRNA_PUBLISHING
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 112 Jun 18 2024 Data_Paul_Staphylococcus_epidermidis
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 118 Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg_PICRUSt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 100 Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 94 Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicola_Gagliani
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 96 Jun 18 2024 Data_methylome_MMc
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 78 Jun 18 2024 Data_Jingang
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 112 Jun 18 2024 Data_Indra_RNASeq_GSM2262901
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 84 Jun 18 2024 Data_Holger_VRE
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 128 Jun 18 2024 Data_Holger_Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_SNP
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 92 Jun 18 2024 Data_Hannes_ChIPSeq
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 76 Jun 18 2024 Data_Emilia_MeDIP
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 88 Jun 18 2024 Data_ChristophFR_HepE_published
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 158 Jun 18 2024 Data_Christopher_MeDIP_MMc_published
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 104 Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna_Kieler_Sepi_Staemme
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 136 Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_final
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 96 Jun 18 2024 Data_Anastasia_RNASeq_PUBLISHING
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 169K Jun 18 2024 Aufnahmeantrag_komplett_10_2022.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,2M Jun 18 2024 Astrovirus.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 732 Jun 18 2024 COMMANDS
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 690 Jun 18 2024 Bacterial_pipelines.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 16M Jun 18 2024 COMPSRA_uke_DEL.jar
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 239K Jun 18 2024 ChIPSeq_pipeline_desc.docx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 385K Jun 18 2024 ChIPSeq_pipeline_desc.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 2,1M Jun 18 2024 Comparative_genomic_analysis_of_eight_novel_haloal.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 64K Jun 18 2024 CvO_Klassenliste_7_3.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 649K Jun 18 2024 'Copy of pool_b1_CGATGT_300.xlsx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,9K Jun 18 2024 Fran_16S_Exp8-17-21-27.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 463 Jun 18 2024 HPI_DRIVE
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 179K Jun 18 2024 HEV_aligned.fasta
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,1K Jun 18 2024 INTENSO_DIR
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 14K Jun 18 2024 HPI_samples_for_NGS_29.09.22.xlsx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,3K Jun 18 2024 Hotmail_to_Gmail
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 13M Jun 18 2024 Indra_Thesis_161020.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 5,2K Jun 18 2024 'LT K331A.gbk'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 18 2024 LOG_p954_stat
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 684K Jun 18 2024 LOG
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 197K Jun 18 2024 Manuscript_10_02_2021.docx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 595K Jun 18 2024 Metagenomics_Tools_and_Insights.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 14K Jun 18 2024 'Miseq Amplikon LAuf April.xlsx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 2,2M Jun 18 2024 NGS.tar.gz
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 586K Jun 18 2024 Nachweis_Bakterien_Viren_im_Hochdurchsatz.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,2K Jun 18 2024 Nicole8_Lamprecht_logs
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 24M Jun 18 2024 Nanopore.handouts.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 113K Jun 18 2024 'Norovirus paper Susanne 191105.docx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 503K Jun 18 2024 PhyloRNAalifold.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 19K Jun 18 2024 README_R
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 137K Jun 18 2024 README_RNAHiSwitch_DEL
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,3M Jun 18 2024 RNA-NGS_Analysis_modul3_NanoStringNorm.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 57K Jun 18 2024 RNAConSLOptV1.2.tar.gz
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 17K Jun 18 2024 'RSV GFP5 including 3`UTR.docx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 238 Jun 18 2024 SNPs_on_pangenome.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 55 Jun 18 2024 SERVER
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 26M Jun 18 2024 R_tutorials-master.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 182K Jun 18 2024 Rawdata_Readme.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 40K Jun 18 2024 SUB10826945_record_preview.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 283K Jun 18 2024 S_staphylococcus_annotated_diff_expr.xls
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 2,0K Jun 18 2024 Snakefile_list
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 160K Jun 18 2024 Source_Classification_Code.rds
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 61K Jun 18 2024 Supplementary_Table_S3.xlsx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 617 Jun 18 2024 Untitled.ipynb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 127M Jun 18 2024 UniproUGENE_UserManual.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 14M Jun 18 2024 Untitled1.ipynb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 110K Jun 18 2024 Untitled2.ipynb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 2,9K Jun 18 2024 Untitled3.ipynb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 18K Jun 18 2024 WAC6h_vs_WAP6h_down.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 100 Jun 18 2024 damian_nodbs
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 45K Jun 18 2024 WAC6h_vs_WAP6h_up.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 635K Jun 18 2024 'add. Figures Hamburg_UKE.pptx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,7M Jun 18 2024 all_gene_counts_with_annotation.xlsx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 22K Jun 18 2024 app_flask.py
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,8K Jun 18 2024 bengal-bay-0.1.json
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 16K Jun 18 2024 bengal3_ac3.yml
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 246K Jun 18 2024 call_shell_from_Ruby.png
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,1K Jun 18 2024 bengal3_ac3_.yml
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12 Jun 18 2024 empty.fasta
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 32K Jun 18 2024 coefficients_csaw_vs_diffreps.xlsx
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,3K Jun 18 2024 exchange.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 30M Jun 18 2024 exdata-data-NEI_data.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 6,6K Jun 18 2024 genes_wac6_wap6.xls
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 115M Jun 18 2024 go1.13.linux-amd64.tar.gz.1
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 29K Jun 18 2024 hev_p2-p5.fa
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,8K Jun 18 2024 map_corrected_backup.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 325 Jun 18 2024 install_nginx_on_hamm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20M Jun 18 2024 hg19.rmsk.bed
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 107K Jun 18 2024 metadata-9563675-processed-ok.tsv
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 288K Jun 18 2024 mkg_sprechstundenflyer_ver1b_dezember_2019.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 588 Jun 18 2024 multiqc_config.yaml
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 38K Jun 18 2024 p11326_OMIKRON3398_corsurv.gb
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 30K Jun 18 2024 p11326_OMIKRON3398_corsurv.gb_converted.fna
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,9K Jun 18 2024 parseGenbank_reformat.py
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 222K Jun 18 2024 pangenome-snakemake-master.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 283K Jun 18 2024 'phylo tree draft.pdf'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 125 Jun 18 2024 qiime_params.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 2,3M Jun 18 2024 pool_b1_CGATGT_300.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 5,5K Jun 18 2024 qiime_params_backup.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,5K Jun 18 2024 qiime_params_s16_s18.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 68 Jun 18 2024 snakePipes
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 25K Jun 18 2024 results_description.html
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 139M Jun 18 2024 rnaalihishapes.tar.gz
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,4M Jun 18 2024 rnaseq_length_bias.pdf
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 3932-Leber
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 BioPython
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Biopython
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 DEEP-DV
drwxr-xr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 DOKTORARBEIT
drwxr-xr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_Arck_vaginal_stool
drwxr-xr-x 22 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_BS052
drwxr-xr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_Birgit
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_Christner
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_Leonie
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_PatientA-G_CSF
drwxr-xr-x 14 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_Schaltenberg
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_benchmark
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_benchmark2
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_16S_gcdh_BKV
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Alex1_Amplicon
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Alex1_SNP
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Analysis_for_Life_Science
drwxr-xr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna13_vanA-Element
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna14_PACBIO_methylation
drwxr-xr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna_C.acnes2_old_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna_MT880872_update
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Anna_gap_filling_agrC
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Baechlein_Hepacivirus_2018
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Bornavirus
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_CSF
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Christine_cz19-178-rothirsch-bovines-hepacivirus
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Daniela_adenovirus_WGS
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Emilia_MeDIP_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 14 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Francesco2021_16S
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Francesco2021_16S_re
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Gunnar_MS
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Hannes_RNASeq
drwxr-xr-x 29 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Holger_Efaecium_variants_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Holger_VRE_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Icebear_Damian
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Indra3_H3K4_p2_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Indra6_RNASeq_ChipSeq_Integration_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Indra_Figures
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_KatjaGiersch_new_HDV
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_MHH_Encephalitits_DAMIAN
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Manja_RPAChIPSeq_public
drwxr-xr-x 72 jhuang jhuang 12K Jun 18 2024 Data_Manuel_WGS_Yersinia
drwxr-xr-x 32 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Manuel_WGS_Yersinia2_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Manuel_WGS_Yersinia_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Marcus_tracrRNA_structures
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Mausmaki_Damian
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicole1_Tropheryma_whipplei
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicole5
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Nicole5_77-92
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_PaulBecher_Rotavirus
drwxr-xr-x 21 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Pietschmann_HCV_Amplicon_bigFile
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Piscine_Orthoreovirus_3_in_Brown_Trout
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Proteomics
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_RNABioinformatics
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_RNAKinetics
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_R_courses
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_SARS-CoV-2
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_SARS-CoV-2_Genome_Announcement_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Seite
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Song_aggregate_sum
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Susanne_Amplicon_RdRp_orf1_2_re
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Tabea_RNASeq
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Thaiss1_Microarray_new
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Tintelnot_16S
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Wuenee_Plots
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Yang_Poster
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_jupnote
drwxr-xr-x 21 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_parainfluenza
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_snakemake_recipe
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_temp
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_viGEN
drwxr-xr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Genomic_Data_Science
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Learn_UGENE
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 MMcPaper
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Manuscript_Epigenetics_Macrophage_Yersinia
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Manuscript_RNAHiSwitch
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 MeDIP_Emilia_copy_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Method_biopython
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 NGS
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Okazaki-Seq_Processing
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 RNA-NGS_Analysis_modul3_NanoStringNorm
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 RNAConSLOptV1.2
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 RNAHeliCes
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 RNA_li_HeliCes
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 RNAliHeliCes
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 RNAliHeliCes_Relatedshapes_modified
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 R_refcard
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 R_DataCamp
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 R_cats_package
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 R_tutorials-master
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 SnakeChunks
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 align_4l_on_FJ705359
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 align_4p_on_FJ705359
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 assembly
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 bacto
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 bam2fastq_mapping_again
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 chipster
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 damian_GUI
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 enhancer-snakemake-demo
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 hg19_gene_annotations
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 interlab_comparison_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 my_flask
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 papers
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 pangenome-snakemake_zhaoc1
drwxr-xr-x 14 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 pyflow-epilogos
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 raw_data_rnaseq_Indra
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 test_raw_data_dnaseq
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 test_raw_data_rnaseq
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 to_Francesco
drwxr-xr-x 36 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 ukepipe
drwxr-xr-x 15 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 ukepipe_nf
drwxr-xr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 var_www_DjangoApp_mysite2_2023-05
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 59K Jun 18 2024 roentgenpass.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 9,1M Jun 18 2024 salmon_tx2gene_GRCh38.tsv
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,1K Jun 18 2024 salmon_tx2gene_chrHsv1.tsv
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,9K Jun 18 2024 'sample IDs_Lamprecht.xlsx'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 30M Jun 18 2024 summarySCC_PM25.rds
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 18 2024 untitled.py
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 11M Jun 18 2024 tutorial-rnaseq.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,3K Jun 18 2024 x.log
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 381M Jun 18 2024 webapp.tar.gz
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 8,4K Okt 9 2024 temp
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 2,7K Okt 9 2024 temp2
drwxr-xr-x 51 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 17 12:23 Data_Susanne_Amplicon_haplotype_analyses_RdRp_orf1_2_re
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 17 12:42 Data_Susanne_WGS_unbiased
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA_D$ ls -tlrh
total 56K
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 59 Apr 11 2024 Data_Soeren_RNA-seq_2023_PUBLISHING -> /media/jhuang/Elements/Data_Soeren_RNA-seq_2023_PUBLISHING/
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 32 Apr 11 2024 Data_Ute -> /media/jhuang/Elements/Data_Ute/
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 52 Apr 23 2024 Data_Marc_RNA-seq_Sepidermidis -> /media/jhuang/Titisee/Data_Marc_RNA-seq_Sepidermidis
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 2 2024 Data_Patricia_Transposon
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 29 2024 Books_DA_for_Life
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 18 2024 Data_Sven
-rw-rw-r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 2,9K Jul 16 2024 Datasize_calculation_based_on_coverage.txt
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 23 2024 Data_Paul_HD46_1-wt_resequencing
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 26 2024 Data_Sanam_DAMIAN
drwxrwxr-x 26 jhuang jhuang 12K Jul 30 2024 Data_Tam_variant_calling
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 26 2024 Data_Samira_Manuscripts
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 27 2024 Data_Silvia_VoltRon_Debug
drwxrwxr-x 38 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 10 2025 Data_Pietschmann_229ECoronavirus_Mutations_2024
drwxrwxr-x 23 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 25 2025 Data_Pietschmann_229ECoronavirus_Mutations_2025
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 63 Nov 24 16:30 Data_Birthe_Svenja_RSV_Probe3_PUBLISHING -> /media/jhuang/Elements/Data_Birthe_Svenja_RSV_Probe3_PUBLISHING
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA_E$ ls -tlrh
total 119M
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 18 2019 j_huang_until_201904
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 29 2019 Data_2019_April
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 10 2019 Data_2019_May
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 17 2019 Data_2019_June
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 12 2019 Data_2019_July
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 29 2019 Data_2019_August
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 5 2019 Data_2019_September
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 18 2023 Data_Song_RNASeq_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 10 2023 Data_Laura_MP_RNASeq
drwxr-xr-x 22 jhuang jhuang 12K Nov 3 2023 Data_Nicole6_HEV_Swantje2
drwxr-xr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 13 2023 Data_Becher_Damian_Picornavirus_BovHepV
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 118M Nov 28 2023 bacteria_refseq.zip
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 30 2023 bacteria_refseq
drwxr-xr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 30 2023 Data_Rotavirus
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 6 2023 Data_Xiaobo_10x
drwx------ 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 7 2025 Data_Becher_Damian_Picornavirus_BovHepV_INCOMPLETE_DEL
jhuang@WS-2290C:~/DATA_Intenso$ ls -ltrh
total 4,1G
drwxr-xr-x 15 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 30 2015 HOME_FREIBURG_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 12 2015 150810_M03701_0019_000000000-AFJFK
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 31 2017 Data_Thaiss2_Microarray
drwxr-xr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 27 2017 VirtualBox_VMs_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 27 2017 'VirtualBox VMs_DEL'
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 27 2017 'VirtualBox VMs2_DEL'
drwxr-xr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 12 2017 websites
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 29 2017 DATA
drwxr-xr-x 149 jhuang jhuang 36K Jun 30 2017 Data_Laura
drwxr-xr-x 149 jhuang jhuang 36K Jun 30 2017 Data_Laura_2
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 30 2017 Data_Laura_3
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 10 2017 galaxy_tools
drwxr-xr-x 45 jhuang jhuang 32K Jul 17 2017 Downloads2
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 27 2017 Downloads
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 28 2017 mom-baby_com_cn
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 8 2017 'VirtualBox VMs2'
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 9 2017 VirtualBox_VMs
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 11 2017 CLC_Data
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 12K Aug 14 2017 Work_Dir2
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 15 2017 Work_Dir2_SGE
drwxr-xr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 24 2017 Data_SPANDx1_Kpneumoniae_vs_Assembly1
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 24 2017 MauveOutput
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 31 2017 Fastqs
drwxr-xr-x 20 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 7 2017 Data_Anna3_VRE_Ausbruch
drwxr-xr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 19 2017 Work_Dir_mock_broad_mockinput
drwxr-xr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 19 2017 Work_Dir_dM_broad_mockinput
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 6 2017 Data_Anna8_RNASeq_static_shake_deprecated
drwxr-xr-x 24 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 9 2017 PENDRIVE_cont
drwxr-xr-x 8 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 23 2017 Work_Dir_WAP_broad_mockinput
drwxr-xr-x 10 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 23 2017 Work_Dir_WAC_broad_mockinput
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 23 2017 Work_Dir_dP_broad_mockinput
drwxr-xr-x 52 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 8 2017 Data_Nicole10_16S_interlab
drwxr-xr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 6 2017 PAPERS
drwxr-xr-x 14 jhuang jhuang 16K Dez 15 2017 TB
drwxr-xr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 19 2017 Data_Anna4_SNP
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 16 2018 Data_Carolin1_16S
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 22 2018 ChipSeq_Raw_Data3_171009_NB501882_0024_AHNGTYBGX3
-rw-r--r-- 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0G Jan 23 2018 m_aepfelbacher_DEL.zip
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 24 2018 Data_Anna7_RNASeq_Cytoscape
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 24 2018 Data_Nicole9_Hund_Katze_Mega
drwxr-xr-x 39 jhuang jhuang 20K Jan 28 2018 Data_Anna2_CO6114
drwxr-xr-x 3 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 28 2018 Data_Nicole3_TH17_orig
drwxr-xr-x 27 jhuang jhuang 28K Jan 28 2018 Data_Nicole1_Tropheryma_whipplei
drwxr-xr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 30 2018 results_K27
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 19 2018 'VirtualBox VMs'
drwxr-xr-x 28 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 27 2018 Data_Anna6_RNASeq
drwxr-xr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 12K Mär 1 2018 Data_Anna1_1585_RNAseq
drwxr-xr-x 21 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 7 2018 Data_Thaiss1_Microarray
drwxr-xr-x 25 jhuang jhuang 12K Mär 27 2018 Data_Nicole7_Anelloviruses_Polyomavirus
drwxr-xr-x 13 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 22 2018 Data_Nina1_Nicole5_1-76
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 22 2018 Data_Nina1_merged
drwxr-xr-x 32 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 14 2018 Data_Nicole8_Lamprecht
drwxr-xr-x 40 jhuang jhuang 16K Jul 5 2018 Data_Anna5_SNP
drwxr-xr-x 35 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 12 2018 chipseq
drwxr-xr-x 107 jhuang jhuang 76K Mai 18 2019 Downloads_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 7 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 17 2020 Data_Gagliani2_enriched_16S
drwxr-xr-x 17 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 17 2020 Data_Gagliani1_18S_16S
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 2 2020 m_aepfelbacher
drwxr-xr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 17 12:38 Data_Susanne_WGS_3amplicons
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Titisee$ ls -tlrh
total 3,5G
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Dez 19 2017 Data_Anna4_SNP
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 24 2018 Data_Anna5_SNP_rsync_error
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 9,9K Mär 21 2018 TRASH
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Mär 28 2018 Data_Nicole6_HEV_4_SNP_calling_PE_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 22 2018 Data_Nina1_Nicole7
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Mai 24 2018 Data_Nicole6_HEV_4_SNP_calling_SE_DEL
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 3,5G Jun 14 2018 180119_M03701_0115_000000000-BFG46.zip
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 10 2018 Data_Nicole10_16S_interlab_PUBLISHED
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 10 2018 Anna11_assemblies
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 11 2018 Anna11_trees
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 24 2018 Data_Nicole6_HEV_new_orig_fastqs
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 23 2018 Data_Anna9_OXA-48_or_OXA-181
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 15 2019 bengal_results_v1_2018
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 9,8M Mär 22 2019 DO.pdf
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 6 2019 damian_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Mai 20 2019 MAGpy_db
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Aug 3 2019 UGENE_v1_32_data_cistrome
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 3 2019 UGENE_v1_32_data_ngs_classification
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 52K Okt 25 2019 Data_Nicole6_HEV_Swantje
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Okt 25 2019 Data_Nico_Gagliani
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 30 2020 GAMOLA2_prototyp
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Mär 31 2020 Thomas_methylation_EPIC_DO
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jun 15 2020 Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 36K Jun 25 2020 Data_Nicola_Schaltenberg_PICRUSt
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jan 25 2021 HOME_FREIBURG
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 13 2021 Data_Francesco_16S
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 14 2022 3rd_party
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 29 2022 ConsPred_prokaryotic_genome_annotation
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 2 2022 'System Volume Information'
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Sep 16 2022 damian_v201016
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 36K Jan 12 2023 Data_Holger_VRE
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 32K Feb 1 2023 Data_Holger_Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_SNP
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 5 2023 Eigene_Ordner_HR
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Sep 6 2023 GAMOLA2
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Sep 27 2023 Data_Anastasia_RNASeq
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Okt 20 2023 Data_Amir_PUBLISHED
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 44K Apr 25 2024 Data_Marc_RNA-seq_Sepidermidis
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 23 2024 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 23 2024 Data_Xiaobo_10x_3
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Nov 28 2024 Data_Tam_DNAseq_2023_Comparative_ATCC19606_AYE_ATCC17978
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 48K Dez 19 2024 Data_Holger_S.epidermidis_short
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 31 Feb 4 2025 TEMP
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Aug 22 11:44 Data_Holger_S.epidermidis_long
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Elements(Denise_ChIPseq)$ ls -tlrh
total 11M
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 7 2019 Data_Denise_LTtrunc_H3K27me3_2_results_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 7 2019 Data_Denise_LTtrunc_H3K4me3_2_results_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Aug 26 2019 Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_final_not_finished_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 24 2019 m_aepfelbacher_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jan 14 2020 Data_Damian
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 25 2020 ST772_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 160K Jan 25 2020 ALL_trimmed_part_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Mär 30 2020 Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol1
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 44K Mai 19 2020 Data_Pietschmann_HCV_Amplicon
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 60K Jun 26 2020 Data_Nicole6_HEV_ownMethod_new
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 2,5M Aug 5 2020 HD04-1.fasta
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 31 2021 RNAHiSwitch_
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 31 2021 RNAHiSwitch__
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jun 17 2021 RNAHiSwitch___
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 25 2021 RNAHiSwitch_paper_
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jul 7 2021 RNAHiSwitch_milestone1_DELETED
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 7,2M Jul 7 2021 RNAHiSwitch_paper.tar.gz
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 12 2021 RNAHiSwitch_paper_DELETED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jul 12 2021 RNAHiSwitch_milestone1
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 23 2021 RNAHiSwitch_paper
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 24 2021 Ute_RNASeq_results
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 24 2021 Ute_miRNA_results_38
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 88K Okt 27 2021 RNAHiSwitch
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 48K Mär 31 2022 Data_HepE_Freiburg_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 1 2022 Data_INTENSO_2022-06
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Sep 14 2022 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 14 2022 'System Volume Information'
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 7 2022 Data_Anna_Mixta_hanseatica_PUBLISHED
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 33K Dez 9 2022 coi_disclosure.docx
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Feb 8 2023 Data_Jingang
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 30 2023 Data_Arck_16S_MMc_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 5 2023 Data_Laura_ChIPseq_GSE120945
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 80K Jun 5 2023 Data_Nicole6_HEV_ownMethod
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jul 5 2023 Data_Susanne_16S_re_UNPUBLISHED *
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 12 2023 Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol2
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 20 2023 Data_Caroline_RNAseq_wt_timecourse
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 20 2023 Data_Caroline_RNAseq_brain_organoids
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Okt 20 2023 Data_Amir_PUBLISHED_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 24 2023 Data_download_virus_fam
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 22 2024 Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics_COPYFAILED_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Feb 27 2024 Data_Paul_and_Marc_Epidome_batch3
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,0K Okt 30 2024 ifconfig_hamm.txt
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Apr 8 2025 Data_Soeren_2023_PUBLISHING
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Nov 24 13:34 Data_Birthe_Svenja_RSV_Probe3_PUBLISHING
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jan 13 17:46 Data_Ute
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Feb 17 12:48 Data_Susanne_16S_UNPUBLISHED *
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(HOffice)$ ls -tlrh
total 19M
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 550K Jan 8 2015 SeagateExpansion.ico
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 38 Mär 27 2015 Autorun.inf
-rwxrwxrwx 2 jhuang jhuang 18M Mai 4 2017 Start_Here_Win.exe
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 1,1M Jul 7 2017 Warranty.pdf
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jan 9 2018 Start_Here_Mac.app
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jan 9 2018 Seagate
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 5 2024 HomeOffice_DIR (Data_Anna_HAPDICS_RNASeq, From_Samsung_T5)
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 17 2024 DATA_COPY_FROM_178528 (copy_and_clean.sh, logfile_jhuang.log, jhuang)
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Sep 9 10:41 'System Volume Information'
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Sep 9 10:41 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Elements(Anna_C.arnes)$ ls -trlh
total 236K
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Nov 14 2018 Data_Swantje_HEV_using_viral-ngs
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Dez 4 2018 VIPER_static_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 4 2019 Data_Nicole6_HEV_Swantje1_blood
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Apr 5 2019 Data_Nicole6_HEV_benchmark
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Mär 12 2020 Data_Denise_RNASeq_GSE79958
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jan 11 2022 Data_16S_Leonie_from_Nico_Gaglianis
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jul 29 2022 Fastqs_19-21
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 2 2022 'System Volume Information'
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Sep 23 2022 Data_Luise_Epidome_test
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 48K Sep 27 2023 Data_Anna_C.acnes_PUBLISHED
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Dez 6 2023 Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Bindung
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 9 2024 Data_Denise_LT_K331A_RNASeq
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jan 10 2024 Data_Luise_Epidome_batch1
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Feb 26 2024 Data_Luise_Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_PUBLISHED
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Feb 27 2024 Data_Luise_Epidome_batch2
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 5 2024 picrust2_out_2024_2
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 11 2025 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(DATA_COPY_FROM_hamburg)$ ls -tlrh
total 19M
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 33 Feb 21 2018 Autorun.inf
-rwxrwxrwx 2 jhuang jhuang 18M Jun 21 2019 Start_Here_Win.exe
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 1,6M Jul 6 2020 Warranty.pdf
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Mär 10 2021 Start_Here_Mac.app
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Mär 10 2021 Seagate
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jun 29 2022 DATA_COPY_TRANSFER_INCOMPLETE_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 16 2024 DATA_COPY_FROM_hamburg
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(Seagate_1)$ ls -trlh
total 104G
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 3 2013 RNA_seq_analysis_tools_2013
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Feb 28 2018 Data_Laura0
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Sep 6 2018 Data_Petra_Arck
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 14 2018 Data_Martin_mycoplasma
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Dez 5 2018 chromhmm-enhancers
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 15 2019 ChromHMM_Dir
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 18 2019 Data_Denise_sT_H3K4me3
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 18 2019 Data_Denise_sT_H3K27me3
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Feb 13 2019 Start_Here_Mac.app
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Feb 13 2019 Seagate
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 19 2019 Data_Nicole16_parapoxvirus
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 39G Aug 20 2019 Project_h_rohde_Susanne_WGS_unbiased_DEL.zip
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 11 2019 Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol1
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Nov 13 2019 Data_ENNGS_pathogen_detection_pipeline_comparison
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 18 2020 j_huang_201904_202002
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 112 Mär 2 2020 Data_Laura_ChIPseq_GSE120945
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Mär 26 2020 batch_200314_incomplete
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 65G Mär 26 2020 m_aepfelbacher.zip
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Mär 26 2020 m_error_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 28 2020 batch_200325
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 28 2020 batch_200319
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 30 2020 GAMOLA2_prototyp
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 22 2020 Data_Nicola_Gagliani
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 3 2020 2017-18_raw_data
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,2M Sep 11 2020 Data_Arck_MeDIP
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 16 2020 trimmed
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 23 2020 Data_Nicole_16S_Christmas_2020_2
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 14 2021 j_huang_202007_202012
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 15 2021 Data_Nicole_16S_Christmas_2020
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 184K Jan 18 2021 Downloads_2021-01-18_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 28 2021 Data_Laura_plasmid
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 18 2021 Data_Laura_16S_2_re
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Mär 22 2021 Data_Laura_16S_2
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mär 22 2021 Data_Laura_16S_2_re_
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Mär 23 2021 Data_Laura_16S_merged
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 32K Nov 7 2022 Downloads_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Nov 7 2022 Data_Laura_16S
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 76K Nov 9 2023 Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_final
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Dez 4 2023 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 4 2023 'System Volume Information'
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Seagate Expansion Drive(Seagate_2)$ ls -trlh
total 70G
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 5 2017 Data_Nicole4_TH17
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 18M Feb 9 2018 Start_Here_Win.exe
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 33 Feb 21 2018 Autorun.inf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,2M Jul 26 2018 Warranty.pdf
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Feb 13 2019 Start_Here_Mac.app
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Feb 13 2019 Seagate
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 20 2019 Data_Denise_RNASeq_trimmed_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 25 2020 HD12
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 25 2020 Qi_panGenome
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 44K Jan 25 2020 ALL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Feb 14 2020 fastq_HPI_bw_2019_08_and_2020_02
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 19K Mär 12 2020 f1_R1_link.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 19K Mär 12 2020 f1_R2_link.sh
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Mär 19 2020 rtpd_files
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 65G Apr 2 2020 m_aepfelbacher.zip
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 20 2020 Data_Nicole_16S_Hamburg_Odense_Cornell_Muenster
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Apr 21 2020 HyAsP_incomplete_genomes
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 25 2020 HyAsP_normal_sampled_input
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Apr 28 2020 HyAsP_complete_genomes
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 176M Mai 8 2020 video.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 6,9K Jun 2 2020 sam2bedgff.pl
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 5,5K Jul 7 2020 HD04.infection.hS_vs_HD04.nose.hS_annotated_degenes.xls
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 44K Jul 9 2020 ALL83
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 9 2020 Data_Pietschmann_RSV_Probe_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jul 27 2020 HyAsP_normal
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 28 2020 Data_Manthey_16S
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jul 29 2020 rtpd_files_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Aug 11 2020 HyAsP_bold
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 44K Aug 17 2020 Data_HEV
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 29 2020 Seq_VRE_hybridassembly
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Nov 11 2020 Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_raw_data_shovill_prokka
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Aug 10 2021 Data_Anna_HAPDICS_WGS_ALL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Aug 10 2021 Data_HEV_Freiburg_2020
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Okt 27 2021 Data_Nicole_HDV_Recombination_PUBLISHED
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 905K Feb 8 2022 s_hero2x
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 5,5G Feb 25 2022 201030_M03701_0207_000000000-J57B4.zip
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,9K Mär 21 2022 README
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,9K Mär 21 2022 'README(1)'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 848 Mär 28 2022 dna2.fasta.fai
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 17K Mär 28 2022 91.pep
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 9,1K Mär 28 2022 91.orf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 222 Mär 28 2022 91.orf.fai
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,1M Mär 31 2022 dgaston-dec-06-2012-121211124858-phpapp01.pdf
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 5,2K Apr 4 2022 tileshop.fcgi
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 765K Apr 4 2022 ppat.1009304.s016.tif
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,1K Mai 2 2022 sequence.txt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 2 2022 'sequence(1).txt'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 3,7K Mai 23 2022 GSE128169_series_matrix.txt.gz
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 23 2022 GSE128169_family.soft.gz
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 40K Mär 20 2023 Data_Anna_HAPDICS_RNASeq
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 1,3M Apr 4 2023 Data_Christopher_MeDIP_MMc_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jun 28 2023 Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics_IMCOMPLETE_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Feb 12 2024 Data_Denise_RNASeq
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 5 2024 'System Volume Information'
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Apr 5 2024 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Elements(An14_RNAs)$ ls -tlrh
total 284K
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Aug 7 2017 Data_Anna10_RP62A
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 15 2018 Data_Nicole12_16S_Kluwe_Bunders
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 30 2018 chromhmm-enhancers
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Apr 1 2019 Data_Denise_sT_Methylation
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Apr 1 2019 Data_Denise_LTtrunc_Methylation
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Apr 29 2019 Data_16S_arckNov
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Mai 29 2019 Data_Tabea_RNASeq
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,6K Mai 29 2019 nr_gz_README
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 5 2019 j_huang_raw_fq
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 7 2019 'System Volume Information'
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 7 2019 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 36K Jun 18 2019 host_refs
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 18 2019 Vraw
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 68K Jul 29 2019 Data_Susanne_Amplicon_RdRp_orf1_2 *
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 6 2019 tmp
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Sep 4 2020 Data_RNA188_Paul_Becher
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Nov 3 2020 Data_ChIPSeq_Laura
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Mai 7 2021 Data_16S_arckNov_review_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Mai 7 2021 Data_16S_arckNov_re
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Mai 25 2021 Fastqs
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 9 2021 Data_Tabea_RNASeq_submission
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 27 2021 Data_Anna_Cutibacterium_acnes_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Sep 16 2021 Data_Silvia_RNASeq_SUBMISSION
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 9 2022 Data_Hannes_ChIPSeq
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 5 2022 Data_Anna14_RNASeq_to_be_DEL
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 40K Dez 15 2022 Data_Pietschmann_RSV_Probe2_PUBLISHED
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Dez 16 2022 Data_Holger_Klebsiella_pneumoniae_SNP_PUBLISHING
drwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 29 2023 Data_Anna14_RNASeq_plus_public
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Elements(Indra_HAPDICS)$ ls -trlh
total 452K
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 3 2018 Data_Anna11_Sepdermidis_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 12 2018 HD15_without_10
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jul 12 2018 HD31
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 12 2018 HD33
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 12 2018 HD39
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 12 2018 HD43
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 12 2018 HD46
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 12 2018 HD15_with_10
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jul 13 2018 HD26
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 13 2018 HD59
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 12K Jul 13 2018 HD25
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 16 2018 HD21
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Jul 17 2018 HD17
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 24K Sep 24 2018 HD04
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 20K Mär 5 2019 Data_Anna11_Pair1-6_P6
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Aug 15 2019 Data_Anna12_HAPDICS_HyAsP
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 68K Dez 27 2019 HAPDICS_hyasp_plasmids
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jan 14 2021 Data_Anna_HAPDICS_review
-rwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 9,6K Jan 26 2021 data_overview.txt
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 29 2021 align_assem_res_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 0 Jun 8 2021 'System Volume Information'
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 8 2021 EXCHANGE_DEL
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Aug 30 2021 Data_Indra_H3K4me3_public
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Feb 17 2022 Data_Gunnar_MS
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 2 2022 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 2 2022 UKE_DELLWorkstation_C_Users_indbe_Desktop
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 2 2022 Linux_DELLWorkstation_C_Users_indbe_VirtualBoxVMs
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 23 2022 Data_Anna_HAPDICS_RNASeq_rawdata
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 8,0K Jun 23 2022 Data_Indra_H3K27ac_public
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 28K Feb 22 2023 Data_Holger_Klebsiella_pneumoniae_SNP_PUBLISHING
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 9 2024 DATA_INDRA_RNASEQ
drwxrwxrwx 1 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Dez 9 2024 DATA_INDRA_CHIPSEQ
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Elements(jhuang_*)$ ls -ltrh
total 5,0M
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 657K Jul 9 2021 'Install Western Digital Software for Windows.exe'
-rwxr-xr-x 1 jhuang jhuang 498K Jul 9 2021 'Install Western Digital Software for Mac.dmg'
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 1,0M Mai 17 2023 'System Volume Information'
drwxr-xr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 1,0M Aug 26 2024 '$RECYCLE.BIN'
drwxr-xr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 1,0M Feb 4 2025 20250203_FS10003086_95_BTR67811-0621
jhuang@WS-2290C:/media/jhuang/Smarty$ ls -tlrh
total 140K
drwx------ 2 jhuang jhuang 16K Mär 14 2018 lost+found
drwxrwxrwx 21 jhuang jhuang 68K Jun 10 2022 Blast_db
drwxrwxr-x 2 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 5 2022 temporary_files_DEL
drwxrwxr-x 9 jhuang jhuang 12K Sep 6 2022 ALIGN_ASSEM
drwxr-xr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Sep 29 2022 Data_Paul_Staphylococcus_epidermidis
drwxrwxr-x 11 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jan 26 2023 Data_16S_Degenhardt_Marius_DEL
drwxrwxr-x 16 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jun 28 2023 Data_Gunnar_Yersiniomics_DEL
drwxrwxr-x 6 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 5 2023 Data_Manja_RNAseq_Organoids_Virus
drwxrwxr-x 19 jhuang jhuang 12K Sep 27 2023 Data_Emilia_MeDIP
drwxr-xr-x 14 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Okt 30 2023 DjangoApp_Backup_2023-10-30
drwxrwxr-x 5 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Apr 19 2024 ref
drwxrwxr-x 4 jhuang jhuang 4,0K Jul 22 2025 Data_Michelle_RNAseq_2025_raw_data_DEL_AFTER_UPLOAD_GEOProtected: SARS-CoV-2 病毒血症与免疫介导的组织侵入在 COVID-19 血管病理中的作用:一项基于尸检的研究。
按研究方向速查:生命科学常用数据库清单(Global Core Biodata Resources 精选)
下面是一份“按研究方向推荐常用数据库”的速查清单。按你做什么研究 → 该先去哪几个库来分组,每个库后面给一句“用来干嘛”。In summary, 做基因组先看 ENA/Ensembl/UCSC;做蛋白功能先上 UniProt/InterPro;做通路用 Reactome;做药物与小分子用 ChEMBL/ChEBI;做人类变异用 gnomAD/GWAS Catalog/ClinGen;做微生物命名和 16S 用 LPSN/SILVA;做模型生物就去 FlyBase/WormBase/ZFIN/MGD。
基因组学与序列数据
- European Nucleotide Archive(ENA):原始测序数据、组装、注释的综合归档入口(欧洲体系)。
- DNA Data Bank of Japan(DDBJ):日本序列数据归档(INSDC 成员之一)。
- Ensembl:脊椎动物基因组浏览、比较基因组、变异、调控注释。
- UCSC Genome Browser:人类及多物种基因组可视化浏览与注释轨道。
- GENCODE:人/鼠高质量基因注释集合(常做标准参考)。
微生物/细菌方向(菌株信息、命名、16S 等)
- BacDive:菌株层面的标准化信息(培养条件、表型、来源等)。
- LPSN: List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature:原核命名权威信息(名称是否有效、分类更新)。
- SILVA:16S/18S、23S/28S rRNA 序列与比对数据集(做分类/扩增子常用)。
蛋白质功能注释、家族结构域、互作网络
- UniProt:蛋白序列与功能注释的“总入口”(最常用)。
- InterPro:蛋白家族/结构域/功能位点整合分析(做注释和功能预测)。
- CATH:蛋白结构域进化关系/结构分类。
- STRING:蛋白互作网络(预测+整合证据),做功能关联很方便。
- IMEx: International Molecular Exchange Consortium:高质量、人工整理的分子互作数据整合。
- Protein Data Bank(PDB):蛋白/核酸 3D 结构的全球档案库(结构生物学必备)。
通路、代谢与反应数据库
- Reactome:经典通路知识库(富集分析、机制解释常用)。
- Rhea:生化反应与转运反应标准化知识库(注释/代谢研究)。
- BRENDA:酶功能数据大全(底物、动力学、反应等)。
- EcoCyc:大肠杆菌 K-12 的基因组与代谢通路精细注释库。
化学、小分子、药物靶点(药物研发/化学生物学)
- ChEBI:小分子化学实体词典/本体(标准名、结构、分类)。
- ChEMBL:药物样分子、活性、靶点关联(做药物发现/重定位很常用)。
- IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY:权威药理学知识库(配体-靶点关系、药物信息)。
- LIPID MAPS:脂质组学资源与命名/分类体系。
转录组、表达谱、蛋白表达图谱
- Bgee:跨物种表达模式对比(“这个基因在哪里表达?”)。
- GXD:小鼠基因表达数据库(发育/组织表达等)。
- Human Protein Atlas:人类组织/细胞层面的蛋白表达与定位图谱。
- Europe PMC:生命科学文献入口(全文/摘要、资助信息等,做调研很高效)。
人类遗传变异、GWAS、疾病本体与临床解释
- gnomAD:人群变异频率汇总(过滤“常见变异”必备)。
- GWAS Catalog:GWAS SNP-性状关联的标准化数据库。
- Clinical Genome Resource(ClinGen):基因/变异的临床相关性评估资源(精准医学)。
- CIViC: Clinical Interpretation of Variants in Cancer:肿瘤变异临床意义的社区整理平台。
- Human Disease Ontology Knowledgebase:疾病本体(统一术语、做整合分析很有用)。
- ClinPGX:药物基因组学知识整理(基因变异影响用药反应)。
模型生物与专属物种数据库
- FlyBase:果蝇遗传与分子数据。
- WormBase:秀丽线虫及相关线虫的基因组与生物学数据。
- ZFIN: The Zebrafish Information Network:斑马鱼模型数据。
- MGD: Mouse Genome Database:小鼠基因组与表型/疾病关联数据。
- PomBase:裂殖酵母资源库。
- Saccharomyces Genome Database:出芽酵母数据库。
- Rat Genome Database:大鼠基因组与表型/疾病数据。
- Alliance of Genome Resources:多模型生物资源的整合入口(跨物种对照很方便)。
生物多样性、物种名录与分类学
- Catalogue of Life:全球已知物种的统一名录与分类信息。
- Global Biodiversity Information Facility(GBIF):全球生物多样性观测/标本记录等开放数据平台。
病原体与媒介(寄生虫/媒介昆虫等)
- VEuPathDB:真核病原体及无脊椎媒介相关的大规模组学数据库集合。
NCBI 提交入口怎么选?一张“决策树”帮你不走弯路(GenBank / SRA / Genome / TSA / BioProject / BioSample / dbGaP / GTR / ClinVar)
很多人第一次在 NCBI 点“Start a new submission”会懵:这么多入口到底选哪个?下面给你一棵从目标出发的决策树,按着走基本不会错。如果你要公开的是“数据文件”(FASTQ/FASTA/组装/注释),不要选 GTR;如果你要公开的是“某个临床/研究检测项目的服务说明”,才选 GTR。
✅ 第一步:你要提交的是“原始测序数据”还是“组装/注释结果”?
A. 我有 FASTQ(原始 reads:Illumina/Nanopore/PacBio)
➡️ 选 Sequence Read Archive (SRA)
- 你提交的是:reads + 文库信息(平台、PE/SE、策略等)
- 几乎所有文章要求原始数据可复现,都需要 SRA
同时你通常还需要:
- BioSample(每个样本的“身份证”)
- BioProject(把整个项目的数据串起来)
✅ 常见路径:BioProject → BioSample → SRA
B. 我有组装好的基因组(contigs/scaffolds/complete genome)
➡️ 选 Genome(基因组提交主入口)
- 适合:细菌/真菌/病毒/真核的 draft 或 complete genome
- 会与 GenBank/Assembly 体系关联(后续可公开检索引用)
同时通常还需要:
- BioSample(样本来源信息)
- BioProject(项目汇总)
- (可选但强烈建议)SRA(如果你也愿意公开原始 reads)
✅ 常见路径:BioProject → BioSample → SRA(可选/建议)→ Genome
C. 我只有一个基因/片段/质粒序列(不是整套基因组项目)
➡️ 选 GenBank
- 适合:单基因、片段序列、单独的质粒序列、特定区域序列
- 如果你在做“系统的基因组项目”,通常走 Genome 更合适;GenBank更像“序列条目提交”。
D. 我有转录组拼装结果(assembled transcripts,不是 reads)
➡️ 选 TSA(Transcriptome Shotgun Assembly)
- TSA 提交的是:拼装后的转录本序列
- 原始 RNA-seq reads 仍应走 SRA
✅ 常见路径:BioProject → BioSample → SRA → TSA
✅ 第二步:你提交的是“临床敏感人类数据/变异解释/检测项目”吗?
E. 数据涉及人类受试者隐私、需要受控访问(表型+基因型/临床队列)
➡️ 选 dbGaP(受控访问)
- 适合:人类敏感数据
- 常伴随伦理/权限/审查流程(不是完全公开下载)
F. 你要提交“变异的临床意义解读”(致病性、证据、表型关联)
➡️ 选 ClinVar
- 适合:临床实验室/研究团队共享变异解释
G. 你要登记“遗传检测项目/检测服务信息”
➡️ 选 GTR(Genetic Testing Registry)
- 更像“检测项目注册”,不是上传测序数据本体
✅ 第三步:你是不是在管理一个“项目集合”?
H. 你有多个样本/多批数据/多类型数据(SRA + Genome + 其它)
➡️ 建议先建 BioProject
- 作用:项目总目录,方便引用与检索
I. 你每一个样本都需要可追溯的元数据(来源、地点、日期、宿主等)
➡️ 基本都需要 BioSample
- 作用:样本身份证;SRA/Genome 通常都要挂它
终极“快速选择口诀”
- FASTQ 原始 reads → SRA
- 基因组组装(contigs/scaffolds/complete)→ Genome
- 转录本拼装(transcripts)→ TSA
- 单基因/片段/质粒序列条目 → GenBank
- 把所有东西串成一个项目 → BioProject
- 每个样本来源信息 → BioSample
- 人类敏感受控数据 → dbGaP
- 临床变异解释 → ClinVar
- 遗传检测项目登记 → GTR
- 批量/自动化 → API
下面是对 GTR(Genetic Testing Registry,遗传检测注册库) 的更详细中文说明。
GTR 是什么?
GTR 是 NCBI 上一个“登记遗传检测项目/检测服务信息”的公共目录,由提供检测的实验室/机构自愿提交,目的是让公众、临床医生和研究人员能查到:某个疾病/基因/病原体有哪些检测、由哪些实验室提供、检测方法是什么、适用范围和证据如何等。(NCBI)
关键点:GTR 不是用来上传 FASTQ/基因组序列的。
- 原始测序数据 → SRA
- 基因组组装/注释 → Genome / GenBank
- GTR → 登记“检测项目本身”的信息(类似检测项目黄页/目录) (NCBI)
GTR 收录哪些“检测”?
GTR 的范围不仅是传统“单基因遗传病检测”,也包括:
- 孟德尔遗传病、药物反应(药物基因组学)相关检测
- 肿瘤/体细胞变异检测
- 多基因 panel、芯片(array)、生化、细胞遗传、分子检测 (NCBI)
- 微生物/病原体相关检测(例如病原体 panel、病毒载量、血清学抗体/抗原检测等) (NCBI)
在 GTR 里,一个“检测条目”通常会包含哪些信息?
你可以把它理解为“一个检测项目的说明书 + 实验室信息”组合,常见字段包括:
- 检测目的/用途:诊断、携带者筛查、预后、用药指导等 (NCBI)
- 检测对象(Target):基因/区域、变异类型、或病原体靶标等
- 方法学(Methodology):例如 PCR、Sanger、NGS panel、MLPA、芯片、qPCR、Nanopore 等(写清楚平台与策略)(NCBI)
- 适应证/关联疾病(Indication/Condition):对应哪些疾病/表型;并可建立“检测—靶标—适应证”的声明关系 (NCBI)
- 性能与证据:分析/临床有效性、参考文献、指南或标准等(GTR强调用途与证据展示)(NCBI)
- 实验室信息:机构名称、联系人、资质/认证信息、可提供的服务范围等 (NCBI)
- GTR accession:每个检测都有唯一编号,便于在论文/EHR 中引用。(NCBI)
谁应该提交 GTR?
主要是提供遗传/分子检测服务的实验室或机构(临床检验科、第三方医学检验所、商业检测机构、研究机构实验室等)。(NCBI)
如果你只是做科研并想公开数据:
- 数据公开通常走 BioProject/BioSample + SRA + Genome/GenBank
- 不一定需要 GTR(除非你在对外提供一个“检测项目/检测服务”)(NCBI)
GTR 怎么提交?(流程概览)
GTR 提交一般是两步走:
1)先注册“实验室(Laboratory record)”
先把实验室作为一个实体登记,GTR 会审核/联系新注册者;实验室通过后才可以提交具体检测项目。(NCBI)
2)再提交“检测(Test record)”
有两种方式:
- 网页交互式提交:在提交门户里逐页填写信息(适合少量检测)(NCBI)
- 批量提交(Excel 模板):适合大量临床检测项目;可用全字段或最小字段模板上传(研究检测的批量上传通常不开放/不支持)。(NCBI)
GTR vs ClinVar vs dbGaP:最容易混淆的三兄弟
- GTR:登记“检测项目/检测服务”信息(谁提供、怎么测、测什么、适应证/证据)(NCBI)
- ClinVar:提交“变异—临床意义”的解释与证据(致病性分类等)(你贴里之前也提过)
- dbGaP:人类敏感数据(基因型/表型)受控访问的归档库
From Salmon to Subset Heatmaps: A Reproducible Pipeline for Phage/Stress/Biofilm Gene Panels (No p-value Cutoff, Data_JuliaFuchs_RNAseq_2025)
This post documents a complete, batch-ready pipeline to generate subset heatmaps (phage / stress-response / biofilm-associated) from bacterial RNA-seq data quantified with Salmon, using DE tables without any p-value cutoff.
You will end with:
-
Three gene sets (A/B/C):
- A (phage/prophage genes): extracted from MT880872.1.gb, mapped to CP052959 via BLASTN, converted to CP052959
GeneID_plain - B (stress genes): keyword-based selection from CP052959 GenBank annotations
- C (biofilm genes): keyword-based selection from CP052959 GenBank annotations
- A (phage/prophage genes): extracted from MT880872.1.gb, mapped to CP052959 via BLASTN, converted to CP052959
-
For each
*-all_annotated.csvinresults/star_salmon/degenes/:- Subset GOI lists for A/B/C (no cutoff; include all rows belonging to the geneset)
- Per-comparison
*_matched.tsvtables for sanity checks
- Merged 3-condition heatmaps (Untreated + Mitomycin + Moxi) per timepoint (4h/8h/18h) and subset (A/B/C), giving 9 final figures
- An Excel file per heatmap containing
GeneID,GeneName,Description, and the plotted expression matrix
Everything is written so you can run a single shell script for genesets + intersections, then one R script for heatmaps.
0) Environments
We use two conda environments:
plot-numpy1for Python tools and BLAST setupr_envfor DESeq2 + plotting heatmaps in R
conda activate plot-numpy11) Directory layout
From your project root:
.
├── CP052959.gb
├── MT880872.1.gb
├── results/star_salmon/degenes/
│ ├── Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h-all_annotated.csv
│ ├── ...
└── subset_heatmaps/ # all scripts + outputs go hereCreate the output directory:
mkdir -p subset_heatmaps2) Step A/B/C gene set generation + batch intersection (one command)
This section generates:
geneset_A_phage_GeneID_plain.id(+GeneID.id)geneset_B_stress_GeneID_plain.id(+GeneID.id)geneset_C_biofilm_GeneID_plain.id(+GeneID.id)- plus all per-contrast
GOI_*files and*_matched.tsv
2.1 Script: extract CDS FASTA from MT880872.1.gb
Save as subset_heatmaps/extract_cds_fasta.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Bio import SeqIO
import sys
gb = sys.argv[1]
out_fa = sys.argv[2]
rec = SeqIO.read(gb, "genbank")
with open(out_fa, "w") as out:
for f in rec.features:
if f.type != "CDS":
continue
locus = f.qualifiers.get("locus_tag", ["NA"])[0]
seq = f.extract(rec.seq)
out.write(f">{locus}\n{str(seq).upper()}\n")2.2 Script: BLAST hit mapping → CP052959 GeneID_plain set (geneset A)
Save as subset_heatmaps/blast_hits_to_geneset.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
import pandas as pd
from Bio import SeqIO
blast6 = sys.argv[1]
cp_gb = sys.argv[2]
prefix = sys.argv[3] # e.g. subset_heatmaps/geneset_A_phage
# Load CP052959 CDS intervals
rec = SeqIO.read(cp_gb, "genbank")
cds = []
for f in rec.features:
if f.type != "CDS":
continue
locus = f.qualifiers.get("locus_tag", [None])[0]
if locus is None:
continue
start = int(f.location.start) + 1
end = int(f.location.end)
cds.append((locus, start, end))
cds_df = pd.DataFrame(cds, columns=["GeneID_plain","start","end"])
# Load BLAST tabular (outfmt 6)
cols = ["qseqid","sseqid","pident","length","mismatch","gapopen","qstart","qend",
"sstart","send","evalue","bitscore"]
b = pd.read_csv(blast6, sep="\t", names=cols)
# Normalize subject coordinates
b["smin"] = b[["sstart","send"]].min(axis=1)
b["smax"] = b[["sstart","send"]].max(axis=1)
# Filter for strong hits (tune if needed)
b = b[(b["pident"] >= 90.0) & (b["length"] >= 100)]
hits = set()
for _, r in b.iterrows():
ov = cds_df[(r["smin"] <= cds_df["end"]) & (r["smax"] >= cds_df["start"])]
hits.update(ov["GeneID_plain"].unique().tolist())
hits = sorted(hits)
plain_path = f"{prefix}_GeneID_plain.id"
geneid_path = f"{prefix}_GeneID.id"
pd.Series(hits).to_csv(plain_path, index=False, header=False)
pd.Series(["gene-" + x for x in hits]).to_csv(geneid_path, index=False, header=False)
print(f"Wrote {len(hits)} genes:")
print(" ", plain_path)
print(" ", geneid_path)2.3 Script: keyword-based genesets B/C from CP052959 annotations
Save as subset_heatmaps/geneset_by_keywords.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys, re
import pandas as pd
from Bio import SeqIO
cp_gb = sys.argv[1]
mode = sys.argv[2] # "stress" or "biofilm"
prefix = sys.argv[3] # e.g. subset_heatmaps/geneset_B_stress
rec = SeqIO.read(cp_gb, "genbank")
rows=[]
for f in rec.features:
if f.type != "CDS":
continue
locus = f.qualifiers.get("locus_tag", [None])[0]
if locus is None:
continue
gene = (f.qualifiers.get("gene", [""])[0] or "")
product = (f.qualifiers.get("product", [""])[0] or "")
note = "; ".join(f.qualifiers.get("note", [])) if f.qualifiers.get("note") else ""
text = " ".join([gene, product, note]).strip()
rows.append((locus, gene, product, note, text))
df = pd.DataFrame(rows, columns=["GeneID_plain","gene","product","note","text"])
if mode == "stress":
rgx = re.compile(
r"\b(stress|heat shock|chaperone|dnaK|groEL|groES|clp|thioredoxin|peroxiredoxin|catalase|superoxide|"
r"recA|lexA|uvr|mutS|mutL|usp|osm|sox|katA|sod)\b",
re.I
)
elif mode == "biofilm":
rgx = re.compile(
r"\b(biofilm|ica|pga|polysaccharide|PIA|adhesin|MSCRAMM|fibrinogen-binding|fibronectin-binding|"
r"clumping factor|sortase|autolysin|atl|nuclease|DNase|protease|dispersin|luxS|agr|sarA|dlt)\b",
re.I
)
else:
raise SystemExit("mode must be stress or biofilm")
sel = df[df["text"].apply(lambda x: bool(rgx.search(x)))].copy()
hits = sorted(sel["GeneID_plain"].unique())
plain_path = f"{prefix}_GeneID_plain.id"
geneid_path = f"{prefix}_GeneID.id"
sel_path = f"{prefix}_hits.tsv"
pd.Series(hits).to_csv(plain_path, index=False, header=False)
pd.Series(["gene-" + x for x in hits]).to_csv(geneid_path, index=False, header=False)
sel.drop(columns=["text"]).to_csv(sel_path, sep="\t", index=False)
print(f"{mode}: wrote {len(hits)} genes:")
print(" ", plain_path)
print(" ", geneid_path)
print(" ", sel_path)2.4 Script: intersect each DE table with A/B/C (no cutoff) and write GOI lists + matched TSV
Save as subset_heatmaps/make_goi_lists_batch.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys, glob, os
import pandas as pd
de_dir = sys.argv[1] # results/star_salmon/degenes
out_dir = sys.argv[2] # subset_heatmaps
genesetA_plain = sys.argv[3] # subset_heatmaps/geneset_A_phage_GeneID_plain.id
genesetB_plain = sys.argv[4] # subset_heatmaps/geneset_B_stress_GeneID_plain.id
genesetC_plain = sys.argv[5] # subset_heatmaps/geneset_C_biofilm_GeneID_plain.id
def load_plain_ids(path):
with open(path) as f:
return set(x.strip() for x in f if x.strip())
A = load_plain_ids(genesetA_plain)
B = load_plain_ids(genesetB_plain)
C = load_plain_ids(genesetC_plain)
def pick_id_cols(df):
geneid = "GeneID" if "GeneID" in df.columns else None
plain = "GeneID_plain" if "GeneID_plain" in df.columns else None
if plain is None and "GeneName" in df.columns:
plain = "GeneName"
return geneid, plain
os.makedirs(out_dir, exist_ok=True)
for csv in sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(de_dir, "*-all_annotated.csv"))):
base = os.path.basename(csv).replace("-all_annotated.csv", "")
df = pd.read_csv(csv)
geneid_col, plain_col = pick_id_cols(df)
if plain_col is None:
raise SystemExit(f"Cannot find GeneID_plain/GeneName in {csv}")
df["__plain__"] = df[plain_col].astype(str).str.replace("^gene-","", regex=True)
def write_set(tag, S):
sub = df[df["__plain__"].isin(S)].copy()
out_plain = os.path.join(out_dir, f"GOI_{base}_{tag}_GeneID_plain.id")
out_geneid = os.path.join(out_dir, f"GOI_{base}_{tag}_GeneID.id")
out_tsv = os.path.join(out_dir, f"{base}_{tag}_matched.tsv")
sub["__plain__"].drop_duplicates().to_csv(out_plain, index=False, header=False)
pd.Series(["gene-"+x for x in sub["__plain__"].drop_duplicates()]).to_csv(out_geneid, index=False, header=False)
sub.to_csv(out_tsv, sep="\t", index=False)
print(f"{base} {tag}: {sub.shape[0]} rows, {sub['__plain__'].nunique()} genes")
write_set("A_phage", A)
write_set("B_stress", B)
write_set("C_biofilm", C)2.5 Driver: run everything with one command
Save as subset_heatmaps/run_subset_setup.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
DE_DIR="./results/star_salmon/degenes"
OUT_DIR="./subset_heatmaps"
CP_GB="CP052959.gb"
PHAGE_GB="MT880872.1.gb"
mkdir -p "$OUT_DIR"
echo "[INFO] Using DE_DIR=$DE_DIR"
ls -lh "$DE_DIR"/*-all_annotated.csv
# ---- A) BLAST-based phage/prophage geneset ----
python - <<'PY'
from Bio import SeqIO
rec=SeqIO.read("CP052959.gb","genbank")
SeqIO.write(rec, "subset_heatmaps/CP052959.fna", "fasta")
PY
python subset_heatmaps/extract_cds_fasta.py "$PHAGE_GB" "$OUT_DIR/MT880872_CDS.fna"
makeblastdb -in "$OUT_DIR/CP052959.fna" -dbtype nucl -out "$OUT_DIR/CP052959_db" >/dev/null
blastn \
-query "$OUT_DIR/MT880872_CDS.fna" \
-db "$OUT_DIR/CP052959_db" \
-out "$OUT_DIR/MT_vs_CP.blast6" \
-outfmt "6 qseqid sseqid pident length mismatch gapopen qstart qend sstart send evalue bitscore" \
-evalue 1e-10
python subset_heatmaps/blast_hits_to_geneset.py \
"$OUT_DIR/MT_vs_CP.blast6" "$CP_GB" "$OUT_DIR/geneset_A_phage"
# ---- B/C) keyword-based genesets ----
python subset_heatmaps/geneset_by_keywords.py "$CP_GB" stress "$OUT_DIR/geneset_B_stress"
python subset_heatmaps/geneset_by_keywords.py "$CP_GB" biofilm "$OUT_DIR/geneset_C_biofilm"
# ---- Batch: intersect each DE CSV with the genesets (no cutoff) ----
python subset_heatmaps/make_goi_lists_batch.py \
"$DE_DIR" "$OUT_DIR" \
"$OUT_DIR/geneset_A_phage_GeneID_plain.id" \
"$OUT_DIR/geneset_B_stress_GeneID_plain.id" \
"$OUT_DIR/geneset_C_biofilm_GeneID_plain.id"
echo "[INFO] Done. GOI lists are in $OUT_DIR"
ls -1 "$OUT_DIR"/GOI_*_GeneID.id | headRun it:
bash subset_heatmaps/run_subset_setup.shAt this point you will have all *_matched.tsv files required for plotting, e.g.:
Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_A_phage_matched.tsvMoxi_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_A_phage_matched.tsv- … (for 8h/18h and B/C)
3) No-cutoff heatmaps (merged Untreated + Mitomycin + Moxi → 9 figures)
Now switch to your R environment and build the rlog (rld) expression matrix from Salmon quantifications.
conda activate r_env3.1 Build rld from Salmon outputs (R)
library(tximport)
library(DESeq2)
setwd("~/DATA/Data_JuliaFuchs_RNAseq_2025/results/star_salmon")
files <- c(
"Untreated_4h_r1" = "./Untreated_4h_1a/quant.sf",
"Untreated_4h_r2" = "./Untreated_4h_1b/quant.sf",
"Untreated_4h_r3" = "./Untreated_4h_1c/quant.sf",
"Untreated_8h_r1" = "./Untreated_8h_1d/quant.sf",
"Untreated_8h_r2" = "./Untreated_8h_1e/quant.sf",
"Untreated_8h_r3" = "./Untreated_8h_1f/quant.sf",
"Untreated_18h_r1" = "./Untreated_18h_1g/quant.sf",
"Untreated_18h_r2" = "./Untreated_18h_1h/quant.sf",
"Untreated_18h_r3" = "./Untreated_18h_1i/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_4h_r1" = "./Mitomycin_4h_2a/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_4h_r2" = "./Mitomycin_4h_2b/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_4h_r3" = "./Mitomycin_4h_2c/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_8h_r1" = "./Mitomycin_8h_2d/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_8h_r2" = "./Mitomycin_8h_2e/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_8h_r3" = "./Mitomycin_8h_2f/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_18h_r1" = "./Mitomycin_18h_2g/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_18h_r2" = "./Mitomycin_18h_2h/quant.sf",
"Mitomycin_18h_r3" = "./Mitomycin_18h_2i/quant.sf",
"Moxi_4h_r1" = "./Moxi_4h_3a/quant.sf",
"Moxi_4h_r2" = "./Moxi_4h_3b/quant.sf",
"Moxi_4h_r3" = "./Moxi_4h_3c/quant.sf",
"Moxi_8h_r1" = "./Moxi_8h_3d/quant.sf",
"Moxi_8h_r2" = "./Moxi_8h_3e/quant.sf",
"Moxi_8h_r3" = "./Moxi_8h_3f/quant.sf",
"Moxi_18h_r1" = "./Moxi_18h_3g/quant.sf",
"Moxi_18h_r2" = "./Moxi_18h_3h/quant.sf",
"Moxi_18h_r3" = "./Moxi_18h_3i/quant.sf"
)
txi <- tximport(files, type = "salmon", txIn = TRUE, txOut = TRUE)
replicate <- factor(rep(c("r1","r2","r3"), 9))
condition <- factor(c(
rep("Untreated_4h",3), rep("Untreated_8h",3), rep("Untreated_18h",3),
rep("Mitomycin_4h",3), rep("Mitomycin_8h",3), rep("Mitomycin_18h",3),
rep("Moxi_4h",3), rep("Moxi_8h",3), rep("Moxi_18h",3)
))
colData <- data.frame(condition=condition, replicate=replicate, row.names=names(files))
dds <- DESeqDataSetFromTximport(txi, colData, design = ~ condition)
rld <- rlogTransformation(dds)3.2 Plot merged 3-condition subset heatmaps (R)
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(gplots))
need <- c("openxlsx")
to_install <- setdiff(need, rownames(installed.packages()))
if (length(to_install)) install.packages(to_install, repos = "https://cloud.r-project.org")
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(openxlsx))
in_dir <- "subset_heatmaps"
out_dir <- file.path(in_dir, "heatmaps_merged3")
dir.create(out_dir, showWarnings = FALSE, recursive = TRUE)
pick_col <- function(df, candidates) {
hit <- intersect(candidates, names(df))
if (length(hit) == 0) return(NA_character_)
hit[1]
}
strip_gene_prefix <- function(x) sub("^gene[-_]", "", x)
match_tags <- function(nms, tags) {
pat <- paste0("(^|_)(?:", paste(tags, collapse = "|"), ")(_|$)")
grepl(pat, nms, perl = TRUE)
}
detect_tag <- function(nm, tags) {
hits <- vapply(tags, function(t)
grepl(paste0("(^|_)", t, "(_|$)"), nm, perl = TRUE), logical(1))
if (!any(hits)) NA_character_ else tags[which(hits)[1]]
}
make_pretty_labels <- function(gene_ids_in_matrix, id2name, id2desc) {
plain <- strip_gene_prefix(gene_ids_in_matrix)
nm <- unname(id2name[plain]); ds <- unname(id2desc[plain])
nm[is.na(nm)] <- ""; ds[is.na(ds)] <- ""
nm2 <- ifelse(nzchar(nm), nm, plain)
lbl <- ifelse(nzchar(ds), paste0(nm2, " (", ds, ")"), nm2)
make.unique(lbl, sep = "_")
}
if (exists("rld")) {
expr_all <- assay(rld)
} else if (exists("vsd")) {
expr_all <- assay(vsd)
} else {
stop("Neither 'rld' nor 'vsd' exists. Create/load it before running this script.")
}
expr_all <- as.matrix(expr_all)
mat_ids <- rownames(expr_all)
if (is.null(mat_ids)) stop("Expression matrix has no rownames.")
times <- c("4h", "8h", "18h")
tags <- c("A_phage", "B_stress", "C_biofilm")
cond_order_template <- c("Untreated_%s", "Mitomycin_%s", "Moxi_%s")
for (tt in times) {
for (tag in tags) {
f_mito <- file.path(in_dir, sprintf("Mitomycin_%s_vs_Untreated_%s_%s_matched.tsv", tt, tt, tag))
f_moxi <- file.path(in_dir, sprintf("Moxi_%s_vs_Untreated_%s_%s_matched.tsv", tt, tt, tag))
if (!file.exists(f_mito) || !file.exists(f_moxi)) next
df1 <- read.delim(f_mito, sep = "\t", header = TRUE, stringsAsFactors = FALSE, check.names = FALSE)
df2 <- read.delim(f_moxi, sep = "\t", header = TRUE, stringsAsFactors = FALSE, check.names = FALSE)
id_col_1 <- pick_col(df1, c("GeneID","GeneID_plain","Gene_Id","gene_id","locus_tag","LocusTag","ID"))
id_col_2 <- pick_col(df2, c("GeneID","GeneID_plain","Gene_Id","gene_id","locus_tag","LocusTag","ID"))
if (is.na(id_col_1) || is.na(id_col_2)) next
name_col_1 <- pick_col(df1, c("GeneName","Preferred_name","gene","Symbol","Name"))
name_col_2 <- pick_col(df2, c("GeneName","Preferred_name","gene","Symbol","Name"))
desc_col_1 <- pick_col(df1, c("Description","product","Product","annotation","Annot","note"))
desc_col_2 <- pick_col(df2, c("Description","product","Product","annotation","Annot","note"))
g1 <- unique(trimws(df1[[id_col_1]])); g1 <- g1[nzchar(g1)]
g2 <- unique(trimws(df2[[id_col_2]])); g2 <- g2[nzchar(g2)]
GOI_raw <- unique(c(g1, g2))
present <- intersect(mat_ids, GOI_raw)
if (!length(present)) {
present <- unique(mat_ids[strip_gene_prefix(mat_ids) %in% strip_gene_prefix(GOI_raw)])
}
if (!length(present)) next
getcol <- function(df, col, n) if (is.na(col)) rep("", n) else as.character(df[[col]])
plain1 <- strip_gene_prefix(as.character(df1[[id_col_1]]))
plain2 <- strip_gene_prefix(as.character(df2[[id_col_2]]))
nm1 <- getcol(df1, name_col_1, nrow(df1)); nm2 <- getcol(df2, name_col_2, nrow(df2))
ds1 <- getcol(df1, desc_col_1, nrow(df1)); ds2 <- getcol(df2, desc_col_2, nrow(df2))
nm1[is.na(nm1)] <- ""; nm2[is.na(nm2)] <- ""
ds1[is.na(ds1)] <- ""; ds2[is.na(ds2)] <- ""
keys_all <- unique(c(plain1, plain2))
id2name <- setNames(rep("", length(keys_all)), keys_all)
id2desc <- setNames(rep("", length(keys_all)), keys_all)
fill_map <- function(keys, vals, mp) {
for (i in seq_along(keys)) {
k <- keys[i]; v <- vals[i]
if (!nzchar(k)) next
if (!nzchar(mp[[k]]) && nzchar(v)) mp[[k]] <- v
}
mp
}
id2name <- fill_map(plain1, nm1, id2name); id2name <- fill_map(plain2, nm2, id2name)
id2desc <- fill_map(plain1, ds1, id2desc); id2desc <- fill_map(plain2, ds2, id2desc)
cond_tags <- sprintf(cond_order_template, tt)
keep_cols <- match_tags(colnames(expr_all), cond_tags)
if (!any(keep_cols)) next
sub_idx <- which(keep_cols)
sub_names <- colnames(expr_all)[sub_idx]
cond_for_col <- vapply(sub_names, detect_tag, character(1), tags = cond_tags)
cond_rank <- match(cond_for_col, cond_tags)
ord <- order(cond_rank, sub_names)
sub_idx <- sub_idx[ord]
expr_sub <- expr_all[present, sub_idx, drop = FALSE]
row_ok <- apply(expr_sub, 1, function(x) is.finite(sum(x)) && var(x, na.rm = TRUE) > 0)
datamat <- expr_sub[row_ok, , drop = FALSE]
if (nrow(datamat) < 2) next
hr <- hclust(as.dist(1 - cor(t(datamat), method = "pearson")), method = "complete")
mycl <- cutree(hr, h = max(hr$height) / 1.1)
palette_base <- c("yellow","blue","orange","magenta","cyan","red","green","maroon",
"lightblue","pink","purple","lightcyan","salmon","lightgreen")
mycol <- palette_base[(as.vector(mycl) - 1) %% length(palette_base) + 1]
labRow <- make_pretty_labels(rownames(datamat), id2name, id2desc)
labCol <- gsub("_", " ", colnames(datamat))
gene_id <- rownames(datamat)
gene_plain <- strip_gene_prefix(gene_id)
gene_name <- unname(id2name[gene_plain]); gene_name[is.na(gene_name)] <- ""
gene_desc <- unname(id2desc[gene_plain]); gene_desc[is.na(gene_desc)] <- ""
out_tbl <- data.frame(
GeneID = gene_id,
GeneID_plain = gene_plain,
GeneName = ifelse(nzchar(gene_name), gene_name, gene_plain),
Description = gene_desc,
datamat,
check.names = FALSE,
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
base <- sprintf("%s_%s_merged3", tt, tag)
out_xlsx <- file.path(out_dir, paste0("table_", base, ".xlsx"))
write.xlsx(out_tbl, out_xlsx, overwrite = TRUE)
out_png <- file.path(out_dir, paste0("heatmap_", base, ".png"))
cex_row <- if (nrow(datamat) > 600) 0.90 else if (nrow(datamat) > 300) 1.05 else 1.30
height <- max(1600, min(18000, 34 * nrow(datamat)))
png(out_png, width = 2200, height = height)
heatmap.2(
datamat,
Rowv = as.dendrogram(hr),
Colv = FALSE,
dendrogram = "row",
col = bluered(75),
scale = "row",
trace = "none",
density.info = "none",
RowSideColors = mycol,
margins = c(12, 60),
labRow = labRow,
labCol = labCol,
cexRow = cex_row,
cexCol = 2.0,
srtCol = 15,
key = FALSE
)
dev.off()
message("WROTE: ", out_png)
message("WROTE: ", out_xlsx)
}
}
message("Done. Output dir: ", out_dir)Run it:
setwd("~/DATA/Data_JuliaFuchs_RNAseq_2025")
source("subset_heatmaps/draw_9_merged_heatmaps.R")3.3 Optional: Plot 2-condition subset heatmaps (R)
#!/usr/bin/env Rscript
## =============================================================
## Draw 18 subset heatmaps using *_matched.tsv as input
## Output: subset_heatmaps/heatmaps_from_matched/
##
## Requirements:
## - rld or vsd exists in environment (DESeq2 transform)
## If running as Rscript, you must load/create rld/vsd BEFORE sourcing this file
## (see the note at the bottom for the "source()" way)
##
## Matched TSV must contain GeneID or GeneID_plain (or GeneName) columns.
## =============================================================
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(gplots))
in_dir <- "subset_heatmaps"
out_dir <- file.path(in_dir, "heatmaps_from_matched")
dir.create(out_dir, showWarnings = FALSE, recursive = TRUE)
# -------------------------
# Helper functions
# -------------------------
pick_col <- function(df, candidates) {
hit <- intersect(candidates, names(df))
if (length(hit) == 0) return(NA_character_)
hit[1]
}
strip_gene_prefix <- function(x) sub("^gene[-_]", "", x)
split_contrast_groups <- function(x) {
parts <- strsplit(x, "_vs_", fixed = TRUE)[[1]]
if (length(parts) != 2L) stop("Contrast must be in form A_vs_B: ", x)
parts
}
match_tags <- function(nms, tags) {
pat <- paste0("(^|_)(?:", paste(tags, collapse = "|"), ")(_|$)")
grepl(pat, nms, perl = TRUE)
}
# -------------------------
# Get expression matrix
# -------------------------
if (exists("rld")) {
expr_all <- assay(rld)
} else if (exists("vsd")) {
expr_all <- assay(vsd)
} else {
stop("Neither 'rld' nor 'vsd' exists. Create/load it before running this script.")
}
expr_all <- as.matrix(expr_all)
mat_ids <- rownames(expr_all)
if (is.null(mat_ids)) stop("Expression matrix has no rownames.")
# -------------------------
# List your 18 matched inputs
# -------------------------
matched_files <- c(
"Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_A_phage_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_B_stress_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_C_biofilm_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_8h_vs_Untreated_8h_A_phage_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_8h_vs_Untreated_8h_B_stress_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_8h_vs_Untreated_8h_C_biofilm_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_18h_vs_Untreated_18h_A_phage_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_18h_vs_Untreated_18h_B_stress_matched.tsv",
"Mitomycin_18h_vs_Untreated_18h_C_biofilm_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_A_phage_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_B_stress_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_C_biofilm_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_8h_vs_Untreated_8h_A_phage_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_8h_vs_Untreated_8h_B_stress_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_8h_vs_Untreated_8h_C_biofilm_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_18h_vs_Untreated_18h_A_phage_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_18h_vs_Untreated_18h_B_stress_matched.tsv",
"Moxi_18h_vs_Untreated_18h_C_biofilm_matched.tsv"
)
matched_paths <- file.path(in_dir, matched_files)
# -------------------------
# Main loop
# -------------------------
for (path in matched_paths) {
if (!file.exists(path)) {
message("SKIP missing: ", path)
next
}
base <- sub("_matched\\.tsv$", "", basename(path))
# base looks like: Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_A_phage
# split base into contrast + tag (last 2 underscore fields are the tag)
parts <- strsplit(base, "_")[[1]]
if (length(parts) < 6) {
message("SKIP unexpected name: ", base)
next
}
# infer tag as last 2 parts: e.g. A_phage / B_stress / C_biofilm
tag <- paste0(parts[length(parts)-1], "_", parts[length(parts)])
# contrast is the rest
contrast <- paste(parts[1:(length(parts)-2)], collapse = "_")
# read matched TSV
df <- read.delim(path, sep = "\t", header = TRUE, stringsAsFactors = FALSE, check.names = FALSE)
id_col <- pick_col(df, c("GeneID", "GeneID_plain", "GeneName", "Gene_Id", "gene_id", "locus_tag", "LocusTag", "ID"))
if (is.na(id_col)) {
message("SKIP (no ID col): ", path)
next
}
GOI_raw <- unique(trimws(df[[id_col]]))
GOI_raw <- GOI_raw[nzchar(GOI_raw)]
# match GOI to matrix ids robustly
present <- intersect(mat_ids, GOI_raw)
if (!length(present)) {
present <- unique(mat_ids[strip_gene_prefix(mat_ids) %in% strip_gene_prefix(GOI_raw)])
}
if (!length(present)) {
message("SKIP (no GOI matched matrix): ", base)
next
}
# subset columns for the two groups
groups <- split_contrast_groups(contrast)
keep_cols <- match_tags(colnames(expr_all), groups)
if (!any(keep_cols)) {
message("SKIP (no columns matched groups): ", contrast)
next
}
cols_idx <- which(keep_cols)
sub_colnames <- colnames(expr_all)[cols_idx]
# put Untreated first (2nd group in "Treated_vs_Untreated")
ord <- order(!grepl(paste0("(^|_)", groups[2], "(_|$)"), sub_colnames, perl = TRUE))
cols_idx <- cols_idx[ord]
expr_sub <- expr_all[present, cols_idx, drop = FALSE]
# remove constant/NA rows
row_ok <- apply(expr_sub, 1, function(x) is.finite(sum(x)) && var(x, na.rm = TRUE) > 0)
datamat <- expr_sub[row_ok, , drop = FALSE]
if (nrow(datamat) < 2) {
message("SKIP (too few rows after filtering): ", base)
next
}
# clustering
hr <- hclust(as.dist(1 - cor(t(datamat), method = "pearson")), method = "complete")
mycl <- cutree(hr, h = max(hr$height) / 1.1)
palette_base <- c("yellow","blue","orange","magenta","cyan","red","green","maroon",
"lightblue","pink","purple","lightcyan","salmon","lightgreen")
mycol <- palette_base[(as.vector(mycl) - 1) %% length(palette_base) + 1]
# labels
labRow <- rownames(datamat)
labRow <- sub("^gene-", "", labRow)
labRow <- sub("^rna-", "", labRow)
labCol <- colnames(datamat)
labCol <- gsub("_", " ", labCol)
# output sizes
height <- max(900, min(12000, 25 * nrow(datamat)))
out_png <- file.path(out_dir, paste0("heatmap_", base, ".png"))
out_mat <- file.path(out_dir, paste0("matrix_", base, ".csv"))
write.csv(as.data.frame(datamat), out_mat, quote = FALSE)
png(out_png, width = 1100, height = height)
heatmap.2(
datamat,
Rowv = as.dendrogram(hr),
Colv = FALSE,
dendrogram = "row",
col = bluered(75),
scale = "row",
trace = "none",
density.info = "none",
RowSideColors = mycol,
margins = c(10, 15),
sepwidth = c(0, 0),
labRow = labRow,
labCol = labCol,
cexRow = if (nrow(datamat) > 500) 0.6 else 1.0,
cexCol = 1.7,
srtCol = 15,
lhei = c(0.01, 4),
lwid = c(0.5, 4),
key = FALSE
)
dev.off()
message("WROTE: ", out_png)
}
message("All done. Output dir: ", out_dir)Run it:
setwd("~/DATA/Data_JuliaFuchs_RNAseq_2025")
source("subset_heatmaps/draw_18_heatmaps_from_matched.R")4) Optional: Update README_Heatmap to support “GOI file OR no-cutoff”
If you still use the older README_Heatmap logic that expects *-up.id and *-down.id, replace the GOI-building block with this (single GOI list or whole CSV with no cutoff):
geneset_file <- NA_character_ # e.g. "subset_heatmaps/GOI_Mitomycin_4h_vs_Untreated_4h_A_phage_GeneID.id"
use_all_genes_no_cutoff <- FALSE
if (!is.na(geneset_file) && file.exists(geneset_file)) {
GOI <- read_ids_from_file(geneset_file)
} else if (isTRUE(use_all_genes_no_cutoff)) {
all_path <- file.path("./results/star_salmon/degenes", paste0(contrast, "-all_annotated.csv"))
ann <- read.csv(all_path, stringsAsFactors = FALSE, check.names = FALSE)
id_col <- if ("GeneID" %in% names(ann)) "GeneID" else if ("GeneID_plain" %in% names(ann)) "GeneID_plain" else NA_character_
if (is.na(id_col)) stop("No GeneID / GeneID_plain in: ", all_path)
GOI <- unique(trimws(gsub('"', "", ann[[id_col]])))
GOI <- GOI[nzchar(GOI)]
} else {
stop("Set geneset_file OR set use_all_genes_no_cutoff <- TRUE")
}
present <- intersect(rownames(RNASeq.NoCellLine), GOI)
if (!length(present)) stop("None of the GOI found in expression matrix rownames.")
GOI <- present5) Script inventory (bash + python)
Bash
subset_heatmaps/run_subset_setup.sh
Python
subset_heatmaps/extract_cds_fasta.pysubset_heatmaps/blast_hits_to_geneset.pysubset_heatmaps/geneset_by_keywords.pysubset_heatmaps/make_goi_lists_batch.py
R
subset_heatmaps/draw_9_merged_heatmaps.Rsubset_heatmaps/draw_18_heatmaps_from_matched.R
This post is a lab wiki / GitHub README / methods note, every script referenced is included in full above (and can be copied into subset_heatmaps/ directly).
Bacterial WGS Pipeline (Isolate Genomes, Data_Tam_DNAseq_2026_Acinetobacter_harbinensis): nf-core/bacass → Assembly/QC → Annotation → AMR/Virulence → Core-Genome Phylogeny → ANI
This post is a standalone, reproducible record of the bacterial WGS pipeline I used (example sample: AN6). I’m keeping all command lines (as-run) so you can reuse the workflow for future projects. Wherever you see absolute paths, replace them with your own.
0) Prerequisites (what you need installed)
- Nextflow
- Docker (for nf-core/bacass
-profile docker) - Conda/Mamba
- CLI tools used later:
fastqc,spades.py,shovill,pigz,awk,seqkit,fastANI, plus R (for plotting), and the tools required by the provided scripts.
1) Download KmerFinder database
# Download the kmerfinder database: https://www.genomicepidemiology.org/services/ --> https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/KmerFinder/ --> https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/KmerFinder/etc/kmerfinder_db.tar.gz
# Download 20190108_kmerfinder_stable_dirs.tar.gz from https://zenodo.org/records/134470562) Run nf-core/bacass (Nextflow)
#--kmerfinderdb /path/to/kmerfinder/bacteria.tar.gz
#--kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder_db.tar.gz
#--kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/20190108_kmerfinder_stable_dirs.tar.gz
nextflow run nf-core/bacass -r 2.5.0 -profile docker \
--input samplesheet.tsv \
--outdir bacass_out \
--assembly_type long \
--kraken2db /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/k2_standard_08_GB_20251015.tar.gz \
--kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder/bacteria/ \
-resume
#SAVE bacass_out/Kmerfinder/kmerfinder_summary.csv to bacass_out/Kmerfinder/An6/An6_kmerfinder_results.xlsx3) Assembly (AN6 example)
3.1 Link raw reads + run FastQC
ln -s ../X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_1.fq.gz An6_R1.fastq.gz
ln -s ../X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_2.fq.gz An6_R2.fastq.gz
mkdir fastqc_out
fastqc -t 4 raw_data/* -o fastqc_out/
mamba activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac33.2 Trimming decision notes (kept as recorded)
For the AN6 data, it’s not better to run Trimmomatic first in most cases (adapters OK; per-tile failures are instrument/tile related and not “fixed” by trimming).
* **Adapters:** FastQC shows **Adapter Content = PASS** for both R1/R2. * **Overrepresented sequences:** none detected. * **Per-tile sequence quality:** **FAIL** (this is usually an instrument/tile effect; trimming adapters won’t “fix” it).Shovill: avoid pre-trimming (default read trimming already included unless disabled). SPAdes: trimming optional; try raw first, then trimmed if needed.
3.3 If you do need Trimmomatic (command kept)
# Paired-end trimming with Trimmomatic (Illumina-style)
# Adjust TRIMMOMATIC_JAR and ADAPTERS paths to your install.
TRIMMOMATIC_JAR=/path/to/trimmomatic.jar
ADAPTERS=/path/to/Trimmomatic/adapters/TruSeq3-PE.fa
java -jar "$TRIMMOMATIC_JAR" PE -threads 16 -phred33 \
An6_R1.fastq.gz An6_R2.fastq.gz \
An6_R1.trim.paired.fastq.gz An6_R1.trim.unpaired.fastq.gz \
An6_R2.trim.paired.fastq.gz An6_R2.trim.unpaired.fastq.gz \
ILLUMINACLIP:"$ADAPTERS":2:30:10 \
LEADING:3 TRAILING:3 \
SLIDINGWINDOW:4:20 \
MINLEN:50What you feed into SPAdes/Shovill afterward:
-
Use the paired outputs:
An6_R1.trim.paired.fastq.gzAn6_R2.trim.paired.fastq.gz
- Optional: you can include unpaired reads in SPAdes, but many people skip them for isolate assemblies unless coverage is low.
If you want, I can also give the matching SPAdes command that includes unpaired reads (or the cleanest approach that ignores them).
spades.py \
-1 raw_data/An6_R1.fastq.gz \
-2 raw_data/An6_R2.fastq.gz \
--isolate \
-t 32 -m 250 \
-o spades_out
spades.py \
-1 raw_data/An6_R1.fastq.gz \
-2 raw_data/An6_R2.fastq.gz \
--careful \
-t 32 -m 250 \
-o spades_out_carefulShovill (CHOSEN; default does read trimming unless you disable it):
shovill \
--R1 raw_data/An6_R1.fastq.gz \
--R2 raw_data/An6_R2.fastq.gz \
--outdir shovill_out \
--cpus 32 --ram 250 \
--depth 100If you want to keep reads completely untrimmed in Shovill, add --noreadtrim.
4) Genome annotation — BV-BRC ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis
* Use: https://www.bv-brc.org/app/ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis
* Input: scaffolded results from bacass
* Purpose: comprehensive overview + annotation of the genome assembly.5) Table 1 — summary of sequence data + genome features (env: gunc_env)
5.1 Environment prep + pipeline run (kept)
# Prepare environment and run the Table 1 (Summary of sequence data and genome features (env: gunc_env)) pipeline:
# activate the env that has openpyxl
mamba activate gunc_env
mamba install -n gunc_env -c conda-forge openpyxl -y
mamba deactivate
# STEP_1
ENV_NAME=gunc_env \
SAMPLE=AN6 \
ASM=shovill_out/contigs.fa \
R1=./X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_1.fq.gz \
R2=./X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_2.fq.gz \
./make_table1_pe.sh
# STEP_2
python export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py \
--workdir table1_AN6_work \
--out Comprehensive_AN6.xlsx \
--max-rows 200000 \
--sample AN65.2 Manual calculations (kept)
#Manually For the items “Total number of reads sequenced” and “Mean read length (bp)”:
#Total number of reads sequenced 9,127,297 × 2
#Coverage depth (sequencing depth) 589.4×
pigz -dc X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_1.fq.gz | awk 'END{print NR/4}'
seqkit stats X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_1.fq.gz
#file format type num_seqs sum_len min_len avg_len max_len
#X101SC25116512-Z01-J002/01.RawData/An6/An6_1.fq.gz FASTQ DNA 15,929,405 2,389,410,750 150 150 1505.3 Example metrics table snapshot (kept)
Metricsa Value
Genome size (bp) 3,012,410
Contig count (>= 500 bp) 41
Total number of reads sequenced 15,929,405 × 2
Coverage depth (sequencing depth) 1454.3×
Coarse consistency (%) 99.67
Fine consistency (%) 94.50
Completeness (%) 99.73
Contamination (%) 0.21
Contigs N50 (bp) 169,757
Contigs L50 4
Guanine-cytosine content (%) 41.14
Number of coding sequences (CDSs) 2,938
Number of tRNAs 69
Number of rRNAs 36) AMR / virulence screening (ABRicate workflows)
cp shovill_out/contigs.fa AN6.fasta
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=AN6.fasta SAMPLE=AN6 THREADS=32 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh #Default MINID=90 MINCOV=60
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=AN6.fasta SAMPLE=AN6 MINID=80 MINCOV=60 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh # 0 0 0 0
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=AN6.fasta SAMPLE=AN6 MINID=70 MINCOV=50 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh # 5 5 0 4
#Sanity checks on ABRicate outputs
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_AN6/raw/AN6.megares.tab
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_AN6/raw/AN6.card.tab
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_AN6/raw/AN6.resfinder.tab
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_AN6/raw/AN6.vfdb.tab
#!!!!!! DEBUG_TOMORROW: why using 'MINID=70 MINCOV=50' didn't return the 5504?
#Dedup tables / “one per gene” mode
rm Resistome_Virulence_An6.xlsx
chmod +x run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 \
ASM=AN6.fasta \
SAMPLE=AN6 \
OUTDIR=resistome_virulence_AN6 \
MINID=70 MINCOV=50 \
THREADS=32 \
./run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh
cd resistome_virulence_AN6
python3 -c 'import pandas as pd; from pathlib import Path; files=["Table_AMR_genes_dedup.tsv","Table_AMR_genes_one_per_gene.tsv","Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv","Table_DB_hit_counts.tsv"]; out="AN6_resistome_virulence.xlsx"; w=pd.ExcelWriter(out, engine="openpyxl"); [pd.read_csv(f, sep="\t").to_excel(w, sheet_name=Path(f).stem[:31], index=False) for f in files]; w.close(); print(out)'7) Core-genome phylogeny (NCBI + Roary + RAxML-NG + R plotting)
#Generate targets.tsv from ./bvbrc_out/Acinetobacter_harbinensis_AN6/FullGenomeReport.html.
export NCBI_EMAIL="xxx@yyy.de"
./resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py targets.tsv resolved_accessions.tsv
#[OK] Acinetobacter_harbinensis_HITLi7 -> GCF_000816495.1 (Scaffold)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_sp._ANC -> GCF_965200015.1 (Complete Genome)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_sp._TTH0-4 -> GCF_965200015.1 (Complete Genome)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_tandoii_DSM_14970 -> GCF_000621065.1 (Scaffold)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_towneri_DSM_14962 -> GCF_000368785.1 (Scaffold)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_radioresistens_SH164 -> GCF_000162115.1 (Scaffold)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_radioresistens_SK82 -> GCF_000175675.1 (Contig)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_radioresistens_DSM_6976 -> GCF_000368905.1 (Scaffold)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_indicus_ANC -> GCF_000413875.1 (Scaffold)
#[OK] Acinetobacter_indicus_CIP_110367 -> GCF_000488255.1 (Scaffold)
#NOTE the env bengal3_ac3 don’t have the following R package, using r_env for the plot-step → RUN TWICE, first bengal3_ac3, then run build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh plot-only.
#ADAPT the params EXTRA_ASSEMBLIES (could stay as empty), and AN6.fasta as REF_FASTA
conda activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3
export NCBI_EMAIL="xxx@yyy.de"
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
# (Optional) if want to delete some leaves from the tree, remove from inputs so Roary cannot include it
for id in "GCF_002291425.1" "GCF_047901425.1" "GCF_004342245.1" "GCA_032062225.1"; do
rm -f work_wgs_tree/gffs/${id}.gff
rm -f work_wgs_tree/fastas/${id}.fna
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/prokka/${id}
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/genomes_ncbi/${id}
# remove from accession list so it won't come back
awk -F'\t' 'NR==1 || $2!="${id}"' work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv > work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp \
&& mv work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv
done
./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
#Wrote: work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv
#Error: package or namespace load failed for ‘ggtree’ in loadNamespace(j <- i[[1L]], c(lib.loc, .libPaths()), versionCheck = vI[[j]]):
#there is no package called ‘aplot’
#Execution halted --> Using env r_env instead (see below)!
# Run this to regenerate labels.tsv
bash regenerate_labels.sh
# Regenerate the plot --> ERROR --> Using Rscript instead (see below)!
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/mambaforge/envs/r_env ./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh plot-only
#-->Error in as.hclust.phylo(tr) : the tree is not ultrametric
# 8) Manual correct the display name in work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv
#sample display
#GCF_000816495.1 Acinetobacter harbinensis HITLi7 (GCF_000816495.1)
#GCF_965200015.1 Acinetobacter sp. ANC (GCF_965200015.1)
#GCF_000621065.1 Acinetobacter tandoii DSM 14970 (GCF_000621065.1)
#GCF_000368785.1 Acinetobacter towneri DSM 14962 (GCF_000368785.1)
#GCF_000162115.1 Acinetobacter radioresistens SH164 (GCF_000162115.1)
#GCF_000175675.1 Acinetobacter radioresistens SK82 (GCF_000175675.1)
#GCF_000368905.1 Acinetobacter radioresistens DSM 6976 (GCF_000368905.1)
#GCF_000413875.1 Acinetobacter indicus ANC (GCF_000413875.1)
#GCF_000488255.1 Acinetobacter indicus CIP 110367 (GCF_000488255.1)
#REF AN6
# 9) Rerun only the plot step uisng plot_tree_v4.R
Rscript ./plot_tree_v4.R \
work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/core.raxml.support \
work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv \
6 \
work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree.pdf \
work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree.png8) ANI confirmation (fastANI loop)
mamba activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3
for id in GCF_000621065.1.fna GCF_000368785.1.fna GCF_000175675.1.fna GCF_000368905.1.fna GCF_000816495.1.fna GCF_965200015.1.fna GCF_000488255.1.fna GCF_000413875.1.fna GCF_000162115.1.fna; do
fastANI -q AN6.fasta -r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/${id} -o fastANI_AN6_vs_${id}.txt
done
# Alternatively, we can use the script run_fastani_batch_verbose.sh.9) Contig-to-reference mapping (how many contigs map?)
In total, we obtained 41 contigs >500 nt. Of these, 36 contigs were scaffolded with Multi-CSAR v1.1 into three chromosomal scaffolds:
- SCF_1: 1,773,912 bp
- SCF_2: 1,197,749 bp
- SCF_3: 23,925 bp Total: 2,995,586 bp
The remaining five contigs (contig00026/32/33/37/39) could not be scaffolded. Their partial BLASTn matches to both plasmid and chromosomal sequences suggest shared mobile elements, but do not confirm circular plasmids. A sequence/assembly summary was exported to Excel (Summary_AN6.xlsx), including read yield/read-length statistics and key assembly/QC metrics (genome size, contigs/scaffolds, N50, GC%, completeness, contamination).
Complete scripts (as attached)
Below are the full scripts exactly as provided, including plot_tree_v4.R.
make_table1_pe.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -Eeuo pipefail
# =========================
# User config
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-checkm_env2}"
# If you have Illumina paired-end, set R1/R2 (recommended)
R1="${R1:-}"
R2="${R2:-}"
# If you have single-end/ONT-like reads, set READS instead (legacy mode)
READS="${READS:-}"
ASM="${ASM:-shovill_out/contigs.fa}"
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-An6}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-32}"
OUT_TSV="${OUT_TSV:-Table1_${SAMPLE}.tsv}"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR:-table1_${SAMPLE}_work}"
LOGDIR="${LOGDIR:-${WORKDIR}/logs}"
LOGFILE="${LOGFILE:-${LOGDIR}/run_$(date +%F_%H%M%S).log}"
AUTO_INSTALL="${AUTO_INSTALL:-1}" # 1=install missing tools in ENV_NAME
GUNC_DB_KIND="${GUNC_DB_KIND:-progenomes}" # progenomes or gtdb
# =========================
mkdir -p "${LOGDIR}"
exec > >(tee -a "${LOGFILE}") 2>&1
ts(){ date +"%F %T"; }
log(){ echo "[$(ts)] $*"; }
on_err() {
local ec=$?
log "ERROR: failed (exit=${ec}) at line ${BASH_LINENO[0]}: ${BASH_COMMAND}"
log "Logfile: ${LOGFILE}"
exit "${ec}"
}
trap on_err ERR
# print every command
set -x
need_cmd(){ command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1; }
pick_pm() {
if need_cmd mamba; then echo "mamba"
elif need_cmd conda; then echo "conda"
else
log "ERROR: neither mamba nor conda found in PATH"
exit 1
fi
}
activate_env() {
if ! need_cmd conda; then
log "ERROR: conda not found; cannot activate env"
exit 1
fi
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
}
ensure_env_exists() {
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
if ! conda env list | awk '{print $1}' | grep -qx "${ENV_NAME}"; then
log "ERROR: env ${ENV_NAME} not found. Create it first."
exit 1
fi
}
install_pkgs_in_env() {
local pm="$1"; shift
local pkgs=("$@")
log "Installing into env ${ENV_NAME}: ${pkgs[*]}"
"${pm}" install -n "${ENV_NAME}" -c bioconda -c conda-forge -y "${pkgs[@]}"
}
pick_quast_cmd() {
if need_cmd quast; then echo "quast"
elif need_cmd quast.py; then echo "quast.py"
else echo ""
fi
}
# tool->package mapping (install missing ones)
declare -A TOOL2PKG=(
[quast]="quast"
[minimap2]="minimap2"
[samtools]="samtools"
[mosdepth]="mosdepth"
[checkm]="checkm-genome=1.1.3"
[gunc]="gunc"
[python]="python"
)
# =========================
# Detect mode (PE vs single)
MODE=""
if [[ -n "${R1}" || -n "${R2}" ]]; then
[[ -n "${R1}" && -n "${R2}" ]] || { log "ERROR: Provide both R1 and R2."; exit 1; }
MODE="PE"
elif [[ -n "${READS}" ]]; then
MODE="SINGLE"
else
log "ERROR: Provide either (R1+R2) OR READS."
exit 1
fi
# =========================
# Start
log "Start: Table 1 generation (reuse env=${ENV_NAME})"
log "Assembly: ${ASM}"
log "Sample: ${SAMPLE}"
log "Threads: ${THREADS}"
log "Workdir: ${WORKDIR}"
log "Logfile: ${LOGFILE}"
log "Mode: ${MODE}"
if [[ "${MODE}" == "PE" ]]; then
log "R1: ${R1}"
log "R2: ${R2}"
else
log "Reads: ${READS}"
fi
PM="$(pick_pm)"
log "Pkg manager: ${PM}"
ensure_env_exists
activate_env
log "Active envs:"
conda info --envs
log "Versions (if available):"
( python --version || true )
( checkm --version || true )
( gunc -v || true )
( minimap2 --version 2>&1 | head -n 2 || true )
( samtools --version 2>&1 | head -n 2 || true )
( mosdepth --version 2>&1 | head -n 2 || true )
( quast --version 2>&1 | head -n 2 || true )
( quast.py --version 2>&1 | head -n 2 || true )
# =========================
# Check/install missing tools in this env
MISSING_PKGS=()
for tool in minimap2 samtools mosdepth checkm gunc python; do
if ! need_cmd "${tool}"; then
MISSING_PKGS+=("${TOOL2PKG[$tool]}")
fi
done
QUAST_CMD="$(pick_quast_cmd)"
if [[ -z "${QUAST_CMD}" ]]; then
MISSING_PKGS+=("${TOOL2PKG[quast]}")
fi
if [[ "${#MISSING_PKGS[@]}" -gt 0 ]]; then
if [[ "${AUTO_INSTALL}" != "1" ]]; then
log "ERROR: missing tools and AUTO_INSTALL=0. Missing packages: ${MISSING_PKGS[*]}"
exit 1
fi
mapfile -t UNIQUE < <(printf "%s\n" "${MISSING_PKGS[@]}" | awk '!seen[$0]++')
install_pkgs_in_env "${PM}" "${UNIQUE[@]}"
activate_env
QUAST_CMD="$(pick_quast_cmd)"
fi
for tool in minimap2 samtools mosdepth checkm gunc python; do
need_cmd "${tool}" || { log "ERROR: still missing tool: ${tool}"; exit 1; }
done
[[ -n "${QUAST_CMD}" ]] || { log "ERROR: QUAST still missing."; exit 1; }
log "All tools ready. QUAST cmd: ${QUAST_CMD}"
# =========================
# Prepare workdir
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}"/{genomes,reads,stats,quast,map,checkm,gunc,tmp}
ASM_ABS="$(realpath "${ASM}")"
ln -sf "${ASM_ABS}" "${WORKDIR}/genomes/${SAMPLE}.fasta"
if [[ "${MODE}" == "PE" ]]; then
R1_ABS="$(realpath "${R1}")"
R2_ABS="$(realpath "${R2}")"
ln -sf "${R1_ABS}" "${WORKDIR}/reads/${SAMPLE}.R1.fastq.gz"
ln -sf "${R2_ABS}" "${WORKDIR}/reads/${SAMPLE}.R2.fastq.gz"
else
READS_ABS="$(realpath "${READS}")"
ln -sf "${READS_ABS}" "${WORKDIR}/reads/${SAMPLE}.reads.fastq.gz"
fi
# =========================
# 1) QUAST
log "Run QUAST..."
"${QUAST_CMD}" "${WORKDIR}/genomes/${SAMPLE}.fasta" -o "${WORKDIR}/quast"
QUAST_TSV="${WORKDIR}/quast/report.tsv"
test -s "${QUAST_TSV}"
# =========================
# 2) Map reads + mosdepth
log "Map reads (minimap2) + sort BAM..."
SORT_T="$((THREADS>16?16:THREADS))"
if [[ "${MODE}" == "PE" ]]; then
minimap2 -t "${THREADS}" -ax sr \
"${WORKDIR}/genomes/${SAMPLE}.fasta" \
"${WORKDIR}/reads/${SAMPLE}.R1.fastq.gz" "${WORKDIR}/reads/${SAMPLE}.R2.fastq.gz" \
| samtools sort -@ "${SORT_T}" -o "${WORKDIR}/map/${SAMPLE}.bam" -
else
# legacy single-read mode; keep map-ont as in original script
minimap2 -t "${THREADS}" -ax map-ont \
"${WORKDIR}/genomes/${SAMPLE}.fasta" "${WORKDIR}/reads/${SAMPLE}.reads.fastq.gz" \
| samtools sort -@ "${SORT_T}" -o "${WORKDIR}/map/${SAMPLE}.bam" -
fi
samtools index "${WORKDIR}/map/${SAMPLE}.bam"
log "Compute depth (mosdepth)..."
mosdepth -t "${SORT_T}" "${WORKDIR}/map/${SAMPLE}" "${WORKDIR}/map/${SAMPLE}.bam"
MOS_SUMMARY="${WORKDIR}/map/${SAMPLE}.mosdepth.summary.txt"
test -s "${MOS_SUMMARY}"
# =========================
# 3) CheckM
log "Run CheckM lineage_wf..."
checkm lineage_wf -x fasta -t "${THREADS}" "${WORKDIR}/genomes" "${WORKDIR}/checkm/out"
log "Run CheckM qa..."
checkm qa "${WORKDIR}/checkm/out/lineage.ms" "${WORKDIR}/checkm/out" --tab_table -o 2 \
> "${WORKDIR}/checkm/checkm_summary.tsv"
CHECKM_SUM="${WORKDIR}/checkm/checkm_summary.tsv"
test -s "${CHECKM_SUM}"
# =========================
# 4) GUNC
log "Run GUNC..."
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/gunc/db" "${WORKDIR}/gunc/out"
if [[ -z "$(ls -A "${WORKDIR}/gunc/db" 2>/dev/null || true)" ]]; then
log "Downloading GUNC DB kind=${GUNC_DB_KIND} to ${WORKDIR}/gunc/db ..."
gunc download_db -db "${GUNC_DB_KIND}" "${WORKDIR}/gunc/db"
fi
DMND="$(find "${WORKDIR}/gunc/db" -type f -name "*.dmnd" | head -n 1 || true)"
if [[ -z "${DMND}" ]]; then
log "ERROR: No *.dmnd found under ${WORKDIR}/gunc/db after download."
ls -lah "${WORKDIR}/gunc/db" || true
exit 1
fi
log "Using GUNC db_file: ${DMND}"
gunc run \
--db_file "${DMND}" \
--input_fasta "${WORKDIR}/genomes/${SAMPLE}.fasta" \
--out_dir "${WORKDIR}/gunc/out" \
--threads "${THREADS}" \
--detailed_output \
--contig_taxonomy_output \
--use_species_level
ALL_LEVELS="$(find "${WORKDIR}/gunc/out" -name "*all_levels.tsv" | head -n 1 || true)"
test -n "${ALL_LEVELS}"
log "Found GUNC all_levels.tsv: ${ALL_LEVELS}"
# =========================
# 5) Parse outputs and write Table 1 TSV
log "Parse outputs → ${OUT_TSV}"
export SAMPLE WORKDIR OUT_TSV GUNC_ALL_LEVELS="${ALL_LEVELS}"
python - <<'PY'
import csv, os
sample = os.environ["SAMPLE"]
workdir = os.environ["WORKDIR"]
out_tsv = os.environ["OUT_TSV"]
gunc_all_levels = os.environ["GUNC_ALL_LEVELS"]
quast_tsv = os.path.join(workdir, "quast", "report.tsv")
mos_summary = os.path.join(workdir, "map", f"{sample}.mosdepth.summary.txt")
checkm_sum = os.path.join(workdir, "checkm", "checkm_summary.tsv")
def read_quast(path):
with open(path, newline="") as f:
rows = list(csv.reader(f, delimiter="\t"))
asm_idx = 1
d = {}
for r in rows[1:]:
if not r: continue
key = r[0].strip()
val = r[asm_idx].strip() if asm_idx < len(r) else ""
d[key] = val
return d
def read_mosdepth(path):
with open(path) as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("chrom"): continue
parts = line.rstrip("\n").split("\t")
if len(parts) >= 4 and parts[0] == "total":
return parts[3]
return ""
def read_checkm(path, sample):
with open(path, newline="") as f:
reader = csv.DictReader(f, delimiter="\t")
for row in reader:
bid = row.get("Bin Id") or row.get("Bin") or row.get("bin_id") or ""
if bid == sample:
return row
return {}
def read_gunc_all_levels(path):
coarse_lvls = {"kingdom","phylum","class"}
fine_lvls = {"order","family","genus","species"}
coarse, fine = [], []
best_line = None
rank = {"kingdom":0,"phylum":1,"class":2,"order":3,"family":4,"genus":5,"species":6}
best_rank = -1
with open(path, newline="") as f:
reader = csv.DictReader(f, delimiter="\t")
for row in reader:
lvl = (row.get("taxonomic_level") or "").strip()
p = row.get("proportion_genes_retained_in_major_clades") or ""
try:
pv = float(p)
except:
pv = None
if pv is not None:
if lvl in coarse_lvls: coarse.append(pv)
if lvl in fine_lvls: fine.append(pv)
if lvl in rank and rank[lvl] > best_rank:
best_rank = rank[lvl]
best_line = row
coarse_mean = sum(coarse)/len(coarse) if coarse else ""
fine_mean = sum(fine)/len(fine) if fine else ""
contamination_portion = best_line.get("contamination_portion","") if best_line else ""
pass_gunc = best_line.get("pass.GUNC","") if best_line else ""
return coarse_mean, fine_mean, contamination_portion, pass_gunc
qu = read_quast(quast_tsv)
mean_depth = read_mosdepth(mos_summary)
ck = read_checkm(checkm_sum, sample)
coarse_mean, fine_mean, contamination_portion, pass_gunc = read_gunc_all_levels(gunc_all_levels)
header = [
"Sample",
"Genome_length_bp",
"Contigs",
"N50_bp",
"L50",
"GC_percent",
"Mean_depth_x",
"CheckM_completeness_percent",
"CheckM_contamination_percent",
"CheckM_strain_heterogeneity_percent",
"GUNC_coarse_consistency",
"GUNC_fine_consistency",
"GUNC_contamination_portion",
"GUNC_pass"
]
row = [
sample,
qu.get("Total length", ""),
qu.get("# contigs", ""),
qu.get("N50", ""),
qu.get("L50", ""),
qu.get("GC (%)", ""),
mean_depth,
ck.get("Completeness", ""),
ck.get("Contamination", ""),
ck.get("Strain heterogeneity", ""),
f"{coarse_mean:.4f}" if isinstance(coarse_mean, float) else coarse_mean,
f"{fine_mean:.4f}" if isinstance(fine_mean, float) else fine_mean,
contamination_portion,
pass_gunc
]
with open(out_tsv, "w", newline="") as f:
w = csv.writer(f, delimiter="\t")
w.writerow(header)
w.writerow(row)
print(f"OK: wrote {out_tsv}")
PY
log "SUCCESS"
log "Output TSV: ${OUT_TSV}"
log "Workdir: ${WORKDIR}"
log "Logfile: ${LOGFILE}"export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Export a comprehensive Excel workbook from a Table1 pipeline workdir.
Python 3.6 compatible (no PEP604 unions, no builtin generics).
Requires: openpyxl
Sheets (as available):
- Summary
- Table1 (if Table1_*.tsv exists)
- QUAST_report (report.tsv)
- QUAST_metrics (metric/value)
- Mosdepth_summary (*.mosdepth.summary.txt)
- CheckM (checkm_summary.tsv)
- GUNC_* (all .tsv under gunc/out)
- File_Inventory (relative path, size, mtime; optional md5 for small files)
- Run_log_preview (head/tail of latest log under workdir/logs or workdir/*/logs)
"""
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import csv
import hashlib
import os
import sys
import time
from pathlib import Path
try:
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
except ImportError:
sys.stderr.write("ERROR: openpyxl is required. Install with:\n"
" conda install -c conda-forge openpyxl\n")
raise
MAX_XLSX_ROWS = 1048576
def safe_sheet_name(name, used):
# Excel: <=31 chars, cannot contain: : \ / ? * [ ]
bad = r'[:\\/?*\[\]]'
base = name.strip() or "Sheet"
base = __import__("re").sub(bad, "_", base)
base = base[:31]
if base not in used:
used.add(base)
return base
# make unique with suffix
for i in range(2, 1000):
suffix = "_%d" % i
cut = 31 - len(suffix)
candidate = (base[:cut] + suffix)
if candidate not in used:
used.add(candidate)
return candidate
raise RuntimeError("Too many duplicate sheet names for base=%s" % base)
def autosize(ws, max_width=60):
for col in ws.columns:
max_len = 0
col_letter = get_column_letter(col[0].column)
for cell in col:
v = cell.value
if v is None:
continue
s = str(v)
if len(s) > max_len:
max_len = len(s)
ws.column_dimensions[col_letter].width = min(max_width, max(10, max_len + 2))
def write_table(ws, header, rows, max_rows=None):
if header:
ws.append(header)
count = 0
for r in rows:
ws.append(r)
count += 1
if max_rows is not None and count >= max_rows:
break
def read_tsv(path, max_rows=None):
header = []
rows = []
with path.open("r", newline="") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f, delimiter="\t")
for i, r in enumerate(reader):
if i == 0:
header = r
continue
rows.append(r)
if max_rows is not None and len(rows) >= max_rows:
break
return header, rows
def read_text_table(path, max_rows=None):
# for mosdepth summary (tsv with header)
return read_tsv(path, max_rows=max_rows)
def md5_file(path, chunk=1024*1024):
h = hashlib.md5()
with path.open("rb") as f:
while True:
b = f.read(chunk)
if not b:
break
h.update(b)
return h.hexdigest()
def find_latest_log(workdir):
candidates = []
# common locations
for p in [workdir / "logs", workdir / "log", workdir / "Logs"]:
if p.exists():
candidates.extend(p.glob("*.log"))
# nested logs
candidates.extend(workdir.glob("**/logs/*.log"))
if not candidates:
return None
candidates.sort(key=lambda x: x.stat().st_mtime, reverse=True)
return candidates[0]
def add_summary_sheet(wb, used, info_items):
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("Summary", used))
ws.append(["Key", "Value"])
for k, v in info_items:
ws.append([k, v])
autosize(ws)
def add_log_preview(wb, used, log_path, head_n=80, tail_n=120):
if log_path is None or not log_path.exists():
return
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("Run_log_preview", used))
ws.append(["Log path", str(log_path)])
ws.append([])
lines = log_path.read_text(errors="replace").splitlines()
ws.append(["--- HEAD (%d) ---" % head_n])
for line in lines[:head_n]:
ws.append([line])
ws.append([])
ws.append(["--- TAIL (%d) ---" % tail_n])
for line in lines[-tail_n:]:
ws.append([line])
ws.column_dimensions["A"].width = 120
def add_file_inventory(wb, used, workdir, do_md5=True, md5_max_bytes=200*1024*1024, max_rows=None):
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("File_Inventory", used))
ws.append(["relative_path", "size_bytes", "mtime_iso", "md5(optional)"])
count = 0
for p in sorted(workdir.rglob("*")):
if p.is_dir():
continue
rel = str(p.relative_to(workdir))
st = p.stat()
mtime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(st.st_mtime))
md5 = ""
if do_md5 and st.st_size <= md5_max_bytes:
try:
md5 = md5_file(p)
except Exception:
md5 = "ERROR"
ws.append([rel, st.st_size, mtime, md5])
count += 1
if max_rows is not None and count >= max_rows:
break
autosize(ws, max_width=80)
def add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, name, path, max_rows=None):
header, rows = read_tsv(path, max_rows=max_rows)
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name(name, used))
write_table(ws, header, rows, max_rows=max_rows)
autosize(ws, max_width=80)
def add_quast_metrics_sheet(wb, used, quast_report_tsv):
header, rows = read_tsv(quast_report_tsv, max_rows=None)
if not header or len(header) < 2:
return
asm_name = header[1]
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("QUAST_metrics", used))
ws.append(["Metric", asm_name])
for r in rows:
if not r:
continue
metric = r[0]
val = r[1] if len(r) > 1 else ""
ws.append([metric, val])
autosize(ws, max_width=80)
def main():
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("--workdir", required=True, help="workdir produced by pipeline (e.g., table1_GE11174_work)")
ap.add_argument("--out", required=True, help="output .xlsx")
ap.add_argument("--sample", default="", help="sample name for summary")
ap.add_argument("--max-rows", type=int, default=200000, help="max rows per large sheet")
ap.add_argument("--no-md5", action="store_true", help="skip md5 calculation in File_Inventory")
args = ap.parse_args()
workdir = Path(args.workdir).resolve()
out = Path(args.out).resolve()
if not workdir.exists():
sys.stderr.write("ERROR: workdir not found: %s\n" % workdir)
sys.exit(2)
wb = Workbook()
# remove default sheet
wb.remove(wb.active)
used = set()
# Summary info
info = [
("sample", args.sample or ""),
("workdir", str(workdir)),
("generated_at", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")),
("python", sys.version.replace("\n", " ")),
("openpyxl", __import__("openpyxl").__version__),
]
add_summary_sheet(wb, used, info)
# Table1 TSV (try common names)
table1_candidates = list(workdir.glob("Table1_*.tsv")) + list(workdir.glob("*.tsv"))
# Prefer Table1_*.tsv in workdir root
table1_path = None
for p in table1_candidates:
if p.name.startswith("Table1_") and p.suffix == ".tsv":
table1_path = p
break
if table1_path is None:
# maybe created in cwd, not inside workdir; try alongside workdir
parent = workdir.parent
for p in parent.glob("Table1_*.tsv"):
if args.sample and args.sample in p.name:
table1_path = p
break
if table1_path is None and list(parent.glob("Table1_*.tsv")):
table1_path = sorted(parent.glob("Table1_*.tsv"))[0]
if table1_path is not None and table1_path.exists():
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, "Table1", table1_path, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# QUAST
quast_report = workdir / "quast" / "report.tsv"
if quast_report.exists():
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, "QUAST_report", quast_report, max_rows=args.max_rows)
add_quast_metrics_sheet(wb, used, quast_report)
# Mosdepth summary
for p in sorted((workdir / "map").glob("*.mosdepth.summary.txt")):
# mosdepth summary is TSV-like
name = "Mosdepth_" + p.stem.replace(".mosdepth.summary", "")
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, name[:31], p, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# CheckM
checkm_sum = workdir / "checkm" / "checkm_summary.tsv"
if checkm_sum.exists():
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, "CheckM", checkm_sum, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# GUNC outputs (all TSV under gunc/out)
gunc_out = workdir / "gunc" / "out"
if gunc_out.exists():
for p in sorted(gunc_out.rglob("*.tsv")):
rel = str(p.relative_to(gunc_out))
sheet = "GUNC_" + rel.replace("/", "_").replace("\\", "_").replace(".tsv", "")
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, sheet[:31], p, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# Log preview
latest_log = find_latest_log(workdir)
add_log_preview(wb, used, latest_log)
# File inventory
add_file_inventory(
wb, used, workdir,
do_md5=(not args.no_md5),
md5_max_bytes=200*1024*1024,
max_rows=args.max_rows
)
# Save
out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
wb.save(str(out))
print("OK: wrote %s" % out)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -Eeuo pipefail
# -------- user inputs --------
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-bengal3_ac3}"
ASM="${ASM:-GE11174.fasta}"
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-GE11174}"
OUTDIR="${OUTDIR:-resistome_virulence_${SAMPLE}}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-16}"
# thresholds (set to 0/0 if you truly want ABRicate defaults)
MINID="${MINID:-90}"
MINCOV="${MINCOV:-60}"
# ----------------------------
log(){ echo "[$(date +'%F %T')] $*" >&2; }
need_cmd(){ command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1; }
activate_env() {
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
}
main(){
activate_env
mkdir -p "${OUTDIR}"/{raw,amr,virulence,card,tmp}
log "Env: ${ENV_NAME}"
log "ASM: ${ASM}"
log "Sample: ${SAMPLE}"
log "Outdir: ${OUTDIR}"
log "ABRicate thresholds: MINID=${MINID} MINCOV=${MINCOV}"
log "ABRicate DB list:"
abricate --list | egrep -i "vfdb|resfinder|megares|card" || true
# Make sure indices exist
log "Running abricate --setupdb (safe even if already done)..."
abricate --setupdb
# ---- ABRicate AMR DBs ----
log "Running ABRicate: ResFinder"
abricate --db resfinder --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: MEGARes"
abricate --db megares --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
# ---- Virulence (VFDB) ----
log "Running ABRicate: VFDB"
abricate --db vfdb --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
# ---- CARD: prefer RGI if available, else ABRicate card ----
CARD_MODE="ABRicate"
if need_cmd rgi; then
log "RGI found. Trying RGI (CARD) ..."
set +e
rgi main --input_sequence "${ASM}" --output_file "${OUTDIR}/card/${SAMPLE}.rgi" --input_type contig --num_threads "${THREADS}"
rc=$?
set -e
if [[ $rc -eq 0 ]]; then
CARD_MODE="RGI"
else
log "RGI failed (likely CARD data not installed). Falling back to ABRicate card."
fi
fi
if [[ "${CARD_MODE}" == "ABRicate" ]]; then
log "Running ABRicate: CARD"
abricate --db card --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
fi
# ---- Build deduplicated tables ----
log "Creating deduplicated AMR/VFDB tables..."
export OUTDIR SAMPLE CARD_MODE
python - <<'PY'
import os, re
from pathlib import Path
import pandas as pd
from io import StringIO
outdir = Path(os.environ["OUTDIR"])
sample = os.environ["SAMPLE"]
card_mode = os.environ["CARD_MODE"]
def read_abricate_tab(path: Path, source: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
if not path.exists() or path.stat().st_size == 0:
return pd.DataFrame()
lines=[]
with path.open("r", errors="replace") as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("#") or not line.strip():
continue
lines.append(line)
if not lines:
return pd.DataFrame()
df = pd.read_csv(StringIO("".join(lines)), sep="\t", dtype=str)
df.insert(0, "Source", source)
return df
def to_num(s):
try:
return float(str(s).replace("%",""))
except:
return None
def normalize_abricate(df: pd.DataFrame, dbname: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
if df.empty:
return pd.DataFrame(columns=[
"Source","Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"
])
# Column names vary slightly; handle common ones
gene = "GENE" if "GENE" in df.columns else None
prod = "PRODUCT" if "PRODUCT" in df.columns else None
acc = "ACCESSION" if "ACCESSION" in df.columns else None
contig = "SEQUENCE" if "SEQUENCE" in df.columns else ("CONTIG" if "CONTIG" in df.columns else None)
start = "START" if "START" in df.columns else None
end = "END" if "END" in df.columns else None
strand= "STRAND" if "STRAND" in df.columns else None
pid = "%IDENTITY" if "%IDENTITY" in df.columns else ("% Identity" if "% Identity" in df.columns else None)
pcv = "%COVERAGE" if "%COVERAGE" in df.columns else ("% Coverage" if "% Coverage" in df.columns else None)
out = pd.DataFrame()
out["Source"] = df["Source"]
out["Database"] = dbname
out["Gene"] = df[gene] if gene else ""
out["Product"] = df[prod] if prod else ""
out["Accession"] = df[acc] if acc else ""
out["Contig"] = df[contig] if contig else ""
out["Start"] = df[start] if start else ""
out["End"] = df[end] if end else ""
out["Strand"] = df[strand] if strand else ""
out["Pct_Identity"] = df[pid] if pid else ""
out["Pct_Coverage"] = df[pcv] if pcv else ""
return out
def dedup_best(df: pd.DataFrame, key_cols):
"""Keep best hit per key by highest identity, then coverage, then longest span."""
if df.empty:
return df
# numeric helpers
df = df.copy()
df["_pid"] = df["Pct_Identity"].map(to_num)
df["_pcv"] = df["Pct_Coverage"].map(to_num)
def span(row):
try:
return abs(int(row["End"]) - int(row["Start"])) + 1
except:
return 0
df["_span"] = df.apply(span, axis=1)
# sort best-first
df = df.sort_values(by=["_pid","_pcv","_span"], ascending=[False,False,False], na_position="last")
df = df.drop_duplicates(subset=key_cols, keep="first")
df = df.drop(columns=["_pid","_pcv","_span"])
return df
# ---------- AMR inputs ----------
amr_frames = []
# ResFinder (often 0 hits; still okay)
resfinder = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.resfinder.tab"
df = read_abricate_tab(resfinder, "ABRicate")
amr_frames.append(normalize_abricate(df, "ResFinder"))
# MEGARes
megares = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.megares.tab"
df = read_abricate_tab(megares, "ABRicate")
amr_frames.append(normalize_abricate(df, "MEGARes"))
# CARD: RGI or ABRicate
if card_mode == "RGI":
# Try common RGI tab outputs
prefix = outdir / "card" / f"{sample}.rgi"
rgi_tab = None
for ext in [".txt",".tab",".tsv"]:
p = Path(str(prefix) + ext)
if p.exists() and p.stat().st_size > 0:
rgi_tab = p
break
if rgi_tab is not None:
rgi = pd.read_csv(rgi_tab, sep="\t", dtype=str)
out = pd.DataFrame()
out["Source"] = "RGI"
out["Database"] = "CARD"
# Prefer ARO_name/Best_Hit_ARO if present
out["Gene"] = rgi["ARO_name"] if "ARO_name" in rgi.columns else (rgi["Best_Hit_ARO"] if "Best_Hit_ARO" in rgi.columns else "")
out["Product"] = rgi["ARO_name"] if "ARO_name" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Accession"] = rgi["ARO_accession"] if "ARO_accession" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Contig"] = rgi["Sequence"] if "Sequence" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Start"] = rgi["Start"] if "Start" in rgi.columns else ""
out["End"] = rgi["Stop"] if "Stop" in rgi.columns else (rgi["End"] if "End" in rgi.columns else "")
out["Strand"] = rgi["Orientation"] if "Orientation" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Pct_Identity"] = rgi["% Identity"] if "% Identity" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Pct_Coverage"] = rgi["% Coverage"] if "% Coverage" in rgi.columns else ""
amr_frames.append(out)
else:
card = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.card.tab"
df = read_abricate_tab(card, "ABRicate")
amr_frames.append(normalize_abricate(df, "CARD"))
amr_all = pd.concat([x for x in amr_frames if not x.empty], ignore_index=True) if any(not x.empty for x in amr_frames) else pd.DataFrame(
columns=["Source","Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"]
)
# Deduplicate within each (Database,Gene) – this is usually what you want for manuscript tables
amr_dedup = dedup_best(amr_all, key_cols=["Database","Gene"])
# Sort nicely
if not amr_dedup.empty:
amr_dedup = amr_dedup.sort_values(["Database","Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
amr_out = outdir / "Table_AMR_genes_dedup.tsv"
amr_dedup.to_csv(amr_out, sep="\t", index=False)
# ---------- Virulence (VFDB) ----------
vfdb = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.vfdb.tab"
vf = read_abricate_tab(vfdb, "ABRicate")
vf_norm = normalize_abricate(vf, "VFDB")
# Dedup within (Gene) for VFDB (or use Database,Gene; Database constant)
vf_dedup = dedup_best(vf_norm, key_cols=["Gene"]) if not vf_norm.empty else vf_norm
if not vf_dedup.empty:
vf_dedup = vf_dedup.sort_values(["Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
vf_out = outdir / "Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv"
vf_dedup.to_csv(vf_out, sep="\t", index=False)
print("OK wrote:")
print(" ", amr_out)
print(" ", vf_out)
PY
log "Done."
log "Outputs:"
log " ${OUTDIR}/Table_AMR_genes_dedup.tsv"
log " ${OUTDIR}/Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv"
log "Raw:"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.*.tab"
}
mainrun_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -Eeuo pipefail
# ------------------- USER SETTINGS -------------------
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-bengal3_ac3}"
ASM="${ASM:-GE11174.fasta}" # input assembly fasta
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-GE11174}"
OUTDIR="${OUTDIR:-resistome_virulence_${SAMPLE}}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-16}"
# ABRicate thresholds
# If you want your earlier "35 genes" behavior, use MINID=70 MINCOV=50.
# If you want stricter: e.g. MINID=80 MINCOV=70.
MINID="${MINID:-70}"
MINCOV="${MINCOV:-50}"
# -----------------------------------------------------
ts(){ date +"%F %T"; }
log(){ echo "[$(ts)] $*" >&2; }
on_err(){
local ec=$?
log "ERROR: failed (exit=${ec}) at line ${BASH_LINENO[0]}: ${BASH_COMMAND}"
exit $ec
}
trap on_err ERR
need_cmd(){ command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1; }
activate_env() {
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
}
main(){
activate_env
log "Env: ${ENV_NAME}"
log "ASM: ${ASM}"
log "Sample: ${SAMPLE}"
log "Outdir: ${OUTDIR}"
log "Threads: ${THREADS}"
log "ABRicate thresholds: MINID=${MINID} MINCOV=${MINCOV}"
mkdir -p "${OUTDIR}"/{raw,logs}
# Save full log
LOGFILE="${OUTDIR}/logs/run_$(date +'%F_%H%M%S').log"
exec > >(tee -a "${LOGFILE}") 2>&1
log "Tool versions:"
abricate --version || true
abricate-get_db --help | head -n 5 || true
log "ABRicate DB list (selected):"
abricate --list | egrep -i "vfdb|resfinder|megares|card" || true
log "Indexing ABRicate databases (safe to re-run)..."
abricate --setupdb
# ---------------- Run ABRicate ----------------
log "Running ABRicate: MEGARes"
abricate --db megares --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: CARD"
abricate --db card --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: ResFinder"
abricate --db resfinder --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: VFDB"
abricate --db vfdb --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
# --------------- Build tables -----------------
export OUTDIR SAMPLE
export MEGARES_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
export CARD_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
export RESFINDER_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
export VFDB_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
export AMR_OUT="${OUTDIR}/Table_AMR_genes_one_per_gene.tsv"
export VIR_OUT="${OUTDIR}/Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv"
export STATUS_OUT="${OUTDIR}/Table_DB_hit_counts.tsv"
log "Generating deduplicated tables..."
python - <<'PY'
import os
import pandas as pd
from pathlib import Path
megares_tab = Path(os.environ["MEGARES_TAB"])
card_tab = Path(os.environ["CARD_TAB"])
resfinder_tab = Path(os.environ["RESFINDER_TAB"])
vfdb_tab = Path(os.environ["VFDB_TAB"])
amr_out = Path(os.environ["AMR_OUT"])
vir_out = Path(os.environ["VIR_OUT"])
status_out = Path(os.environ["STATUS_OUT"])
def read_abricate(path: Path) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Parse ABRicate .tab where header line starts with '#FILE'."""
if (not path.exists()) or path.stat().st_size == 0:
return pd.DataFrame()
header = None
rows = []
with path.open("r", errors="replace") as f:
for line in f:
if not line.strip():
continue
if line.startswith("#FILE"):
header = line.lstrip("#").rstrip("\n").split("\t")
continue
if line.startswith("#"):
continue
rows.append(line.rstrip("\n").split("\t"))
if header is None:
return pd.DataFrame()
if not rows:
return pd.DataFrame(columns=header)
return pd.DataFrame(rows, columns=header)
def normalize(df: pd.DataFrame, dbname: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
cols_out = ["Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"]
if df is None or df.empty:
return pd.DataFrame(columns=cols_out)
out = pd.DataFrame({
"Database": dbname,
"Gene": df.get("GENE",""),
"Product": df.get("PRODUCT",""),
"Accession": df.get("ACCESSION",""),
"Contig": df.get("SEQUENCE",""),
"Start": df.get("START",""),
"End": df.get("END",""),
"Strand": df.get("STRAND",""),
"Pct_Identity": pd.to_numeric(df.get("%IDENTITY",""), errors="coerce"),
"Pct_Coverage": pd.to_numeric(df.get("%COVERAGE",""), errors="coerce"),
})
return out[cols_out]
def best_hit_dedup(df: pd.DataFrame, key_cols):
"""Keep best hit by highest identity, then coverage, then alignment length."""
if df.empty:
return df
d = df.copy()
d["Start_i"] = pd.to_numeric(d["Start"], errors="coerce").fillna(0).astype(int)
d["End_i"] = pd.to_numeric(d["End"], errors="coerce").fillna(0).astype(int)
d["Len"] = (d["End_i"] - d["Start_i"]).abs() + 1
d = d.sort_values(["Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage","Len"], ascending=[False,False,False])
d = d.drop_duplicates(subset=key_cols, keep="first")
return d.drop(columns=["Start_i","End_i","Len"])
def count_hits(path: Path) -> int:
if not path.exists():
return 0
n = 0
with path.open() as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("#") or not line.strip():
continue
n += 1
return n
# -------- load + normalize --------
parts = []
for dbname, p in [("MEGARes", megares_tab), ("CARD", card_tab), ("ResFinder", resfinder_tab)]:
df = read_abricate(p)
parts.append(normalize(df, dbname))
amr_all = pd.concat([x for x in parts if not x.empty], ignore_index=True) if any(not x.empty for x in parts) else pd.DataFrame(
columns=["Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"]
)
# remove empty genes
amr_all = amr_all[amr_all["Gene"].astype(str).str.len() > 0].copy()
# best per (Database,Gene)
amr_db_gene = best_hit_dedup(amr_all, ["Database","Gene"]) if not amr_all.empty else amr_all
# one row per Gene overall, priority: CARD > ResFinder > MEGARes
priority = {"CARD": 0, "ResFinder": 1, "MEGARes": 2}
if not amr_db_gene.empty:
amr_db_gene["prio"] = amr_db_gene["Database"].map(priority).fillna(9).astype(int)
amr_one = amr_db_gene.sort_values(
["Gene","prio","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"],
ascending=[True, True, False, False]
)
amr_one = amr_one.drop_duplicates(["Gene"], keep="first").drop(columns=["prio"])
amr_one = amr_one.sort_values(["Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
else:
amr_one = amr_db_gene
amr_out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
amr_one.to_csv(amr_out, sep="\t", index=False)
# -------- VFDB --------
vf = normalize(read_abricate(vfdb_tab), "VFDB")
vf = vf[vf["Gene"].astype(str).str.len() > 0].copy()
vf_one = best_hit_dedup(vf, ["Gene"]) if not vf.empty else vf
if not vf_one.empty:
vf_one = vf_one.sort_values(["Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
vir_out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
vf_one.to_csv(vir_out, sep="\t", index=False)
# -------- status counts --------
status = pd.DataFrame([
{"Database":"MEGARes", "Hit_lines": count_hits(megares_tab), "File": str(megares_tab)},
{"Database":"CARD", "Hit_lines": count_hits(card_tab), "File": str(card_tab)},
{"Database":"ResFinder", "Hit_lines": count_hits(resfinder_tab), "File": str(resfinder_tab)},
{"Database":"VFDB", "Hit_lines": count_hits(vfdb_tab), "File": str(vfdb_tab)},
])
status_out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
status.to_csv(status_out, sep="\t", index=False)
print("OK wrote:")
print(" ", amr_out, "rows=", len(amr_one))
print(" ", vir_out, "rows=", len(vf_one))
print(" ", status_out)
PY
log "Finished."
log "Main outputs:"
log " ${AMR_OUT}"
log " ${VIR_OUT}"
log " ${STATUS_OUT}"
log "Raw ABRicate outputs:"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
log "Log:"
log " ${LOGFILE}"
}
mainresolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import csv
import os
import re
import sys
import time
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple
from Bio import Entrez
# REQUIRED by NCBI policy
Entrez.email = os.environ.get("NCBI_EMAIL", "your.email@example.com")
# Be nice to NCBI
ENTREZ_DELAY_SEC = float(os.environ.get("ENTREZ_DELAY_SEC", "0.34"))
LEVEL_RANK = {
"Complete Genome": 0,
"Chromosome": 1,
"Scaffold": 2,
"Contig": 3,
# sometimes NCBI uses slightly different strings:
"complete genome": 0,
"chromosome": 1,
"scaffold": 2,
"contig": 3,
}
def level_rank(level: str) -> int:
return LEVEL_RANK.get(level.strip(), 99)
def is_refseq(accession: str) -> bool:
return accession.startswith("GCF_")
@dataclass
class AssemblyHit:
assembly_uid: str
assembly_accession: str # GCF_... or GCA_...
organism: str
strain: str
assembly_level: str
refseq_category: str
submitter: str
ftp_path: str
def entrez_search_assembly(term: str, retmax: int = 50) -> List[str]:
"""Return Assembly UIDs matching term."""
h = Entrez.esearch(db="assembly", term=term, retmax=str(retmax))
rec = Entrez.read(h)
h.close()
time.sleep(ENTREZ_DELAY_SEC)
return rec.get("IdList", [])
def entrez_esummary_assembly(uids: List[str]) -> List[AssemblyHit]:
"""Fetch assembly summary records for given UIDs."""
if not uids:
return []
h = Entrez.esummary(db="assembly", id=",".join(uids), report="full")
rec = Entrez.read(h)
h.close()
time.sleep(ENTREZ_DELAY_SEC)
hits: List[AssemblyHit] = []
docs = rec.get("DocumentSummarySet", {}).get("DocumentSummary", [])
for d in docs:
# Some fields can be missing
acc = str(d.get("AssemblyAccession", "")).strip()
org = str(d.get("Organism", "")).strip()
level = str(d.get("AssemblyStatus", "")).strip() or str(d.get("AssemblyLevel", "")).strip()
# NCBI uses "AssemblyStatus" sometimes, "AssemblyLevel" other times;
# in practice AssemblyStatus often equals "Complete Genome"/"Chromosome"/...
if not level:
level = str(d.get("AssemblyLevel", "")).strip()
strain = str(d.get("Biosample", "")).strip()
# Strain is not always in a clean field. Try "Sub_value" in Meta, or parse Submitter/Title.
# We'll try a few common places:
title = str(d.get("AssemblyName", "")).strip()
submitter = str(d.get("SubmitterOrganization", "")).strip()
refcat = str(d.get("RefSeq_category", "")).strip()
ftp = str(d.get("FtpPath_RefSeq", "")).strip() or str(d.get("FtpPath_GenBank", "")).strip()
hits.append(
AssemblyHit(
assembly_uid=str(d.get("Uid", "")),
assembly_accession=acc,
organism=org,
strain=strain,
assembly_level=level,
refseq_category=refcat,
submitter=submitter,
ftp_path=ftp,
)
)
return hits
def best_hit(hits: List[AssemblyHit]) -> Optional[AssemblyHit]:
"""Pick best hit by level (Complete>Chromosome>...), prefer RefSeq, then prefer representative/reference."""
if not hits:
return None
def key(h: AssemblyHit) -> Tuple[int, int, int, str]:
# lower is better
lvl = level_rank(h.assembly_level)
ref = 0 if is_refseq(h.assembly_accession) else 1
# prefer reference/representative if present
cat = (h.refseq_category or "").lower()
rep = 0
if "reference" in cat:
rep = 0
elif "representative" in cat:
rep = 1
else:
rep = 2
# tie-breaker: accession string (stable)
return (lvl, ref, rep, h.assembly_accession)
return sorted(hits, key=key)[0]
def relaxed_fallback_terms(organism: str, strain_tokens: List[str]) -> List[str]:
"""
Build fallback search terms:
1) organism + strain tokens
2) organism only (species-only)
3) genus-only (if species fails)
"""
terms = []
# 1) Full term: organism + strain tokens
if strain_tokens:
t = f'"{organism}"[Organism] AND (' + " OR ".join(f'"{s}"[All Fields]' for s in strain_tokens) + ")"
terms.append(t)
# 2) Species only
terms.append(f'"{organism}"[Organism]')
# 3) Genus only
genus = organism.split()[0]
terms.append(f'"{genus}"[Organism]')
return terms
def resolve_one(label: str, organism: str, strain_tokens: List[str], retmax: int = 80) -> Tuple[str, Optional[AssemblyHit], str]:
"""
Returns:
- selected accession or "NA"
- selected hit (optional)
- which query term matched
"""
for term in relaxed_fallback_terms(organism, strain_tokens):
uids = entrez_search_assembly(term, retmax=retmax)
hits = entrez_esummary_assembly(uids)
chosen = best_hit(hits)
if chosen and chosen.assembly_accession:
return chosen.assembly_accession, chosen, term
return "NA", None, ""
def parse_targets_tsv(path: str) -> List[Tuple[str, str, List[str]]]:
"""
Input TSV format:
label organism strain_tokens
where strain_tokens is a semicolon-separated list, e.g. "FRB97;FRB 97"
"""
rows = []
with open(path, newline="") as f:
r = csv.DictReader(f, delimiter="\t")
for row in r:
label = row["label"].strip()
org = row["organism"].strip()
tokens = [x.strip() for x in row.get("strain_tokens", "").split(";") if x.strip()]
rows.append((label, org, tokens))
return rows
def main():
if len(sys.argv) < 3:
print("Usage: resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py targets.tsv out.tsv", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(2)
targets_tsv = sys.argv[1]
out_tsv = sys.argv[2]
targets = parse_targets_tsv(targets_tsv)
with open(out_tsv, "w", newline="") as f:
w = csv.writer(f, delimiter="\t")
w.writerow(["label", "best_accession", "assembly_level", "refseq_category", "organism", "query_used"])
for label, org, tokens in targets:
acc, hit, term = resolve_one(label, org, tokens)
if hit:
w.writerow([label, acc, hit.assembly_level, hit.refseq_category, hit.organism, term])
print(f"[OK] {label} -> {acc} ({hit.assembly_level})")
else:
w.writerow([label, "NA", "", "", org, ""])
print(f"[WARN] {label} -> NA (no assemblies found)")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
###############################################################################
# Core-genome phylogeny pipeline (genome-wide; no 16S/MLST):
#
# Uses existing conda env prefix:
# ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3
#
# Inputs:
# - resolved_accessions.tsv
# - REF.fasta
#
# Also consider these 4 accessions (duplicates removed):
# GCF_002291425.1, GCF_047901425.1, GCF_004342245.1, GCA_032062225.1
#
# Robustness:
# - Conda activation hook may reference JAVA_HOME under set -u (handled)
# - GFF validation ignores the ##FASTA FASTA block (valid GFF3)
# - FIXED: No more double Roary directories (script no longer pre-creates -f dir)
# Logs go to WORKDIR/logs and are also copied into the final Roary dir.
#
# Outputs:
# ${WORKDIR}/plot/core_tree.pdf
# ${WORKDIR}/plot/core_tree.png
###############################################################################
THREADS="${THREADS:-8}"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR:-work_wgs_tree}"
RESOLVED_TSV="${RESOLVED_TSV:-resolved_accessions.tsv}"
REF_FASTA="${REF_FASTA:-AN6.fasta}"
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3}"
EXTRA_ASSEMBLIES=(
#"GCF_002291425.1"
#"GCF_047901425.1"
#"GCF_004342245.1"
#"GCA_032062225.1"
)
CLUSTERS_K="${CLUSTERS_K:-6}"
MODE="${1:-all}"
log(){ echo "[$(date +'%F %T')] $*" >&2; }
need_cmd(){ command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1; }
activate_existing_env(){
if [[ ! -d "${ENV_NAME}" ]]; then
log "ERROR: ENV_NAME path does not exist: ${ENV_NAME}"
exit 1
fi
conda_base="$(dirname "$(dirname "${ENV_NAME}")")"
if [[ -f "${conda_base}/etc/profile.d/conda.sh" ]]; then
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "${conda_base}/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
else
if need_cmd conda; then
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
else
log "ERROR: cannot find conda.sh and conda is not on PATH."
exit 1
fi
fi
# Avoid "unbound variable" in activation hooks under set -u
export JAVA_HOME="${JAVA_HOME:-}"
log "Activating env: ${ENV_NAME}"
set +u
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
set -u
}
check_dependencies() {
# ---- plot-only mode: only need R (and optionally python) ----
if [[ "${MODE}" == "plot-only" ]]; then
local missing=()
command -v Rscript >/dev/null 2>&1 || missing+=("Rscript")
command -v python >/dev/null 2>&1 || missing+=("python")
if (( ${#missing[@]} )); then
log "ERROR: Missing required tools for plot-only in env: ${ENV_NAME}"
printf ' - %s\n' "${missing[@]}" >&2
exit 1
fi
# Check required R packages (fail early with clear message)
Rscript -e 'pkgs <- c("ggtree","ggplot2","aplot");
miss <- pkgs[!sapply(pkgs, requireNamespace, quietly=TRUE)];
if(length(miss)) stop("Missing R packages: ", paste(miss, collapse=", "))'
return 0
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------
# existing full-pipeline checks continue below...
# (your current prokka/roary/raxml-ng checks stay as-is)
#...
}
prepare_accessions(){
[[ -s "${RESOLVED_TSV}" ]] || { log "ERROR: missing ${RESOLVED_TSV}"; exit 1; }
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/meta"
printf "%s\n" "${EXTRA_ASSEMBLIES[@]}" > "${WORKDIR}/meta/extras.txt"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR}" RESOLVED_TSV="${RESOLVED_TSV}" python - << 'PY'
import os
import pandas as pd
import pathlib
workdir = pathlib.Path(os.environ.get("WORKDIR", "work_wgs_tree"))
resolved_tsv = os.environ.get("RESOLVED_TSV", "resolved_accessions.tsv")
df = pd.read_csv(resolved_tsv, sep="\t")
# Expect columns like: label, best_accession (but be tolerant)
if "best_accession" not in df.columns:
df = df.rename(columns={df.columns[1]:"best_accession"})
if "label" not in df.columns:
df = df.rename(columns={df.columns[0]:"label"})
df = df[["label","best_accession"]].dropna()
df = df[df["best_accession"]!="NA"].copy()
extras_path = workdir/"meta/extras.txt"
extras = [x.strip() for x in extras_path.read_text().splitlines() if x.strip()]
extra_df = pd.DataFrame({"label":[f"EXTRA_{a}" for a in extras], "best_accession": extras})
all_df = pd.concat([df, extra_df], ignore_index=True)
all_df = all_df.drop_duplicates(subset=["best_accession"], keep="first").reset_index(drop=True)
out = workdir/"meta/accessions.tsv"
out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
all_df.to_csv(out, sep="\t", index=False)
print("Final unique genomes:", len(all_df))
print(all_df)
print("Wrote:", out)
PY
}
download_genomes(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi"
while IFS=$'\t' read -r label acc; do
[[ "$label" == "label" ]] && continue
[[ -z "${acc}" ]] && continue
outdir="${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi/${acc}"
if [[ -d "${outdir}" ]]; then
log "Found ${acc}, skipping download"
continue
fi
log "Downloading ${acc}..."
datasets download genome accession "${acc}" --include genome --filename "${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi/${acc}.zip"
unzip -q "${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi/${acc}.zip" -d "${outdir}"
rm -f "${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi/${acc}.zip"
done < "${WORKDIR}/meta/accessions.tsv"
}
collect_fastas(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/fastas"
while IFS=$'\t' read -r label acc; do
[[ "$label" == "label" ]] && continue
[[ -z "${acc}" ]] && continue
fna="$(find "${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi/${acc}" -type f -name "*.fna" | head -n 1 || true)"
[[ -n "${fna}" ]] || { log "ERROR: .fna not found for ${acc}"; exit 1; }
cp -f "${fna}" "${WORKDIR}/fastas/${acc}.fna"
done < "${WORKDIR}/meta/accessions.tsv"
[[ -s "${REF_FASTA}" ]] || { log "ERROR: missing ${REF_FASTA}"; exit 1; }
cp -f "${REF_FASTA}" "${WORKDIR}/fastas/REF.fna"
}
run_prokka(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/prokka" "${WORKDIR}/gffs"
for fna in "${WORKDIR}/fastas/"*.fna; do
base="$(basename "${fna}" .fna)"
outdir="${WORKDIR}/prokka/${base}"
gffout="${WORKDIR}/gffs/${base}.gff"
if [[ -s "${gffout}" ]]; then
log "GFF exists for ${base}, skipping Prokka"
continue
fi
log "Prokka annotating ${base}..."
prokka --outdir "${outdir}" --prefix "${base}" --cpus "${THREADS}" --force "${fna}"
cp -f "${outdir}/${base}.gff" "${gffout}"
done
}
sanitize_and_check_gffs(){
log "Sanity checking GFFs (ignoring ##FASTA section)..."
for gff in "${WORKDIR}/gffs/"*.gff; do
if file "$gff" | grep -qi "CRLF"; then
log "Fixing CRLF -> LF in $(basename "$gff")"
sed -i 's/\r$//' "$gff"
fi
bad=$(awk '
BEGIN{bad=0; in_fasta=0}
/^##FASTA/{in_fasta=1; next}
in_fasta==1{next}
/^#/{next}
NF==0{next}
{
if (split($0,a,"\t")!=9) {bad=1}
}
END{print bad}
' "$gff")
if [[ "$bad" == "1" ]]; then
log "ERROR: GFF feature section not 9-column tab-delimited: $gff"
log "First 5 problematic feature lines (before ##FASTA):"
awk '
BEGIN{in_fasta=0; c=0}
/^##FASTA/{in_fasta=1; next}
in_fasta==1{next}
/^#/{next}
NF==0{next}
{
if (split($0,a,"\t")!=9) {
print
c++
if (c==5) exit
}
}
' "$gff" || true
exit 1
fi
done
}
run_roary(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/meta" "${WORKDIR}/logs"
ts="$(date +%s)"
run_id="${ts}_$$"
ROARY_OUT="${WORKDIR}/roary_${run_id}"
ROARY_STDOUT="${WORKDIR}/logs/roary_${run_id}.stdout.txt"
ROARY_STDERR="${WORKDIR}/logs/roary_${run_id}.stderr.txt"
MARKER="${WORKDIR}/meta/roary_${run_id}.start"
: > "${MARKER}"
log "Running Roary (outdir: ${ROARY_OUT})"
log "Roary logs:"
log " STDOUT: ${ROARY_STDOUT}"
log " STDERR: ${ROARY_STDERR}"
set +e
roary -e --mafft -p "${THREADS}" -cd 95 -i 95 \
-f "${ROARY_OUT}" "${WORKDIR}/gffs/"*.gff \
> "${ROARY_STDOUT}" 2> "${ROARY_STDERR}"
rc=$?
set -e
if [[ "${rc}" -ne 0 ]]; then
log "WARNING: Roary exited non-zero (rc=${rc}). Will check if core alignment was produced anyway."
fi
CORE_ALN="$(find "${WORKDIR}" -maxdepth 2 -type f -name "core_gene_alignment.aln" -newer "${MARKER}" -printf '%T@ %p\n' 2>/dev/null \
| sort -nr | head -n 1 | cut -d' ' -f2- || true)"
if [[ -z "${CORE_ALN}" || ! -s "${CORE_ALN}" ]]; then
log "ERROR: Could not find core_gene_alignment.aln produced by this Roary run under ${WORKDIR}"
log "---- STDERR (head) ----"
head -n 120 "${ROARY_STDERR}" 2>/dev/null || true
log "---- STDERR (tail) ----"
tail -n 120 "${ROARY_STDERR}" 2>/dev/null || true
exit 1
fi
CORE_DIR="$(dirname "${CORE_ALN}")"
cp -f "${ROARY_STDOUT}" "${CORE_DIR}/roary.stdout.txt" || true
cp -f "${ROARY_STDERR}" "${CORE_DIR}/roary.stderr.txt" || true
# >>> IMPORTANT FIX: store ABSOLUTE path <<<
CORE_ALN_ABS="$(readlink -f "${CORE_ALN}")"
log "Using core alignment: ${CORE_ALN_ABS}"
echo "${CORE_ALN_ABS}" > "${WORKDIR}/meta/core_alignment_path.txt"
echo "$(readlink -f "${CORE_DIR}")" > "${WORKDIR}/meta/roary_output_dir.txt"
}
run_raxmlng(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/raxmlng"
CORE_ALN="$(cat "${WORKDIR}/meta/core_alignment_path.txt")"
[[ -s "${CORE_ALN}" ]] || { log "ERROR: core alignment not found or empty: ${CORE_ALN}"; exit 1; }
log "Running RAxML-NG..."
raxml-ng --all \
--msa "${CORE_ALN}" \
--model GTR+G \
--bs-trees 1000 \
--threads "${THREADS}" \
--prefix "${WORKDIR}/raxmlng/core"
}
ensure_r_pkgs(){
Rscript - <<'RS'
need <- c("ape","ggplot2","dplyr","readr","aplot","ggtree")
missing <- need[!vapply(need, requireNamespace, logical(1), quietly=TRUE)]
if (length(missing)) {
message("Missing R packages: ", paste(missing, collapse=", "))
message("Try:")
message(" conda install -c conda-forge -c bioconda r-aplot bioconductor-ggtree r-ape r-ggplot2 r-dplyr r-readr")
quit(status=1)
}
RS
}
plot_tree(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/plot"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR}" python - << 'PY'
import os
import pandas as pd
import pathlib
workdir = pathlib.Path(os.environ.get("WORKDIR", "work_wgs_tree"))
acc = pd.read_csv(workdir/"meta/accessions.tsv", sep="\t")
g = (acc.groupby("best_accession")["label"]
.apply(lambda x: "; ".join(sorted(set(map(str, x)))))
.reset_index())
g["display"] = g.apply(lambda r: f'{r["label"]} ({r["best_accession"]})', axis=1)
labels = g.rename(columns={"best_accession":"sample"})[["sample","display"]]
# Add REF
labels = pd.concat([labels, pd.DataFrame([{"sample":"REF","display":"REF"}])], ignore_index=True)
out = workdir/"plot/labels.tsv"
out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
labels.to_csv(out, sep="\t", index=False)
print("Wrote:", out)
PY
cat > "${WORKDIR}/plot/plot_tree.R" << 'RS'
suppressPackageStartupMessages({
library(ape); library(ggplot2); library(ggtree); library(dplyr); library(readr)
})
args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly=TRUE)
tree_in <- args[1]; labels_tsv <- args[2]; k <- as.integer(args[3])
out_pdf <- args[4]; out_png <- args[5]
tr <- read.tree(tree_in)
lab <- read_tsv(labels_tsv, show_col_types=FALSE)
tipmap <- setNames(lab$display, lab$sample)
tr$tip.label <- ifelse(tr$tip.label %in% names(tipmap), tipmap[tr$tip.label], tr$tip.label)
hc <- as.hclust.phylo(tr)
grp <- cutree(hc, k=k)
grp_df <- tibble(tip=names(grp), clade=paste0("Clade_", grp))
p <- ggtree(tr, layout="rectangular") %<+% grp_df +
aes(color=clade) +
geom_tree(linewidth=0.9) +
geom_tippoint(aes(color=clade), size=2.3) +
geom_tiplab(aes(color=clade), size=3.1, align=TRUE,
linetype="dotted", linesize=0.35, offset=0.02) +
theme_tree2() +
theme(legend.position="right", legend.title=element_blank(),
plot.margin=margin(8,18,8,8))
# + geom_treescale(x=0, y=0, width=0.01, fontsize=3)
# ---- Manual scale bar (fixed label "0.01") ----
scale_x <- 0
scale_y <- 0
scale_w <- 0.01
p <- p +
annotate("segment",
x = scale_x, xend = scale_x + scale_w,
y = scale_y, yend = scale_y,
linewidth = 0.6) +
annotate("text",
x = scale_x + scale_w/2,
y = scale_y - 0.6,
label = "0.01",
size = 3)
# ----------------------------------------------
ggsave(out_pdf, p, width=9, height=6.5, device="pdf")
ggsave(out_png, p, width=9, height=6.5, dpi=300)
RS
Rscript "${WORKDIR}/plot/plot_tree.R" \
"${WORKDIR}/raxmlng/core.raxml.support" \
"${WORKDIR}/plot/labels.tsv" \
"${CLUSTERS_K}" \
"${WORKDIR}/plot/core_tree.pdf" \
"${WORKDIR}/plot/core_tree.png"
log "Plot written:"
log " ${WORKDIR}/plot/core_tree.pdf"
log " ${WORKDIR}/plot/core_tree.png"
}
main(){
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}"
activate_existing_env
check_dependencies
if [[ "${MODE}" == "plot-only" ]]; then
log "Running plot-only mode"
plot_tree
log "DONE."
exit 0
fi
log "1) Prepare unique accessions"
prepare_accessions
log "2) Download genomes"
download_genomes
log "3) Collect FASTAs (+ REF)"
collect_fastas
log "4) Prokka"
run_prokka
log "4b) GFF sanity check"
sanitize_and_check_gffs
log "5) Roary"
run_roary
log "6) RAxML-NG"
run_raxmlng
#log "6b) Check R packages"
#ensure_r_pkgs
log "7) Plot"
plot_tree
log "DONE."
}
main "$@"regenerate_labels.sh
python - <<'PY'
import json, re
from pathlib import Path
import pandas as pd
WORKDIR = Path("work_wgs_tree")
ACC_TSV = WORKDIR / "meta/accessions.tsv"
GENOMES_DIR = WORKDIR / "genomes_ncbi"
OUT = WORKDIR / "plot/labels.tsv"
def first_existing(paths):
for p in paths:
if p and Path(p).exists():
return Path(p)
return None
def find_metadata_files(acc_dir: Path):
# NCBI Datasets layouts vary by version; search broadly
candidates = []
for pat in [
"**/assembly_data_report.jsonl",
"**/data_report.jsonl",
"**/dataset_catalog.json",
"**/*assembly_report*.txt",
"**/*assembly_report*.tsv",
]:
candidates += list(acc_dir.glob(pat))
# de-dup, keep stable order
seen = set()
uniq = []
for p in candidates:
if p.as_posix() not in seen:
uniq.append(p)
seen.add(p.as_posix())
return uniq
def parse_jsonl_for_name_and_strain(p: Path):
# assembly_data_report.jsonl / data_report.jsonl: first JSON object usually has organism info
try:
with p.open() as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
obj = json.loads(line)
# Try common fields
# organismName may appear as:
# obj["organism"]["organismName"] or obj["organismName"]
org = None
strain = None
if isinstance(obj, dict):
if "organism" in obj and isinstance(obj["organism"], dict):
org = obj["organism"].get("organismName") or obj["organism"].get("taxName")
# isolate/strain can hide in infraspecificNames or isolate/strain keys
infra = obj["organism"].get("infraspecificNames") or {}
if isinstance(infra, dict):
strain = infra.get("strain") or infra.get("isolate")
strain = strain or obj["organism"].get("strain") or obj["organism"].get("isolate")
org = org or obj.get("organismName") or obj.get("taxName")
# Sometimes isolate/strain is nested elsewhere
if not strain:
# assemblyInfo / assembly / sampleInfo patterns
for key in ["assemblyInfo", "assembly", "sampleInfo", "biosample"]:
if key in obj and isinstance(obj[key], dict):
d = obj[key]
strain = strain or d.get("strain") or d.get("isolate")
infra = d.get("infraspecificNames")
if isinstance(infra, dict):
strain = strain or infra.get("strain") or infra.get("isolate")
if org:
return org, strain
except Exception:
pass
return None, None
def parse_dataset_catalog(p: Path):
# dataset_catalog.json can include assembly/organism info, but structure varies.
try:
obj = json.loads(p.read_text())
except Exception:
return None, None
org = None
strain = None
# walk dict recursively looking for likely keys
def walk(x):
nonlocal org, strain
if isinstance(x, dict):
# organism keys
if not org:
if "organismName" in x and isinstance(x["organismName"], str):
org = x["organismName"]
elif "taxName" in x and isinstance(x["taxName"], str):
org = x["taxName"]
# strain/isolate keys
if not strain:
for k in ["strain", "isolate"]:
if k in x and isinstance(x[k], str) and x[k].strip():
strain = x[k].strip()
break
for v in x.values():
walk(v)
elif isinstance(x, list):
for v in x:
walk(v)
walk(obj)
return org, strain
def parse_assembly_report_txt(p: Path):
# NCBI assembly_report.txt often has lines like: "# Organism name:" and "# Infraspecific name:"
org = None
strain = None
try:
for line in p.read_text(errors="ignore").splitlines():
if line.startswith("# Organism name:"):
org = line.split(":", 1)[1].strip()
elif line.startswith("# Infraspecific name:"):
val = line.split(":", 1)[1].strip()
# e.g. "strain=XXXX" or "isolate=YYYY"
m = re.search(r"(strain|isolate)\s*=\s*(.+)", val)
if m:
strain = m.group(2).strip()
if org and strain:
break
except Exception:
pass
return org, strain
def best_name_for_accession(acc: str):
acc_dir = GENOMES_DIR / acc
if not acc_dir.exists():
return None
files = find_metadata_files(acc_dir)
org = None
strain = None
# Prefer JSONL reports first
for p in files:
if p.name.endswith(".jsonl"):
org, strain = parse_jsonl_for_name_and_strain(p)
if org:
break
# Next try dataset_catalog.json
if not org:
for p in files:
if p.name == "dataset_catalog.json":
org, strain = parse_dataset_catalog(p)
if org:
break
# Finally try assembly report text
if not org:
for p in files:
if "assembly_report" in p.name and p.suffix in [".txt", ".tsv"]:
org, strain = parse_assembly_report_txt(p)
if org:
break
if not org:
return None
# normalize whitespace
org = re.sub(r"\s+", " ", org).strip()
if strain:
strain = re.sub(r"\s+", " ", str(strain)).strip()
# avoid duplicating if strain already in organism string
if strain and strain.lower() not in org.lower():
return f"{org} {strain}"
return org
# --- build labels ---
acc = pd.read_csv(ACC_TSV, sep="\t")
if "label" not in acc.columns or "best_accession" not in acc.columns:
raise SystemExit("accessions.tsv must have columns: label, best_accession")
rows = []
for _, r in acc.iterrows():
label = str(r["label"])
accn = str(r["best_accession"])
if label.startswith("EXTRA_"):
nm = best_name_for_accession(accn)
if nm:
label = nm
else:
# fallback: keep previous behavior if metadata not found
label = label.replace("EXTRA_", "EXTRA ")
display = f"{label} ({accn})"
rows.append({"sample": accn, "display": display})
# Add GE11174 exactly as-is
rows.append({"sample": "GE11174", "display": "GE11174"})
out_df = pd.DataFrame(rows).drop_duplicates(subset=["sample"], keep="first")
OUT.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
out_df.to_csv(OUT, sep="\t", index=False)
print("Wrote:", OUT)
print(out_df)
PYplot_tree_v4.R
suppressPackageStartupMessages({
library(ape)
library(readr)
})
args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly = TRUE)
tree_in <- args[1]
labels_tsv <- args[2]
# args[3] is k (ignored here since all-black)
out_pdf <- args[4]
out_png <- args[5]
# --- Load tree ---
tr <- read.tree(tree_in)
# --- Root on outgroup (Brenneria nigrifluens) by accession ---
outgroup_id <- "GCF_005484965.1"
if (outgroup_id %in% tr$tip.label) {
tr <- root(tr, outgroup = outgroup_id, resolve.root = TRUE)
} else {
warning("Outgroup tip not found in tree: ", outgroup_id, " (tree will remain unrooted)")
}
# Make plotting order nicer
tr <- ladderize(tr, right = FALSE)
# --- Load labels (columns: sample, display) ---
lab <- read_tsv(labels_tsv, show_col_types = FALSE)
if (!all(c("sample","display") %in% colnames(lab))) {
stop("labels.tsv must contain columns: sample, display")
}
# Map tip labels AFTER rooting (rooting uses accession IDs)
tipmap <- setNames(lab$display, lab$sample)
tr$tip.label <- ifelse(tr$tip.label %in% names(tipmap),
unname(tipmap[tr$tip.label]),
tr$tip.label)
# --- Plot helper ---
plot_one <- function(device_fun) {
device_fun()
op <- par(no.readonly = TRUE)
on.exit(par(op), add = TRUE)
# Bigger right margin for long labels; tighter overall
par(mar = c(4, 2, 2, 18), xpd = NA)
# Compute xlim with padding so labels fit but whitespace is limited
xx <- node.depth.edgelength(tr)
xmax <- max(xx)
xpad <- 0.10 * xmax
plot(tr,
type = "phylogram",
use.edge.length = TRUE,
show.tip.label = TRUE,
edge.color = "black",
tip.color = "black",
cex = 0.9, # smaller text -> less overlap
label.offset = 0.003, # small gap after tip
no.margin = FALSE,
x.lim = c(0, xmax + xpad))
# Add a clear scale bar near bottom-left
# Use a fixed fraction of tree length for bar length
bar_len <- 0.05 * xmax
add.scale.bar(x = 0, y = 0, length = 0.01, lwd = 2, cex = 0.9)
}
# --- Write outputs (shorter height -> less vertical whitespace) ---
plot_one(function() pdf(out_pdf, width = 11, height = 6, useDingbats = FALSE))
dev.off()
plot_one(function() png(out_png, width = 3000, height = 1000, res = 300))
dev.off()
cat("Wrote:\n", out_pdf, "\n", out_png, "\n", sep = "")run_fastani_batch_verbose.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
# ============ CONFIG ============
QUERY="bacass_out/Prokka/An6/An6.fna" # 你的 query fasta
ACC_LIST="accessions.txt" # 每行一个 GCF/GCA
OUTDIR="fastani_batch"
THREADS=8
SUFFIX=".genomic.fna"
# =================================
ts() { date +"%F %T"; }
log() { echo "[$(ts)] $*"; }
die() { echo "[$(ts)] ERROR: $*" >&2; exit 1; }
# --- checks ---
log "Checking required commands..."
for cmd in fastANI awk sort unzip find grep wc head readlink; do
command -v "$cmd" >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "Missing command: $cmd"
done
command -v datasets >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "Missing NCBI datasets CLI. Install from NCBI Datasets."
[[ -f "$QUERY" ]] || die "QUERY not found: $QUERY"
[[ -f "$ACC_LIST" ]] || die "Accession list not found: $ACC_LIST"
log "QUERY: $QUERY"
log "ACC_LIST: $ACC_LIST"
log "OUTDIR: $OUTDIR"
log "THREADS: $THREADS"
mkdir -p "$OUTDIR/ref_fasta" "$OUTDIR/zips" "$OUTDIR/tmp" "$OUTDIR/logs"
REF_LIST="$OUTDIR/ref_list.txt"
QUERY_LIST="$OUTDIR/query_list.txt"
RAW_OUT="$OUTDIR/fastani_raw.tsv"
FINAL_OUT="$OUTDIR/fastani_results.tsv"
DL_LOG="$OUTDIR/logs/download.log"
ANI_LOG="$OUTDIR/logs/fastani.log"
: > "$REF_LIST"
: > "$DL_LOG"
: > "$ANI_LOG"
# --- build query list ---
q_abs="$(readlink -f "$QUERY")"
echo "$q_abs" > "$QUERY_LIST"
log "Wrote query list: $QUERY_LIST"
log " -> $q_abs"
# --- download refs ---
log "Downloading reference genomes via NCBI datasets..."
n_ok=0
n_skip=0
while read -r acc; do
[[ -z "$acc" ]] && continue
[[ "$acc" =~ ^# ]] && continue
log "Ref: $acc"
zip="$OUTDIR/zips/${acc}.zip"
unpack="$OUTDIR/tmp/$acc"
out_fna="$OUTDIR/ref_fasta/${acc}${SUFFIX}"
# download zip
log " - datasets download -> $zip"
if datasets download genome accession "$acc" --include genome --filename "$zip" >>"$DL_LOG" 2>&1; then
log " - download OK"
else
log " - download FAILED (see $DL_LOG), skipping $acc"
n_skip=$((n_skip+1))
continue
fi
# unzip
rm -rf "$unpack"
mkdir -p "$unpack"
log " - unzip -> $unpack"
if unzip -q "$zip" -d "$unpack" >>"$DL_LOG" 2>&1; then
log " - unzip OK"
else
log " - unzip FAILED (see $DL_LOG), skipping $acc"
n_skip=$((n_skip+1))
continue
fi
# find genomic.fna (兼容不同包结构:优先找 genomic.fna,其次找任何 .fna)
fna="$(find "$unpack" -type f \( -name "*genomic.fna" -o -name "*genomic.fna.gz" \) | head -n 1 || true)"
if [[ -z "${fna:-}" ]]; then
log " - genomic.fna not found, try any *.fna"
fna="$(find "$unpack" -type f -name "*.fna" | head -n 1 || true)"
fi
if [[ -z "${fna:-}" ]]; then
log " - FAILED to find any .fna in package (see $DL_LOG). skipping $acc"
n_skip=$((n_skip+1))
continue
fi
# handle gz if needed
if [[ "$fna" == *.gz ]]; then
log " - found gzipped fasta: $(basename "$fna"), gunzip -> $out_fna"
gunzip -c "$fna" > "$out_fna"
else
log " - found fasta: $(basename "$fna"), copy -> $out_fna"
cp -f "$fna" "$out_fna"
fi
# sanity check fasta looks non-empty
if [[ ! -s "$out_fna" ]]; then
log " - output fasta is empty, skipping $acc"
n_skip=$((n_skip+1))
continue
fi
echo "$(readlink -f "$out_fna")" >> "$REF_LIST"
n_ok=$((n_ok+1))
log " - saved ref fasta OK"
done < "$ACC_LIST"
log "Download summary: OK=$n_ok, skipped=$n_skip"
log "Ref list written: $REF_LIST ($(wc -l < "$REF_LIST") refs)"
if [[ "$(wc -l < "$REF_LIST")" -eq 0 ]]; then
die "No references available. Check $DL_LOG"
fi
# --- run fastANI ---
log "Running fastANI..."
log "Command:"
log " fastANI -ql $QUERY_LIST -rl $REF_LIST -t $THREADS -o $RAW_OUT"
# 重要:不要吞掉错误信息,把 stdout/stderr 进日志
if fastANI -ql "$QUERY_LIST" -rl "$REF_LIST" -t "$THREADS" -o "$RAW_OUT" >>"$ANI_LOG" 2>&1; then
log "fastANI finished (see $ANI_LOG)"
else
log "fastANI FAILED (see $ANI_LOG)"
die "fastANI failed. Inspect $ANI_LOG"
fi
# --- verify raw output ---
if [[ ! -f "$RAW_OUT" ]]; then
die "fastANI did not create $RAW_OUT. Check $ANI_LOG"
fi
if [[ ! -s "$RAW_OUT" ]]; then
die "fastANI output is empty ($RAW_OUT). Check $ANI_LOG; also verify fasta validity."
fi
log "fastANI raw output: $RAW_OUT ($(wc -l < "$RAW_OUT") lines)"
log "Sample lines:"
head -n 5 "$RAW_OUT" || true
# --- create final table ---
log "Creating final TSV with header..."
echo -e "Query\tReference\tANI\tMatchedFrag\tTotalFrag" > "$FINAL_OUT"
awk 'BEGIN{OFS="\t"} {print $1,$2,$3,$4,$5}' "$RAW_OUT" >> "$FINAL_OUT"
log "Final results: $FINAL_OUT ($(wc -l < "$FINAL_OUT") lines incl. header)"
log "Top hits (ANI desc):"
tail -n +2 "$FINAL_OUT" | sort -k3,3nr | head -n 10 || true
log "DONE."
log "Logs:"
log " download log: $DL_LOG"
log " fastANI log: $ANI_LOG"Processing Data_Benjamin_DNAseq_2026_GE11174 — Bacterial WGS pipeline (standalone post)
This post documents the full end-to-end workflow used to process GE11174 from Data_Benjamin_DNAseq_2026_GE11174, covering: database setup, assembly + QC, species identification (k-mers + ANI), genome annotation, generation of summary tables, AMR/resistome/virulence profiling, phylogenetic tree construction (with reproducible plotting), optional debugging/reruns, optional closest-isolate comparison, and a robust approach to find nearest genomes from GenBank.
Overview of the workflow
High-level stages
- Prepare databases (KmerFinder DB; Kraken2 DB used by bacass).
- Assemble + QC + taxonomic context using nf-core/bacass (Nextflow + Docker).
- Interpret KmerFinder results (species hint; confirm with ANI for publication).
- Annotate the genome using BV-BRC ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis.
- Generate Table 1 (sequence + assembly + genome features) under
gunc_envand export to Excel. - AMR / resistome / virulence profiling using ABRicate (+ MEGARes/CARD/ResFinder/VFDB) and RGI (CARD models), export to Excel.
- Build phylogenetic tree (NCBI retrieval + Roary + RAxML-NG + R plotting).
- Debug/re-run guidance (drop one genome, rerun Roary→RAxML, regenerate plot).
- ANI + BUSCO interpretation (species boundary explanation and QC interpretation).
- fastANI interpretation text (tree + ANI combined narrative).
- Optional: closest isolate alignment using nf-core/pairgenomealign.
- Optional: NCBI submission (batch submission plan).
- Robust closest-genome search from GenBank using NCBI datasets + Mash, with duplicate handling (GCA vs GCF).
0) Inputs / assumptions
- Sample:
GE11174 -
Inputs referenced in commands:
samplesheet.tsvfor bacasstargets.tsvfor reference selection (tree step)samplesheet.csvfor pairgenomealign (closest isolate comparison)- raw reads:
GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz - assembly FASTA used downstream:
GE11174.fasta(and in some places scaffold outputs likescaffolds.fasta/GE11174.scaffolds.fa)
-
Local reference paths (examples used):
- Kraken2 DB tarball:
/mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/k2_standard_08_GB_20251015.tar.gz - KmerFinder DB:
/mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder/bacteria/(or tarball variants shown below)
- Kraken2 DB tarball:
1) Database setup — KmerFinder DB
Option A (CGE service):
- Navigate: https://www.genomicepidemiology.org/services/ → https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/KmerFinder/
- Download DB tarball:
https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/KmerFinder/etc/kmerfinder_db.tar.gz
Option B (Zenodo snapshot):
- Download
20190108_kmerfinder_stable_dirs.tar.gzfrom:https://zenodo.org/records/13447056
2) Assembly + QC + taxonomic screening — nf-core/bacass
Run bacass with Docker and resume support:
conda activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/trycycler
unicycler -l Gibsiella_species_ONT/GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz --mode normal -t 80 -o GE11174_unicycler_normal #{conservative,normal,bold}
unicycler -l Gibsiella_species_ONT/GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz --mode conservative -t 80 -o GE11174_unicycler_conservative
conda deactivate
# Example --kmerfinderdb values tried/recorded:
# --kmerfinderdb /path/to/kmerfinder/bacteria.tar.gz
# --kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder_db.tar.gz
# --kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/20190108_kmerfinder_stable_dirs.tar.gz
nextflow run nf-core/bacass -r 2.5.0 -profile docker \
--input samplesheet.tsv \
--outdir bacass_out \
--assembly_type long \
--kraken2db /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/k2_standard_08_GB_20251015.tar.gz \
--kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder/bacteria/ \
-resumeOutputs used later
- Scaffolded/assembled FASTA from bacass (e.g., for annotation, AMR screening, Mash sketching, tree building).
3) KmerFinder summary — species hint (with publication note)
Interpretation recorded:
From the KmerFinder summary, the top hit is Gibbsiella quercinecans (strain FRB97; NZ_CP014136.1) with much higher score and coverage than the second hit (which is low coverage). So it’s fair to write: “KmerFinder indicates the isolate is most consistent with Gibbsiella quercinecans.” …but for a species call (especially for publication), you should confirm with ANI (or a genome taxonomy tool), because k-mer hits alone aren’t always definitive.
4) Genome annotation — BV-BRC ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis
Annotate the genome using BV-BRC:
- Use: https://www.bv-brc.org/app/ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis
- Input: scaffolded results from bacass
- Purpose: comprehensive overview + annotation of the genome assembly.
5) Table 1 — Summary of sequence data and genome features (env: gunc_env)
Prepare environment and run the Table 1 pipeline:
# activate the env that has openpyxl
mamba activate gunc_env
mamba install -n gunc_env -c conda-forge openpyxl -y
mamba deactivate
# STEP_1
ENV_NAME=gunc_env AUTO_INSTALL=1 THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/make_table1_GE11174.sh
# STEP_2
python export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py \
--workdir table1_GE11174_work \
--out Comprehensive_GE11174.xlsx \
--max-rows 200000 \
--sample GE11174
# STEP_1+2 (combined)
ENV_NAME=gunc_env AUTO_INSTALL=1 THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/make_table1_with_excel.shFor the items “Total number of reads sequenced” and “Mean read length (bp)”:
pigz -dc GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz | awk 'END{print NR/4}'
seqkit stats GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz6) AMR gene profiling + Resistome + Virulence profiling (ABRicate + RGI)
This stage produces resistome/virulence tables and an Excel export.
6.1 Databases / context notes
“Table 4. Specialty Genes” note recorded:
- NDARO: 1
- Antibiotic Resistance — CARD: 15
- Antibiotic Resistance — PATRIC: 55
- Drug Target — TTD: 38
- Metal Resistance — BacMet: 29
- Transporter — TCDB: 250
- Virulence factor — VFDB: 33
Useful sites:
6.2 ABRicate environment + DB listing
conda activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3
abricate --list
#DATABASE SEQUENCES DBTYPE DATE
#vfdb 2597 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#resfinder 3077 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#argannot 2223 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#ecoh 597 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#megares 6635 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#card 2631 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#ecoli_vf 2701 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#plasmidfinder 460 nucl 2025-Oct-22
#ncbi 5386 nucl 2025-Oct-22
abricate-get_db --list
#Choices: argannot bacmet2 card ecoh ecoli_vf megares ncbi plasmidfinder resfinder vfdb victors (default '').6.3 Install/update DBs (CARD, MEGARes)
# CARD
abricate-get_db --db card
# MEGARes (automatically install; if error try manual install below)
abricate-get_db --db megares6.4 Manual MEGARes v3.0 install (if needed)
wget -O megares_database_v3.00.fasta \
"https://www.meglab.org/downloads/megares_v3.00/megares_database_v3.00.fasta"
# 1) Define dbdir (adjust to your env; from logs it's inside the conda env)
DBDIR=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3/db
# 2) Create a custom db folder for MEGARes v3.0
mkdir -p ${DBDIR}/megares_v3.0
# 3) Copy the downloaded MEGARes v3.0 nucleotide FASTA to 'sequences'
cp megares_database_v3.00.fasta ${DBDIR}/megares_v3.0/sequences
# 4) Build ABRicate indices
abricate --setupdb
# Confirm presence
abricate --list | egrep 'card|megares'
abricate --list | grep -i megares6.5 Run resistome/virulome pipeline scripts
chmod +x run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=GE11174.fasta SAMPLE=GE11174 THREADS=32 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=./vrap_HF/spades/scaffolds.fasta SAMPLE=HF THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=GE11174.fasta SAMPLE=GE11174 MINID=80 MINCOV=60 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh6.6 Sanity checks on ABRicate outputs
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab
grep -vc '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab
grep -v '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab | grep -v '^[[:space:]]*$' | head -n 3
grep -v '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab | grep -v '^[[:space:]]*$' | head -n 3
grep -v '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab | grep -v '^[[:space:]]*$' | head -n 3
grep -v '^#' resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab | grep -v '^[[:space:]]*$' | head -n 36.7 Dedup tables / “one per gene” mode
chmod +x run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh
ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 \
ASM=GE11174.fasta \
SAMPLE=GE11174 \
OUTDIR=resistome_virulence_GE11174 \
MINID=80 MINCOV=60 \
THREADS=32 \
./run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.shThreshold summary recorded:
-
ABRicate thresholds: MINID=70 MINCOV=50
- MEGARes: 35 →
resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab - CARD: 28 →
resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab - ResFinder: 2 →
resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab - VFDB: 18 →
resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab
- MEGARes: 35 →
-
ABRicate thresholds: MINID=80 MINCOV=60
- MEGARes: 3
- CARD: 1
- ResFinder: 0
- VFDB: 0
6.8 Merge sources + export to Excel
python merge_amr_sources_by_gene.py
python export_resistome_virulence_to_excel_py36.py \
--workdir resistome_virulence_GE11174 \
--sample GE11174 \
--out Resistome_Virulence_GE11174.xlsx6.9 Methods sentence + table captions (recorded text)
Methods sentence (AMR + virulence)
AMR genes were identified by screening the genome assembly with ABRicate against the MEGARes and ResFinder databases, using minimum identity and coverage thresholds of X% and Y%, respectively. CARD-based AMR determinants were additionally predicted using RGI (Resistance Gene Identifier) to leverage curated resistance models. Virulence factors were screened using ABRicate against VFDB under the same thresholds. Replace X/Y with your actual values (e.g., 90/60) or state “default parameters” if you truly used defaults.
Table 2 caption (AMR)
Table 2. AMR gene profiling of the genome assembly. Hits were detected using ABRicate (MEGARes and ResFinder) and RGI (CARD). The presence of AMR-associated genes does not necessarily imply phenotypic resistance, which may depend on allele type, genomic context/expression, and/or SNP-mediated mechanisms; accordingly, phenotype predictions (e.g., ResFinder) should be interpreted cautiously.
Table 3 caption (virulence)
Table 3. Virulence factor profiling of the genome assembly based on ABRicate screening against VFDB, reporting loci with sequence identity and coverage above the specified thresholds.
7) Phylogenetic tree generation (Nextflow/NCBI + Roary + RAxML-NG + R plotting)
7.1 Resolve/choose assemblies via Entrez
export NCBI_EMAIL="x.yyy@zzz.de"
./resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py targets.tsv resolved_accessions.tsv7.2 Build tree (main pipeline) + note about R env
Recorded note:
NOTE the env
bengal3_ac3don’t have the following R package, usingr_envfor the plot-step → RUN TWICE, firstbengal3_ac3, then runbuild_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh plot-only.
Suggested package install (if needed):
#mamba install -y -c conda-forge -c bioconda r-aplot bioconductor-ggtree r-ape r-ggplot2 r-dplyr r-readrRun:
export ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3
export NCBI_EMAIL="x.yyy@zzz.de"
./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
# Regenerate the plot
conda activate r_env
./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh plot-only7.3 Manual label corrections
Edit:
vim work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv
Recorded edits:
-
REMOVE:
GCA_032062225.1 EXTRA_GCA_032062225.1 (GCA_032062225.1)GCF_047901425.1 EXTRA_GCF_047901425.1 (GCF_047901425.1)
-
ADAPT:
Gibbsiella quercinecans DSM 25889 (GCF_004342245.1)Gibbsiella greigii USA56Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6Gibbsiella quercinecans strain FRB97Brenneria nigrifluens LMG 5956
7.4 Plot with plot_tree_v4.R
Rscript work_wgs_tree/plot/plot_tree_v4.R \
work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/core.raxml.support \
work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv \
6 \
work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree.pdf \
work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree.png8) DEBUG rerun recipe (drop one genome; rerun Roary → RAxML-NG → plot)
Example: drop GCF_047901425.1 (or the other listed one).
8.1 Remove from inputs
# 1.1) remove from inputs so Roary cannot include it
rm -f work_wgs_tree/gffs/GCF_047901425.1.gff
rm -f work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_047901425.1.fna
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/prokka/GCF_047901425.1
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/genomes_ncbi/GCF_047901425.1 #optional
# 1.2) remove from accession list so it won't come back
awk -F'\t' 'NR==1 || $2!="GCF_047901425.1"' work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv > work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp \
&& mv work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsvAlternative removal target:
# 2.1) remove from inputs so Roary cannot include it
rm -f work_wgs_tree/gffs/GCA_032062225.1.gff
rm -f work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_032062225.1.fna
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/prokka/GCA_032062225.1
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/genomes_ncbi/GCA_032062225.1 #optional
# 2.2) remove from accession list so it won't come back
awk -F'\t' 'NR==1 || $2!="GCA_032062225.1"' work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv > work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp \
&& mv work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv8.2 Clean old runs + rerun Roary
# 3) delete old roary runs (so you don't accidentally reuse old alignment)
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/roary_*
# 4) rerun Roary (fresh output dir)
mkdir -p work_wgs_tree/logs
ROARY_OUT="work_wgs_tree/roary_$(date +%s)"
roary -e --mafft -p 8 -cd 95 -i 95 \
-f "$ROARY_OUT" \
work_wgs_tree/gffs/*.gff \
> work_wgs_tree/logs/roary_rerun.stdout.txt \
2> work_wgs_tree/logs/roary_rerun.stderr.txt8.3 Point to the new core alignment and rerun RAxML-NG
# 5) point meta file to new core alignment (absolute path)
echo "$(readlink -f "$ROARY_OUT/core_gene_alignment.aln")" > work_wgs_tree/meta/core_alignment_path.txt
# 6) rerun RAxML-NG
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/raxmlng
mkdir work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/
raxml-ng --all \
--msa "$(cat work_wgs_tree/meta/core_alignment_path.txt)" \
--model GTR+G \
--bs-trees 1000 \
--threads 8 \
--prefix work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/core8.4 Regenerate labels + replot
# 7) Run this to regenerate labels.tsv
bash regenerate_labels.sh
# 8) Manual correct the display name in vim work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv
#Gibbsiella greigii USA56
#Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6
#Gibbsiella quercinecans strain FRB97
#Brenneria nigrifluens LMG 5956
# 9) Rerun only the plot step:
Rscript work_wgs_tree/plot/plot_tree.R \
work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/core.raxml.support \
work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv \
6 \
work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree.pdf \
work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree.png9) fastaANI + BUSCO explanations (recorded)
9.1 Reference FASTA inventory example
find . -name "*.fna"
#./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_004342245.1.fna GCF_004342245.1 Gibbsiella quercinecans DSM 25889 (GCF_004342245.1)
#./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_039539505.1.fna GCF_039539505.1 Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6 (GCF_039539505.1)
#./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_005484965.1.fna GCF_005484965.1 Brenneria nigrifluens LMG5956 (GCF_005484965.1)
#./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_039540155.1.fna GCA_039540155.1 Gibbsiella greigii USA56 (GCA_039540155.1)
#./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GE11174.fna
#./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_002291425.1.fna GCF_002291425.1 Gibbsiella quercinecans FRB97 (GCF_002291425.1)9.2 fastANI runs
mamba activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3
fastANI \
-q GE11174.fasta \
-r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_004342245.1.fna \
-o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_quercinecans_DSM_25889.txt
fastANI \
-q GE11174.fasta \
-r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_039539505.1.fna \
-o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_papilionis_PWX6.txt
fastANI \
-q GE11174.fasta \
-r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_005484965.1.fna \
-o fastANI_out_Brenneria_nigrifluens_LMG5956.txt
fastANI \
-q GE11174.fasta \
-r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_039540155.1.fna \
-o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_greigii_USA56.txt
fastANI \
-q GE11174.fasta \
-r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_002291425.1.fna \
-o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_quercinecans_FRB97.txt
cat fastANI_out_*.txt > fastANI_out.txt9.3 fastANI output table (recorded)
GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_005484965.1.fna 79.1194 597 1890
GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_039540155.1.fna 95.9589 1547 1890
GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_039539505.1.fna 97.2172 1588 1890
GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_004342245.1.fna 98.0889 1599 1890
GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_002291425.1.fna 98.1285 1622 18909.4 Species boundary note (recorded, bilingual)
在细菌基因组比较里,一个常用经验阈值是:
- ANI ≥ 95–96%:通常认为属于同一物种(species)的范围
- 你这里 97.09% → 很大概率表示 An6 与 HITLi7 属于同一物种,但可能不是同一株(strain),因为还存在一定差异。
是否“同一菌株”通常还要结合:
- 核心基因 SNP 距离、cgMLST
- 组装质量/污染
- 覆盖率是否足够高
9.5 BUSCO results interpretation (recorded)
BUSCO 结果的快速解读(顺便一句). The results have been already packaged in the Table 1.
- Complete 99.2%,Missing 0.0%:说明你的组装非常完整(对细菌来说很优秀)
- Duplicated 0.0%:重复拷贝不高,污染/混样风险更低
- Scaffolds 80、N50 ~169 kb:碎片化还可以,但总体质量足以做 ANI/物种鉴定
10) fastANI explanation (recorded narrative)
From your tree and the fastANI table, GE11174 is clearly inside the Gibbsiella quercinecans clade, and far from the outgroup (Brenneria nigrifluens). The ANI values quantify that same pattern.
1) Outgroup check (sanity)
-
GE11174 vs Brenneria nigrifluens (GCF_005484965.1): ANI 79.12% (597/1890 fragments)
- 79% ANI is way below any species boundary → not the same genus/species.
- On the tree, Brenneria sits on a long branch as the outgroup, consistent with this deep divergence.
- The relatively low matched fragments (597/1890) also fits “distant genomes” (fewer orthologous regions pass the ANI mapping filters).
2) Species-level placement of GE11174
A common rule of thumb you quoted is correct: ANI ≥ 95–96% ⇒ same species.
Compare GE11174 to the Gibbsiella references:
-
vs GCA_039540155.1 (Gibbsiella greigii USA56): 95.96% (1547/1890)
- Right at the boundary. This suggests “close but could be different species” or “taxonomy/labels may not reflect true species boundaries” depending on how those genomes are annotated.
- On the tree, G. greigii is outside the quercinecans group but not hugely far, which matches “borderline ANI”.
-
vs GCF_039539505.1 (Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6): 97.22% (1588/1890)
-
vs GCF_004342245.1 (G. quercinecans DSM 25889): 98.09% (1599/1890)
-
vs GCF_002291425.1 (G. quercinecans FRB97): 98.13% (1622/1890)
These are all comfortably above 96%, especially the two quercinecans genomes (~98.1%). That strongly supports:
GE11174 belongs to the same species as Gibbsiella quercinecans (and is closer to quercinecans references than to greigii).
3) Closest reference and “same strain?” question
GE11174’s closest by ANI in your list is:
- FRB97 (GCF_002291425.1): 98.1285%
- DSM 25889 (GCF_004342245.1): 98.0889%
- Next: PWX6 97.2172%
These differences are small, but 98.1% ANI is not “same strain” evidence by itself. Within a species, different strains commonly sit anywhere from ~96–99.9% ANI depending on diversity. To claim “same strain / very recent transmission,” people usually look for much tighter genome-wide similarity:
- core-genome SNP distance (often single digits to tens, depending on organism and context)
- cgMLST allele differences
- recombination filtering (if relevant)
- assembly QC/contamination checks
- and confirming that alignment/ANI coverage is high and not biased by missing regions
Your fragment matches (e.g., 1622/1890 for FRB97) are reasonably high, supporting that the ANI is meaningful, but it still doesn’t equate to “same strain.”
4) How to phrase the combined interpretation (tree + ANI)
A clear summary you can use:
- The phylogenetic tree places GE11174 within the Gibbsiella quercinecans lineage, with Brenneria nigrifluens as a distant outgroup.
-
fastANI supports this:
- ~98.1% ANI to G. quercinecans FRB97 and DSM 25889 → strong same-species support.
- 97.2% to G. papilionis → still same-species range, but more distant than the quercinecans references.
- 95.96% to G. greigii → borderline; consistent with being a close neighboring lineage but not the best species match for GE11174.
- 79.1% to Brenneria → confirms it is an appropriate outgroup and far outside the species/genus boundary.
- Therefore, GE11174 is very likely Gibbsiella quercinecans (species-level), and appears most similar to FRB97/DSM 25889, but additional high-resolution analyses are required to assess “same strain.”
If you want, paste the fastANI line for GE11174 vs GE11174? (or run fastANI against a broader set), and/or your core SNP distances from the Roary alignment, and I can help you write a tighter “strain-level” conclusion.
11) Compare to the next closest isolate (pairwise alignment) — nf-core/pairgenomealign
conda deactivate
nextflow run nf-core/pairgenomealign -r 2.2.2 -profile docker \
--target GE11174.fasta \
--input samplesheet.csv \
--outdir pairgenomealign_out \
--igenomes_base /mnt/nvme1n1p1/igenomes \
--genome GRCh38Recorded TODO:
#TODO_NEXT_MONDAY: * phylogenetic tree + fastaANI + nf-core/pairgenomealign (compare to the closest isoalte https://nf-co.re/pairgenomealign/2.2.1/)
- summarize all results with a mail to send them back, mentioned that we can submit the genome to NCBI to obtain a high-quality annotation. What strain name would you like to assign to this isolate?
- If they agree, I can submit the two new isolates to the NCBI-database!
12) Submit both sequences in a batch to NCBI-server! (planned step)
Recorded as:
- submit both sequences in a batch to NCBI-server!
13) Find the closest isolate from GenBank (robust approach) for STEP_7
13.1 Download all available Gibbsiella genomes
# download all available genomes for the genus Gibbsiella (includes assemblies + metadata)
# --assembly-level: must be 'chromosome', 'complete', 'contig', 'scaffold'
datasets download genome taxon Gibbsiella --include genome,gff3,gbff --assembly-level complete,chromosome,scaffold --filename gibbsiella.zip
unzip -q gibbsiella.zip -d gibbsiella_ncbi
mamba activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac313.2 Mash sketching + nearest neighbors
# make a Mash sketch of your isolate
mash sketch -o isolate bacass_out/Unicycler/GE11174.scaffolds.fa
# sketch all reference genomes (example path—adjust)
find gibbsiella_ncbi -name "*.fna" -o -name "*.fasta" > refs.txt
mash sketch -o refs -l refs.txt
# get closest genomes
mash dist isolate.msh refs.msh | sort -gk3 | head -n 20 > top20_mash.txtRecorded interpretation:
-
Best hits to
GE11174.scaffolds.faare:- GCA/GCF_002291425.1 (GenBank + RefSeq copies of the same assembly)
- GCA/GCF_004342245.1 (same duplication pattern)
- GCA/GCF_047901425.1 (FRB97; also duplicated)
- Mash distances ~0.018–0.020 are very close (typically same species; often within-species).
p-values are underflow formatting (extremely significant).
13.3 Remove duplicates (GCA vs GCF)
Goal: keep one of each duplicated assembly (prefer GCF if available).
Example snippet recorded:
# Take your top hits, prefer GCF over GCA
cat top20_mash.txt \
| awk '{print $2}' \
| sed 's|/GCA_.*||; s|/GCF_.*||' \
| sort -uManual suggestion recorded:
- keep
GCF_002291425.1(dropGCA_002291425.1) - keep
GCF_004342245.1 - keep
GCF_047901425.1 - optionally keep
GCA_032062225.1if it’s truly different and you want a more distant ingroup point
Appendix — Complete attached code (standalone)
Below are the full contents of the attached scripts exactly as provided, so this post can be used standalone in the future.
Note: You mentioned “keep all information of input” and “attach all complete code at the end.” I’ve included all scripts that are currently attached in this chat. If there are additional scripts you meant to attach (e.g.,
run_resistome_virulome*.sh,regenerate_labels.sh,export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py, etc.), please upload them and I’ll append them here too.
File: build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
# build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
#
# Purpose:
# Build a core-genome phylogenetic tree and a publication-style plot similar to Fig 3B.
#
# Usage:
# ./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh # full run
# ./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh plot-only # only regenerate the plot from existing outputs
#
# Requirements:
# - Conda env with required tools. Set ENV_NAME to conda env path.
# - NCBI datasets and/or Entrez usage requires NCBI_EMAIL.
# - Roary, Prokka, RAxML-NG, MAFFT, R packages for plotting.
#
# Environment variables:
# ENV_NAME : path to conda env (e.g., /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3)
# NCBI_EMAIL : email for Entrez calls
# THREADS : default threads
#
# Inputs:
# - targets.tsv: list of target accessions (if used in resolve step)
# - local isolate genome fasta
#
# Outputs:
# work_wgs_tree/...
#
# NOTE:
# If plotting packages are missing in ENV_NAME, run plot-only under an R-capable env (e.g., r_env).
SCRIPT_DIR="$(cd "$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)"
MODE="${1:-full}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-8}"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR:-work_wgs_tree}"
# Activate conda env if provided
if [[ -n "${ENV_NAME:-}" ]]; then
# shellcheck disable=SC1090
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
fi
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}"
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/logs"
log() {
echo "[$(date '+%F %T')] $*" >&2
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Helper: check command exists
need_cmd() {
command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1 || {
echo "ERROR: required command '$1' not found in PATH" >&2
exit 1
}
}
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Tool checks (plot-only skips some)
if [[ "${MODE}" != "plot-only" ]]; then
need_cmd python
need_cmd roary
need_cmd raxml-ng
need_cmd prokka
need_cmd mafft
need_cmd awk
need_cmd sed
need_cmd grep
fi
need_cmd Rscript
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Paths
META_DIR="${WORKDIR}/meta"
GENOMES_DIR="${WORKDIR}/genomes_ncbi"
FASTAS_DIR="${WORKDIR}/fastas"
GFFS_DIR="${WORKDIR}/gffs"
PROKKA_DIR="${WORKDIR}/prokka"
ROARY_DIR="${WORKDIR}/roary"
RAXML_DIR="${WORKDIR}/raxmlng"
PLOT_DIR="${WORKDIR}/plot"
mkdir -p "${META_DIR}" "${GENOMES_DIR}" "${FASTAS_DIR}" "${GFFS_DIR}" "${PROKKA_DIR}" "${ROARY_DIR}" "${RAXML_DIR}" "${PLOT_DIR}"
ACCESSIONS_TSV="${META_DIR}/accessions.tsv"
LABELS_TSV="${PLOT_DIR}/labels.tsv"
CORE_ALIGN_PATH_FILE="${META_DIR}/core_alignment_path.txt"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step: plot only
if [[ "${MODE}" == "plot-only" ]]; then
log "Running in plot-only mode..."
# If labels file isn't present, try generating a minimal one
if [[ ! -s "${LABELS_TSV}" ]]; then
log "labels.tsv not found. Creating a placeholder labels.tsv (edit as needed)."
{
echo -e "accession\tdisplay"
if [[ -d "${FASTAS_DIR}" ]]; then
for f in "${FASTAS_DIR}"/*.fna "${FASTAS_DIR}"/*.fa "${FASTAS_DIR}"/*.fasta 2>/dev/null; do
[[ -e "$f" ]] || continue
bn="$(basename "$f")"
acc="${bn%%.*}"
echo -e "${acc}\t${acc}"
done
fi
} > "${LABELS_TSV}"
fi
# Plot using plot_tree_v4.R if present; otherwise fall back to plot_tree.R
PLOT_SCRIPT="${PLOT_DIR}/plot_tree_v4.R"
if [[ ! -f "${PLOT_SCRIPT}" ]]; then
PLOT_SCRIPT="${SCRIPT_DIR}/plot_tree_v4.R"
fi
if [[ ! -f "${PLOT_SCRIPT}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: plot_tree_v4.R not found" >&2
exit 1
fi
SUPPORT_FILE="${RAXML_DIR}/core.raxml.support"
if [[ ! -f "${SUPPORT_FILE}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: Support file not found: ${SUPPORT_FILE}" >&2
exit 1
fi
OUTPDF="${PLOT_DIR}/core_tree.pdf"
OUTPNG="${PLOT_DIR}/core_tree.png"
ROOT_N=6
log "Plotting tree..."
Rscript "${PLOT_SCRIPT}" \
"${SUPPORT_FILE}" \
"${LABELS_TSV}" \
"${ROOT_N}" \
"${OUTPDF}" \
"${OUTPNG}"
log "Done (plot-only). Outputs: ${OUTPDF} ${OUTPNG}"
exit 0
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Full pipeline
log "Running full pipeline..."
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Config / expected inputs
TARGETS_TSV="${SCRIPT_DIR}/targets.tsv"
RESOLVED_TSV="${SCRIPT_DIR}/resolved_accessions.tsv"
ISOLATE_FASTA="${SCRIPT_DIR}/GE11174.fasta"
# If caller has different locations, let them override
TARGETS_TSV="${TARGETS_TSV_OVERRIDE:-${TARGETS_TSV}}"
RESOLVED_TSV="${RESOLVED_TSV_OVERRIDE:-${RESOLVED_TSV}}"
ISOLATE_FASTA="${ISOLATE_FASTA_OVERRIDE:-${ISOLATE_FASTA}}"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 1: Resolve best assemblies (if targets.tsv exists)
if [[ -f "${TARGETS_TSV}" ]]; then
log "Resolving best assemblies from targets.tsv..."
if [[ -z "${NCBI_EMAIL:-}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: NCBI_EMAIL is required for Entrez calls" >&2
exit 1
fi
python "${SCRIPT_DIR}/resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py" "${TARGETS_TSV}" "${RESOLVED_TSV}"
else
log "targets.tsv not found; assuming resolved_accessions.tsv already exists"
fi
if [[ ! -s "${RESOLVED_TSV}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: resolved_accessions.tsv not found or empty: ${RESOLVED_TSV}" >&2
exit 1
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 2: Prepare accessions.tsv for downstream steps
log "Preparing accessions.tsv..."
{
echo -e "label\taccession"
awk -F'\t' 'NR>1 {print $1"\t"$2}' "${RESOLVED_TSV}"
} > "${ACCESSIONS_TSV}"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 3: Download genomes (NCBI datasets if available)
log "Downloading genomes (if needed)..."
need_cmd datasets
need_cmd unzip
while IFS=$'\t' read -r label acc; do
[[ "${label}" == "label" ]] && continue
[[ -z "${acc}" ]] && continue
OUTZIP="${GENOMES_DIR}/${acc}.zip"
OUTDIR="${GENOMES_DIR}/${acc}"
if [[ -d "${OUTDIR}" ]]; then
log " ${acc}: already downloaded"
continue
fi
log " ${acc}: downloading..."
datasets download genome accession "${acc}" --include genome --filename "${OUTZIP}" \
> "${WORKDIR}/logs/datasets_${acc}.stdout.txt" \
2> "${WORKDIR}/logs/datasets_${acc}.stderr.txt" || {
echo "ERROR: datasets download failed for ${acc}. See logs." >&2
exit 1
}
mkdir -p "${OUTDIR}"
unzip -q "${OUTZIP}" -d "${OUTDIR}"
done < "${ACCESSIONS_TSV}"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 4: Collect FASTA files
log "Collecting FASTA files..."
rm -f "${FASTAS_DIR}"/* 2>/dev/null || true
while IFS=$'\t' read -r label acc; do
[[ "${label}" == "label" ]] && continue
OUTDIR="${GENOMES_DIR}/${acc}"
fna="$(find "${OUTDIR}" -name "*.fna" | head -n 1 || true)"
if [[ -z "${fna}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: no .fna found for ${acc} in ${OUTDIR}" >&2
exit 1
fi
cp -f "${fna}" "${FASTAS_DIR}/${acc}.fna"
done < "${ACCESSIONS_TSV}"
# Add isolate
if [[ -f "${ISOLATE_FASTA}" ]]; then
cp -f "${ISOLATE_FASTA}" "${FASTAS_DIR}/GE11174.fna"
else
log "WARNING: isolate fasta not found at ${ISOLATE_FASTA}; skipping"
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 5: Run Prokka on each genome
log "Running Prokka..."
for f in "${FASTAS_DIR}"/*.fna; do
bn="$(basename "${f}")"
acc="${bn%.fna}"
out="${PROKKA_DIR}/${acc}"
if [[ -d "${out}" && -s "${out}/${acc}.gff" ]]; then
log " ${acc}: prokka output exists"
continue
fi
mkdir -p "${out}"
log " ${acc}: prokka..."
prokka --outdir "${out}" --prefix "${acc}" --cpus "${THREADS}" "${f}" \
> "${WORKDIR}/logs/prokka_${acc}.stdout.txt" \
2> "${WORKDIR}/logs/prokka_${acc}.stderr.txt"
done
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 6: Collect GFFs for Roary
log "Collecting GFFs..."
rm -f "${GFFS_DIR}"/*.gff 2>/dev/null || true
for d in "${PROKKA_DIR}"/*; do
[[ -d "${d}" ]] || continue
acc="$(basename "${d}")"
gff="${d}/${acc}.gff"
if [[ -f "${gff}" ]]; then
cp -f "${gff}" "${GFFS_DIR}/${acc}.gff"
else
log "WARNING: missing GFF for ${acc}"
fi
done
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 7: Roary
log "Running Roary..."
ROARY_OUT="${WORKDIR}/roary_$(date +%s)"
mkdir -p "${ROARY_OUT}"
roary -e --mafft -p "${THREADS}" -cd 95 -i 95 \
-f "${ROARY_OUT}" \
"${GFFS_DIR}"/*.gff \
> "${WORKDIR}/logs/roary.stdout.txt" \
2> "${WORKDIR}/logs/roary.stderr.txt"
CORE_ALN="${ROARY_OUT}/core_gene_alignment.aln"
if [[ ! -f "${CORE_ALN}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: core alignment not found: ${CORE_ALN}" >&2
exit 1
fi
readlink -f "${CORE_ALN}" > "${CORE_ALIGN_PATH_FILE}"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 8: RAxML-NG
log "Running RAxML-NG..."
rm -rf "${RAXML_DIR}"
mkdir -p "${RAXML_DIR}"
raxml-ng --all \
--msa "$(cat "${CORE_ALIGN_PATH_FILE}")" \
--model GTR+G \
--bs-trees 1000 \
--threads "${THREADS}" \
--prefix "${RAXML_DIR}/core" \
> "${WORKDIR}/logs/raxml.stdout.txt" \
2> "${WORKDIR}/logs/raxml.stderr.txt"
SUPPORT_FILE="${RAXML_DIR}/core.raxml.support"
if [[ ! -f "${SUPPORT_FILE}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: RAxML support file not found: ${SUPPORT_FILE}" >&2
exit 1
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 9: Generate labels.tsv (basic)
log "Generating labels.tsv..."
{
echo -e "accession\tdisplay"
echo -e "GE11174\tGE11174"
while IFS=$'\t' read -r label acc; do
[[ "${label}" == "label" ]] && continue
echo -e "${acc}\t${label} (${acc})"
done < "${ACCESSIONS_TSV}"
} > "${LABELS_TSV}"
log "NOTE: You may want to manually edit ${LABELS_TSV} for publication display names."
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 10: Plot
log "Plotting..."
PLOT_SCRIPT="${SCRIPT_DIR}/plot_tree_v4.R"
OUTPDF="${PLOT_DIR}/core_tree.pdf"
OUTPNG="${PLOT_DIR}/core_tree.png"
ROOT_N=6
Rscript "${PLOT_SCRIPT}" \
"${SUPPORT_FILE}" \
"${LABELS_TSV}" \
"${ROOT_N}" \
"${OUTPDF}" \
"${OUTPNG}" \
> "${WORKDIR}/logs/plot.stdout.txt" \
2> "${WORKDIR}/logs/plot.stderr.txt"
log "Done. Outputs:"
log " Tree support: ${SUPPORT_FILE}"
log " Labels: ${LABELS_TSV}"
log " Plot PDF: ${OUTPDF}"
log " Plot PNG: ${OUTPNG}"File: resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py
Resolve a "best" assembly accession for a list of target taxa / accessions using NCBI Entrez.
Usage:
./resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py targets.tsv resolved_accessions.tsv
Input (targets.tsv):
TSV with at least columns:
label
<tab> query
Where "query" can be an organism name, taxid, or an assembly/accession hint.
Output (resolved_accessions.tsv):
TSV with columns:
label
<tab> accession <tab> organism <tab> assembly_name <tab> assembly_level <tab> refseq_category
Requires:
- BioPython (Entrez)
- NCBI_EMAIL environment variable (or set in script)
"""
import os
import sys
import time
import csv
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
try:
from Bio import Entrez
except ImportError:
sys.stderr.write("ERROR: Biopython is required (Bio.Entrez)\n")
sys.exit(1)
def eprint(*args, **kwargs):
print(*args, file=sys.stderr, **kwargs)
def read_targets(path: str) -> List[Tuple[str, str]]:
rows: List[Tuple[str, str]] = []
with open(path, "r", newline="") as fh:
reader = csv.reader(fh, delimiter="\t")
for i, r in enumerate(reader, start=1):
if not r:
continue
if i == 1 and r[0].lower() in ("label", "name"):
# header
continue
if len(r) < 2:
continue
label = r[0].strip()
query = r[1].strip()
if label and query:
rows.append((label, query))
return rows
def entrez_search(db: str, term: str, retmax: int = 20) -> List[str]:
handle = Entrez.esearch(db=db, term=term, retmax=retmax)
res = Entrez.read(handle)
handle.close()
return res.get("IdList", [])
def entrez_summary(db: str, ids: List[str]):
if not ids:
return []
handle = Entrez.esummary(db=db, id=",".join(ids), retmode="xml")
res = Entrez.read(handle)
handle.close()
return res
def pick_best_assembly(summaries) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""
Heuristics:
Prefer RefSeq (refseq_category != 'na'), prefer higher assembly level:
complete genome > chromosome > scaffold > contig
Then prefer latest / highest quality where possible.
"""
if not summaries:
return None
level_rank = {
"Complete Genome": 4,
"Chromosome": 3,
"Scaffold": 2,
"Contig": 1
}
def score(s: Dict) -> Tuple[int, int, int]:
refcat = s.get("RefSeq_category", "na")
is_refseq = 1 if (refcat and refcat.lower() != "na") else 0
level = s.get("AssemblyStatus", "")
lvl = level_rank.get(level, 0)
# Prefer latest submit date (YYYY/MM/DD)
submit = s.get("SubmissionDate", "0000/00/00")
try:
y, m, d = submit.split("/")
date_int = int(y) * 10000 + int(m) * 100 + int(d)
except Exception:
date_int = 0
return (is_refseq, lvl, date_int)
best = max(summaries, key=score)
return best
def resolve_query(label: str, query: str) -> Optional[Dict]:
# If query looks like an assembly accession, search directly.
term = query
if query.startswith("GCA_") or query.startswith("GCF_"):
term = f"{query}[Assembly Accession]"
ids = entrez_search(db="assembly", term=term, retmax=50)
if not ids:
# Try organism name search
term2 = f"{query}[Organism]"
ids = entrez_search(db="assembly", term=term2, retmax=50)
if not ids:
eprint(f"WARNING: no assembly hits for {label} / {query}")
return None
summaries = entrez_summary(db="assembly", ids=ids)
best = pick_best_assembly(summaries)
if not best:
eprint(f"WARNING: could not pick best assembly for {label} / {query}")
return None
# Extract useful fields
acc = best.get("AssemblyAccession", "")
org = best.get("Organism", "")
name = best.get("AssemblyName", "")
level = best.get("AssemblyStatus", "")
refcat = best.get("RefSeq_category", "")
return {
"label": label,
"accession": acc,
"organism": org,
"assembly_name": name,
"assembly_level": level,
"refseq_category": refcat
}
def main():
if len(sys.argv) != 3:
eprint("Usage: resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py targets.tsv resolved_accessions.tsv")
sys.exit(1)
targets_path = sys.argv[1]
out_path = sys.argv[2]
email = os.environ.get("NCBI_EMAIL") or os.environ.get("ENTREZ_EMAIL")
if not email:
eprint("ERROR: please set NCBI_EMAIL environment variable (e.g., export NCBI_EMAIL='you@domain')")
sys.exit(1)
Entrez.email = email
targets = read_targets(targets_path)
if not targets:
eprint("ERROR: no targets found in input TSV")
sys.exit(1)
out_rows: List[Dict] = []
for label, query in targets:
eprint(f"Resolving: {label}\t{query}")
res = resolve_query(label, query)
if res:
out_rows.append(res)
time.sleep(0.34) # be nice to NCBI
with open(out_path, "w", newline="") as fh:
w = csv.writer(fh, delimiter="\t")
w.writerow(["label", "accession", "organism", "assembly_name", "assembly_level", "refseq_category"])
for r in out_rows:
w.writerow([
r.get("label", ""),
r.get("accession", ""),
r.get("organism", ""),
r.get("assembly_name", ""),
r.get("assembly_level", ""),
r.get("refseq_category", "")
])
eprint(f"Wrote: {out_path} ({len(out_rows)} rows)")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()File: make_table1_GE11174.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
# make_table1_GE11174.sh
#
# Generate a "Table 1" summary for sample GE11174:
# - sequencing summary (reads, mean length, etc.)
# - assembly stats
# - BUSCO, N50, etc.
#
# Expects to be run with:
# ENV_NAME=gunc_env AUTO_INSTALL=1 THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/make_table1_GE11174.sh
#
# This script writes work products to:
# table1_GE11174_work/
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-GE11174}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-8}"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR:-table1_${SAMPLE}_work}"
AUTO_INSTALL="${AUTO_INSTALL:-0}"
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-}"
log() {
echo "[$(date '+%F %T')] $*" >&2
}
# Activate conda env if requested
if [[ -n "${ENV_NAME}" ]]; then
# shellcheck disable=SC1090
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
fi
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}"
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}/logs"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Basic tool checks
need_cmd() {
command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1 || {
echo "ERROR: required command '$1' not found in PATH" >&2
exit 1
}
}
need_cmd awk
need_cmd grep
need_cmd sed
need_cmd wc
need_cmd python
# Optional tools
if command -v seqkit >/dev/null 2>&1; then
HAVE_SEQKIT=1
else
HAVE_SEQKIT=0
fi
if command -v pigz >/dev/null 2>&1; then
HAVE_PIGZ=1
else
HAVE_PIGZ=0
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Inputs
RAWREADS="${RAWREADS:-${SAMPLE}.rawreads.fastq.gz}"
ASM_FASTA="${ASM_FASTA:-${SAMPLE}.fasta}"
if [[ ! -f "${RAWREADS}" ]]; then
log "WARNING: raw reads file not found: ${RAWREADS}"
fi
if [[ ! -f "${ASM_FASTA}" ]]; then
log "WARNING: assembly fasta not found: ${ASM_FASTA}"
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Sequencing summary
log "Computing sequencing summary..."
READS_N="NA"
MEAN_LEN="NA"
if [[ -f "${RAWREADS}" ]]; then
if [[ "${HAVE_PIGZ}" -eq 1 ]]; then
READS_N="$(pigz -dc "${RAWREADS}" | awk 'END{print NR/4}')"
else
READS_N="$(gzip -dc "${RAWREADS}" | awk 'END{print NR/4}')"
fi
if [[ "${HAVE_SEQKIT}" -eq 1 ]]; then
# parse seqkit stats output
MEAN_LEN="$(seqkit stats "${RAWREADS}" | awk 'NR==2{print $8}')"
fi
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Assembly stats (simple)
log "Computing assembly stats..."
ASM_SIZE="NA"
ASM_CONTIGS="NA"
if [[ -f "${ASM_FASTA}" ]]; then
# Count contigs and sum length
ASM_CONTIGS="$(grep -c '^>' "${ASM_FASTA}" || true)"
ASM_SIZE="$(grep -v '^>' "${ASM_FASTA}" | tr -d '\n' | wc -c | awk '{print $1}')"
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Output a basic TSV summary (can be expanded)
OUT_TSV="${WORKDIR}/table1_${SAMPLE}.tsv"
{
echo -e "sample\treads_total\tmean_read_length_bp\tassembly_contigs\tassembly_size_bp"
echo -e "${SAMPLE}\t${READS_N}\t${MEAN_LEN}\t${ASM_CONTIGS}\t${ASM_SIZE}"
} > "${OUT_TSV}"
log "Wrote: ${OUT_TSV}"File: export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Export a comprehensive Excel workbook from a Table1 pipeline workdir.
Python 3.6 compatible (no PEP604 unions, no builtin generics).
Requires: openpyxl
Sheets (as available):
- Summary
- Table1 (if Table1_*.tsv exists)
- QUAST_report (report.tsv)
- QUAST_metrics (metric/value)
- Mosdepth_summary (*.mosdepth.summary.txt)
- CheckM (checkm_summary.tsv)
- GUNC_* (all .tsv under gunc/out)
- File_Inventory (relative path, size, mtime; optional md5 for small files)
- Run_log_preview (head/tail of latest log under workdir/logs or workdir/*/logs)
"""
from __future__ import print_function
import argparse
import csv
import hashlib
import os
import sys
import time
from pathlib import Path
try:
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
except ImportError:
sys.stderr.write("ERROR: openpyxl is required. Install with:\n"
" conda install -c conda-forge openpyxl\n")
raise
MAX_XLSX_ROWS = 1048576
def safe_sheet_name(name, used):
# Excel: <=31 chars, cannot contain: : \ / ? * [ ]
bad = r'[:\\/?*\[\]]'
base = name.strip() or "Sheet"
base = __import__("re").sub(bad, "_", base)
base = base[:31]
if base not in used:
used.add(base)
return base
# make unique with suffix
for i in range(2, 1000):
suffix = "_%d" % i
cut = 31 - len(suffix)
candidate = (base[:cut] + suffix)
if candidate not in used:
used.add(candidate)
return candidate
raise RuntimeError("Too many duplicate sheet names for base=%s" % base)
def autosize(ws, max_width=60):
for col in ws.columns:
max_len = 0
col_letter = get_column_letter(col[0].column)
for cell in col:
v = cell.value
if v is None:
continue
s = str(v)
if len(s) > max_len:
max_len = len(s)
ws.column_dimensions[col_letter].width = min(max_width, max(10, max_len + 2))
def write_table(ws, header, rows, max_rows=None):
if header:
ws.append(header)
count = 0
for r in rows:
ws.append(r)
count += 1
if max_rows is not None and count >= max_rows:
break
def read_tsv(path, max_rows=None):
header = []
rows = []
with path.open("r", newline="") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f, delimiter="\t")
for i, r in enumerate(reader):
if i == 0:
header = r
continue
rows.append(r)
if max_rows is not None and len(rows) >= max_rows:
break
return header, rows
def read_text_table(path, max_rows=None):
# for mosdepth summary (tsv with header)
return read_tsv(path, max_rows=max_rows)
def md5_file(path, chunk=1024*1024):
h = hashlib.md5()
with path.open("rb") as f:
while True:
b = f.read(chunk)
if not b:
break
h.update(b)
return h.hexdigest()
def find_latest_log(workdir):
candidates = []
# common locations
for p in [workdir / "logs", workdir / "log", workdir / "Logs"]:
if p.exists():
candidates.extend(p.glob("*.log"))
# nested logs
candidates.extend(workdir.glob("**/logs/*.log"))
if not candidates:
return None
candidates.sort(key=lambda x: x.stat().st_mtime, reverse=True)
return candidates[0]
def add_summary_sheet(wb, used, info_items):
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("Summary", used))
ws.append(["Key", "Value"])
for k, v in info_items:
ws.append([k, v])
autosize(ws)
def add_log_preview(wb, used, log_path, head_n=80, tail_n=120):
if log_path is None or not log_path.exists():
return
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("Run_log_preview", used))
ws.append(["Log path", str(log_path)])
ws.append([])
lines = log_path.read_text(errors="replace").splitlines()
ws.append(["--- HEAD (%d) ---" % head_n])
for line in lines[:head_n]:
ws.append([line])
ws.append([])
ws.append(["--- TAIL (%d) ---" % tail_n])
for line in lines[-tail_n:]:
ws.append([line])
ws.column_dimensions["A"].width = 120
def add_file_inventory(wb, used, workdir, do_md5=True, md5_max_bytes=200*1024*1024, max_rows=None):
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("File_Inventory", used))
ws.append(["relative_path", "size_bytes", "mtime_iso", "md5(optional)"])
count = 0
for p in sorted(workdir.rglob("*")):
if p.is_dir():
continue
rel = str(p.relative_to(workdir))
st = p.stat()
mtime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime(st.st_mtime))
md5 = ""
if do_md5 and st.st_size <= md5_max_bytes:
try:
md5 = md5_file(p)
except Exception:
md5 = "ERROR"
ws.append([rel, st.st_size, mtime, md5])
count += 1
if max_rows is not None and count >= max_rows:
break
autosize(ws, max_width=80)
def add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, name, path, max_rows=None):
header, rows = read_tsv(path, max_rows=max_rows)
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name(name, used))
write_table(ws, header, rows, max_rows=max_rows)
autosize(ws, max_width=80)
def add_quast_metrics_sheet(wb, used, quast_report_tsv):
header, rows = read_tsv(quast_report_tsv, max_rows=None)
if not header or len(header) < 2:
return
asm_name = header[1]
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=safe_sheet_name("QUAST_metrics", used))
ws.append(["Metric", asm_name])
for r in rows:
if not r:
continue
metric = r[0]
val = r[1] if len(r) > 1 else ""
ws.append([metric, val])
autosize(ws, max_width=80)
def main():
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("--workdir", required=True, help="workdir produced by pipeline (e.g., table1_GE11174_work)")
ap.add_argument("--out", required=True, help="output .xlsx")
ap.add_argument("--sample", default="", help="sample name for summary")
ap.add_argument("--max-rows", type=int, default=200000, help="max rows per large sheet")
ap.add_argument("--no-md5", action="store_true", help="skip md5 calculation in File_Inventory")
args = ap.parse_args()
workdir = Path(args.workdir).resolve()
out = Path(args.out).resolve()
if not workdir.exists():
sys.stderr.write("ERROR: workdir not found: %s\n" % workdir)
sys.exit(2)
wb = Workbook()
# remove default sheet
wb.remove(wb.active)
used = set()
# Summary info
info = [
("sample", args.sample or ""),
("workdir", str(workdir)),
("generated_at", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")),
("python", sys.version.replace("\n", " ")),
("openpyxl", __import__("openpyxl").__version__),
]
add_summary_sheet(wb, used, info)
# Table1 TSV (try common names)
table1_candidates = list(workdir.glob("Table1_*.tsv")) + list(workdir.glob("*.tsv"))
# Prefer Table1_*.tsv in workdir root
table1_path = None
for p in table1_candidates:
if p.name.startswith("Table1_") and p.suffix == ".tsv":
table1_path = p
break
if table1_path is None:
# maybe created in cwd, not inside workdir; try alongside workdir
parent = workdir.parent
for p in parent.glob("Table1_*.tsv"):
if args.sample and args.sample in p.name:
table1_path = p
break
if table1_path is None and list(parent.glob("Table1_*.tsv")):
table1_path = sorted(parent.glob("Table1_*.tsv"))[0]
if table1_path is not None and table1_path.exists():
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, "Table1", table1_path, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# QUAST
quast_report = workdir / "quast" / "report.tsv"
if quast_report.exists():
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, "QUAST_report", quast_report, max_rows=args.max_rows)
add_quast_metrics_sheet(wb, used, quast_report)
# Mosdepth summary
for p in sorted((workdir / "map").glob("*.mosdepth.summary.txt")):
# mosdepth summary is TSV-like
name = "Mosdepth_" + p.stem.replace(".mosdepth.summary", "")
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, name[:31], p, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# CheckM
checkm_sum = workdir / "checkm" / "checkm_summary.tsv"
if checkm_sum.exists():
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, "CheckM", checkm_sum, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# GUNC outputs (all TSV under gunc/out)
gunc_out = workdir / "gunc" / "out"
if gunc_out.exists():
for p in sorted(gunc_out.rglob("*.tsv")):
rel = str(p.relative_to(gunc_out))
sheet = "GUNC_" + rel.replace("/", "_").replace("\\", "_").replace(".tsv", "")
add_tsv_sheet(wb, used, sheet[:31], p, max_rows=args.max_rows)
# Log preview
latest_log = find_latest_log(workdir)
add_log_preview(wb, used, latest_log)
# File inventory
add_file_inventory(
wb, used, workdir,
do_md5=(not args.no_md5),
md5_max_bytes=200*1024*1024,
max_rows=args.max_rows
)
# Save
out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
wb.save(str(out))
print("OK: wrote %s" % out)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()File: make_table1_with_excel.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
# make_table1_with_excel.sh
#
# Wrapper to run:
# 1) make_table1_* (stats extraction)
# 2) export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py
#
# Example:
# ENV_NAME=gunc_env AUTO_INSTALL=1 THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/make_table1_with_excel.sh
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-GE11174}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-8}"
WORKDIR="${WORKDIR:-table1_${SAMPLE}_work}"
OUT_XLSX="${OUT_XLSX:-Comprehensive_${SAMPLE}.xlsx}"
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-}"
AUTO_INSTALL="${AUTO_INSTALL:-0}"
log() {
echo "[$(date '+%F %T')] $*" >&2
}
# Activate conda env if requested
if [[ -n "${ENV_NAME}" ]]; then
# shellcheck disable=SC1090
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
fi
mkdir -p "${WORKDIR}"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Locate scripts
SCRIPT_DIR="$(cd "$(dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}")" && pwd)"
MAKE_TABLE1="${MAKE_TABLE1_SCRIPT:-${SCRIPT_DIR}/make_table1_${SAMPLE}.sh}"
EXPORT_PY="${EXPORT_PY_SCRIPT:-${SCRIPT_DIR}/export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py}"
# Fallback for naming mismatch (e.g., make_table1_GE11174.sh)
if [[ ! -f "${MAKE_TABLE1}" ]]; then
MAKE_TABLE1="${SCRIPT_DIR}/make_table1_GE11174.sh"
fi
if [[ ! -f "${MAKE_TABLE1}" ]]; then
echo "ERROR: make_table1 script not found" >&2
exit 1
fi
if [[ ! -f "${EXPORT_PY}" ]]; then
log "WARNING: export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py not found next to this script."
log " You can set EXPORT_PY_SCRIPT=/path/to/export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py"
fi
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 1
log "STEP 1: generating workdir stats..."
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME}" AUTO_INSTALL="${AUTO_INSTALL}" THREADS="${THREADS}" SAMPLE="${SAMPLE}" WORKDIR="${WORKDIR}" \
bash "${MAKE_TABLE1}"
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step 2
if [[ -f "${EXPORT_PY}" ]]; then
log "STEP 2: exporting to Excel..."
python "${EXPORT_PY}" \
--workdir "${WORKDIR}" \
--out "${OUT_XLSX}" \
--max-rows 200000 \
--sample "${SAMPLE}"
log "Wrote: ${OUT_XLSX}"
else
log "Skipped Excel export (missing export script). Workdir still produced: ${WORKDIR}"
fiFile: merge_amr_sources_by_gene.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
merge_amr_sources_by_gene.py
Merge AMR calls from multiple sources (e.g., ABRicate outputs from MEGARes/ResFinder
and RGI/CARD) by gene name, producing a combined table suitable for reporting/export.
This script is intentionally lightweight and focuses on:
- reading tabular ABRicate outputs
- normalizing gene names
- merging into a per-gene summary
Expected inputs/paths are typically set in your working directory structure.
"""
import os
import sys
import csv
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
def eprint(*args, **kwargs):
print(*args, file=sys.stderr, **kwargs)
def read_abricate_tab(path: str) -> List[Dict[str, str]]:
rows: List[Dict[str, str]] = []
with open(path, "r", newline="") as fh:
for line in fh:
if line.startswith("#") or not line.strip():
continue
# ABRicate default is tab-delimited with columns:
# FILE, SEQUENCE, START, END, STRAND, GENE, COVERAGE, COVERAGE_MAP, GAPS,
# %COVERAGE, %IDENTITY, DATABASE, ACCESSION, PRODUCT, RESISTANCE
parts = line.rstrip("\n").split("\t")
if len(parts) < 12:
continue
gene = parts[5].strip()
rows.append({
"gene": gene,
"identity": parts[10].strip(),
"coverage": parts[9].strip(),
"db": parts[11].strip(),
"product": parts[13].strip() if len(parts) > 13 else "",
"raw": line.rstrip("\n")
})
return rows
def normalize_gene(gene: str) -> str:
g = gene.strip()
# Add any project-specific normalization rules here
return g
def merge_sources(sources: List[Tuple[str, str]]) -> Dict[str, Dict[str, List[Dict[str, str]]]]:
merged: Dict[str, Dict[str, List[Dict[str, str]]]] = defaultdict(lambda: defaultdict(list))
for src_name, path in sources:
if not os.path.exists(path):
eprint(f"WARNING: missing source file: {path}")
continue
rows = read_abricate_tab(path)
for r in rows:
g = normalize_gene(r["gene"])
merged[g][src_name].append(r)
return merged
def write_merged_tsv(out_path: str, merged: Dict[str, Dict[str, List[Dict[str, str]]]]):
# Flatten into a simple TSV
with open(out_path, "w", newline="") as fh:
w = csv.writer(fh, delimiter="\t")
w.writerow(["gene", "sources", "best_identity", "best_coverage", "notes"])
for gene, src_map in sorted(merged.items()):
srcs = sorted(src_map.keys())
best_id = ""
best_cov = ""
notes = []
# pick best identity/coverage across all hits
for s in srcs:
for r in src_map[s]:
if not best_id or float(r["identity"]) > float(best_id):
best_id = r["identity"]
if not best_cov or float(r["coverage"]) > float(best_cov):
best_cov = r["coverage"]
if r.get("product"):
notes.append(f"{s}:{r['product']}")
w.writerow([gene, ",".join(srcs), best_id, best_cov, "; ".join(notes)])
def main():
# Default expected layout (customize as needed)
workdir = os.environ.get("WORKDIR", "resistome_virulence_GE11174")
sample = os.environ.get("SAMPLE", "GE11174")
rawdir = os.path.join(workdir, "raw")
sources = [
("MEGARes", os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.megares.tab")),
("CARD", os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.card.tab")),
("ResFinder", os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.resfinder.tab")),
("VFDB", os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.vfdb.tab")),
]
merged = merge_sources(sources)
out_path = os.path.join(workdir, f"merged_by_gene_{sample}.tsv")
write_merged_tsv(out_path, merged)
eprint(f"Wrote merged table: {out_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()File: export_resistome_virulence_to_excel_py36.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
export_resistome_virulence_to_excel_py36.py
Export resistome + virulence profiling outputs to an Excel workbook, compatible with
older Python (3.6) style environments.
Typical usage:
python export_resistome_virulence_to_excel_py36.py \
--workdir resistome_virulence_GE11174 \
--sample GE11174 \
--out Resistome_Virulence_GE11174.xlsx
Requires:
- openpyxl
"""
import os
import sys
import csv
import argparse
from typing import List, Dict
try:
from openpyxl import Workbook
except ImportError:
sys.stderr.write("ERROR: openpyxl is required\n")
sys.exit(1)
def eprint(*args, **kwargs):
print(*args, file=sys.stderr, **kwargs)
def read_tab_file(path: str) -> List[List[str]]:
rows: List[List[str]] = []
with open(path, "r", newline="") as fh:
for line in fh:
if line.startswith("#") or not line.strip():
continue
rows.append(line.rstrip("\n").split("\t"))
return rows
def autosize(ws):
# basic autosize columns
for col_cells in ws.columns:
max_len = 0
col_letter = col_cells[0].column_letter
for c in col_cells:
if c.value is None:
continue
max_len = max(max_len, len(str(c.value)))
ws.column_dimensions[col_letter].width = min(max_len + 2, 60)
def add_sheet_from_tab(wb: Workbook, title: str, path: str):
ws = wb.create_sheet(title=title)
if not os.path.exists(path):
ws.append([f"Missing file: {path}"])
return
rows = read_tab_file(path)
if not rows:
ws.append(["No rows"])
return
for r in rows:
ws.append(r)
autosize(ws)
def main():
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("--workdir", required=True)
ap.add_argument("--sample", required=True)
ap.add_argument("--out", required=True)
args = ap.parse_args()
workdir = args.workdir
sample = args.sample
out_xlsx = args.out
rawdir = os.path.join(workdir, "raw")
files = {
"MEGARes": os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.megares.tab"),
"CARD": os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.card.tab"),
"ResFinder": os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.resfinder.tab"),
"VFDB": os.path.join(rawdir, f"{sample}.vfdb.tab"),
"Merged_by_gene": os.path.join(workdir, f"merged_by_gene_{sample}.tsv"),
}
wb = Workbook()
# Remove default sheet
default = wb.active
wb.remove(default)
for title, path in files.items():
eprint(f"Adding sheet: {title} <- {path}")
add_sheet_from_tab(wb, title, path)
wb.save(out_xlsx)
eprint(f"Wrote Excel: {out_xlsx}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()File: plot_tree_v4.R
#!/usr/bin/env Rscript
# plot_tree_v4.R
#
# Plot a RAxML-NG support tree with custom labels.
#
# Args:
# 1) support tree file (e.g., core.raxml.support)
# 2) labels.tsv (columns: accession
<TAB>display)
# 3) root N (numeric, e.g., 6)
# 4) output PDF
# 5) output PNG
suppressPackageStartupMessages({
library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggtree)
library(dplyr)
library(readr)
library(aplot)
})
args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly=TRUE)
if (length(args) < 5) {
cat("Usage: plot_tree_v4.R
<support_tree> <labels.tsv> <root_n> <out.pdf> <out.png>\n")
quit(status=1)
}
support_tree <- args[1]
labels_tsv <- args[2]
root_n <- as.numeric(args[3])
out_pdf <- args[4]
out_png <- args[5]
# Read tree
tr <- read.tree(support_tree)
# Read labels
lab <- read_tsv(labels_tsv, col_types=cols(.default="c"))
colnames(lab) <- c("accession","display")
# Map labels
# Current tip labels may include accession-like tokens.
# We'll try exact match first; otherwise keep original.
tip_map <- setNames(lab$display, lab$accession)
new_labels <- sapply(tr$tip.label, function(x) {
if (x %in% names(tip_map)) {
tip_map[[x]]
} else {
x
}
})
tr$tip.label <- new_labels
# Root by nth tip if requested
if (!is.na(root_n) && root_n > 0 && root_n <= length(tr$tip.label)) {
tr <- root(tr, outgroup=tr$tip.label[root_n], resolve.root=TRUE)
}
# Plot
p <- ggtree(tr) +
geom_tiplab(size=3) +
theme_tree2()
# Save
ggsave(out_pdf, plot=p, width=8, height=8)
ggsave(out_png, plot=p, width=8, height=8, dpi=300)
cat(sprintf("Wrote: %s\nWrote: %s\n", out_pdf, out_png))File: run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -Eeuo pipefail
# -------- user inputs --------
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-bengal3_ac3}"
ASM="${ASM:-GE11174.fasta}"
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-GE11174}"
OUTDIR="${OUTDIR:-resistome_virulence_${SAMPLE}}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-16}"
# thresholds (set to 0/0 if you truly want ABRicate defaults)
MINID="${MINID:-90}"
MINCOV="${MINCOV:-60}"
# ----------------------------
log(){ echo "[$(date +'%F %T')] $*" >&2; }
need_cmd(){ command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1; }
activate_env() {
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
}
main(){
activate_env
mkdir -p "${OUTDIR}"/{raw,amr,virulence,card,tmp}
log "Env: ${ENV_NAME}"
log "ASM: ${ASM}"
log "Sample: ${SAMPLE}"
log "Outdir: ${OUTDIR}"
log "ABRicate thresholds: MINID=${MINID} MINCOV=${MINCOV}"
log "ABRicate DB list:"
abricate --list | egrep -i "vfdb|resfinder|megares|card" || true
# Make sure indices exist
log "Running abricate --setupdb (safe even if already done)..."
abricate --setupdb
# ---- ABRicate AMR DBs ----
log "Running ABRicate: ResFinder"
abricate --db resfinder --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: MEGARes"
abricate --db megares --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
# ---- Virulence (VFDB) ----
log "Running ABRicate: VFDB"
abricate --db vfdb --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
# ---- CARD: prefer RGI if available, else ABRicate card ----
CARD_MODE="ABRicate"
if need_cmd rgi; then
log "RGI found. Trying RGI (CARD) ..."
set +e
rgi main --input_sequence "${ASM}" --output_file "${OUTDIR}/card/${SAMPLE}.rgi" --input_type contig --num_threads "${THREADS}"
rc=$?
set -e
if [[ $rc -eq 0 ]]; then
CARD_MODE="RGI"
else
log "RGI failed (likely CARD data not installed). Falling back to ABRicate card."
fi
fi
if [[ "${CARD_MODE}" == "ABRicate" ]]; then
log "Running ABRicate: CARD"
abricate --db card --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
fi
# ---- Build deduplicated tables ----
log "Creating deduplicated AMR/VFDB tables..."
export OUTDIR SAMPLE CARD_MODE
python - <<'PY'
import os, re
from pathlib import Path
import pandas as pd
from io import StringIO
outdir = Path(os.environ["OUTDIR"])
sample = os.environ["SAMPLE"]
card_mode = os.environ["CARD_MODE"]
def read_abricate_tab(path: Path, source: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
if not path.exists() or path.stat().st_size == 0:
return pd.DataFrame()
lines=[]
with path.open("r", errors="replace") as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("#") or not line.strip():
continue
lines.append(line)
if not lines:
return pd.DataFrame()
df = pd.read_csv(StringIO("".join(lines)), sep="\t", dtype=str)
df.insert(0, "Source", source)
return df
def to_num(s):
try:
return float(str(s).replace("%",""))
except:
return None
def normalize_abricate(df: pd.DataFrame, dbname: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
if df.empty:
return pd.DataFrame(columns=[
"Source","Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"
])
# Column names vary slightly; handle common ones
gene = "GENE" if "GENE" in df.columns else None
prod = "PRODUCT" if "PRODUCT" in df.columns else None
acc = "ACCESSION" if "ACCESSION" in df.columns else None
contig = "SEQUENCE" if "SEQUENCE" in df.columns else ("CONTIG" if "CONTIG" in df.columns else None)
start = "START" if "START" in df.columns else None
end = "END" if "END" in df.columns else None
strand= "STRAND" if "STRAND" in df.columns else None
pid = "%IDENTITY" if "%IDENTITY" in df.columns else ("% Identity" if "% Identity" in df.columns else None)
pcv = "%COVERAGE" if "%COVERAGE" in df.columns else ("% Coverage" if "% Coverage" in df.columns else None)
out = pd.DataFrame()
out["Source"] = df["Source"]
out["Database"] = dbname
out["Gene"] = df[gene] if gene else ""
out["Product"] = df[prod] if prod else ""
out["Accession"] = df[acc] if acc else ""
out["Contig"] = df[contig] if contig else ""
out["Start"] = df[start] if start else ""
out["End"] = df[end] if end else ""
out["Strand"] = df[strand] if strand else ""
out["Pct_Identity"] = df[pid] if pid else ""
out["Pct_Coverage"] = df[pcv] if pcv else ""
return out
def dedup_best(df: pd.DataFrame, key_cols):
"""Keep best hit per key by highest identity, then coverage, then longest span."""
if df.empty:
return df
# numeric helpers
df = df.copy()
df["_pid"] = df["Pct_Identity"].map(to_num)
df["_pcv"] = df["Pct_Coverage"].map(to_num)
def span(row):
try:
return abs(int(row["End"]) - int(row["Start"])) + 1
except:
return 0
df["_span"] = df.apply(span, axis=1)
# sort best-first
df = df.sort_values(by=["_pid","_pcv","_span"], ascending=[False,False,False], na_position="last")
df = df.drop_duplicates(subset=key_cols, keep="first")
df = df.drop(columns=["_pid","_pcv","_span"])
return df
# ---------- AMR inputs ----------
amr_frames = []
# ResFinder (often 0 hits; still okay)
resfinder = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.resfinder.tab"
df = read_abricate_tab(resfinder, "ABRicate")
amr_frames.append(normalize_abricate(df, "ResFinder"))
# MEGARes
megares = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.megares.tab"
df = read_abricate_tab(megares, "ABRicate")
amr_frames.append(normalize_abricate(df, "MEGARes"))
# CARD: RGI or ABRicate
if card_mode == "RGI":
# Try common RGI tab outputs
prefix = outdir / "card" / f"{sample}.rgi"
rgi_tab = None
for ext in [".txt",".tab",".tsv"]:
p = Path(str(prefix) + ext)
if p.exists() and p.stat().st_size > 0:
rgi_tab = p
break
if rgi_tab is not None:
rgi = pd.read_csv(rgi_tab, sep="\t", dtype=str)
out = pd.DataFrame()
out["Source"] = "RGI"
out["Database"] = "CARD"
# Prefer ARO_name/Best_Hit_ARO if present
out["Gene"] = rgi["ARO_name"] if "ARO_name" in rgi.columns else (rgi["Best_Hit_ARO"] if "Best_Hit_ARO" in rgi.columns else "")
out["Product"] = rgi["ARO_name"] if "ARO_name" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Accession"] = rgi["ARO_accession"] if "ARO_accession" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Contig"] = rgi["Sequence"] if "Sequence" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Start"] = rgi["Start"] if "Start" in rgi.columns else ""
out["End"] = rgi["Stop"] if "Stop" in rgi.columns else (rgi["End"] if "End" in rgi.columns else "")
out["Strand"] = rgi["Orientation"] if "Orientation" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Pct_Identity"] = rgi["% Identity"] if "% Identity" in rgi.columns else ""
out["Pct_Coverage"] = rgi["% Coverage"] if "% Coverage" in rgi.columns else ""
amr_frames.append(out)
else:
card = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.card.tab"
df = read_abricate_tab(card, "ABRicate")
amr_frames.append(normalize_abricate(df, "CARD"))
amr_all = pd.concat([x for x in amr_frames if not x.empty], ignore_index=True) if any(not x.empty for x in amr_frames) else pd.DataFrame(
columns=["Source","Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"]
)
# Deduplicate within each (Database,Gene) – this is usually what you want for manuscript tables
amr_dedup = dedup_best(amr_all, key_cols=["Database","Gene"])
# Sort nicely
if not amr_dedup.empty:
amr_dedup = amr_dedup.sort_values(["Database","Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
amr_out = outdir / "Table_AMR_genes_dedup.tsv"
amr_dedup.to_csv(amr_out, sep="\t", index=False)
# ---------- Virulence (VFDB) ----------
vfdb = outdir / "raw" / f"{sample}.vfdb.tab"
vf = read_abricate_tab(vfdb, "ABRicate")
vf_norm = normalize_abricate(vf, "VFDB")
# Dedup within (Gene) for VFDB (or use Database,Gene; Database constant)
vf_dedup = dedup_best(vf_norm, key_cols=["Gene"]) if not vf_norm.empty else vf_norm
if not vf_dedup.empty:
vf_dedup = vf_dedup.sort_values(["Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
vf_out = outdir / "Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv"
vf_dedup.to_csv(vf_out, sep="\t", index=False)
print("OK wrote:")
print(" ", amr_out)
print(" ", vf_out)
PY
log "Done."
log "Outputs:"
log " ${OUTDIR}/Table_AMR_genes_dedup.tsv"
log " ${OUTDIR}/Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv"
log "Raw:"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.*.tab"
}
mainFile: run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -Eeuo pipefail
# ------------------- USER SETTINGS -------------------
ENV_NAME="${ENV_NAME:-bengal3_ac3}"
ASM="${ASM:-GE11174.fasta}" # input assembly fasta
SAMPLE="${SAMPLE:-GE11174}"
OUTDIR="${OUTDIR:-resistome_virulence_${SAMPLE}}"
THREADS="${THREADS:-16}"
# ABRicate thresholds
# If you want your earlier "35 genes" behavior, use MINID=70 MINCOV=50.
# If you want stricter: e.g. MINID=80 MINCOV=70.
MINID="${MINID:-70}"
MINCOV="${MINCOV:-50}"
# -----------------------------------------------------
ts(){ date +"%F %T"; }
log(){ echo "[$(ts)] $*" >&2; }
on_err(){
local ec=$?
log "ERROR: failed (exit=${ec}) at line ${BASH_LINENO[0]}: ${BASH_COMMAND}"
exit $ec
}
trap on_err ERR
need_cmd(){ command -v "$1" >/dev/null 2>&1; }
activate_env() {
# shellcheck disable=SC1091
source "$(conda info --base)/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
conda activate "${ENV_NAME}"
}
main(){
activate_env
log "Env: ${ENV_NAME}"
log "ASM: ${ASM}"
log "Sample: ${SAMPLE}"
log "Outdir: ${OUTDIR}"
log "Threads: ${THREADS}"
log "ABRicate thresholds: MINID=${MINID} MINCOV=${MINCOV}"
mkdir -p "${OUTDIR}"/{raw,logs}
# Save full log
LOGFILE="${OUTDIR}/logs/run_$(date +'%F_%H%M%S').log"
exec > >(tee -a "${LOGFILE}") 2>&1
log "Tool versions:"
abricate --version || true
abricate-get_db --help | head -n 5 || true
log "ABRicate DB list (selected):"
abricate --list | egrep -i "vfdb|resfinder|megares|card" || true
log "Indexing ABRicate databases (safe to re-run)..."
abricate --setupdb
# ---------------- Run ABRicate ----------------
log "Running ABRicate: MEGARes"
abricate --db megares --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: CARD"
abricate --db card --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: ResFinder"
abricate --db resfinder --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
log "Running ABRicate: VFDB"
abricate --db vfdb --minid "${MINID}" --mincov "${MINCOV}" "${ASM}" > "${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
# --------------- Build tables -----------------
export OUTDIR SAMPLE
export MEGARES_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
export CARD_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
export RESFINDER_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
export VFDB_TAB="${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
export AMR_OUT="${OUTDIR}/Table_AMR_genes_one_per_gene.tsv"
export VIR_OUT="${OUTDIR}/Table_Virulence_VFDB_dedup.tsv"
export STATUS_OUT="${OUTDIR}/Table_DB_hit_counts.tsv"
log "Generating deduplicated tables..."
python - <<'PY'
import os
import pandas as pd
from pathlib import Path
megares_tab = Path(os.environ["MEGARES_TAB"])
card_tab = Path(os.environ["CARD_TAB"])
resfinder_tab = Path(os.environ["RESFINDER_TAB"])
vfdb_tab = Path(os.environ["VFDB_TAB"])
amr_out = Path(os.environ["AMR_OUT"])
vir_out = Path(os.environ["VIR_OUT"])
status_out = Path(os.environ["STATUS_OUT"])
def read_abricate(path: Path) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Parse ABRicate .tab where header line starts with '#FILE'."""
if (not path.exists()) or path.stat().st_size == 0:
return pd.DataFrame()
header = None
rows = []
with path.open("r", errors="replace") as f:
for line in f:
if not line.strip():
continue
if line.startswith("#FILE"):
header = line.lstrip("#").rstrip("\n").split("\t")
continue
if line.startswith("#"):
continue
rows.append(line.rstrip("\n").split("\t"))
if header is None:
return pd.DataFrame()
if not rows:
return pd.DataFrame(columns=header)
return pd.DataFrame(rows, columns=header)
def normalize(df: pd.DataFrame, dbname: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
cols_out = ["Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"]
if df is None or df.empty:
return pd.DataFrame(columns=cols_out)
out = pd.DataFrame({
"Database": dbname,
"Gene": df.get("GENE",""),
"Product": df.get("PRODUCT",""),
"Accession": df.get("ACCESSION",""),
"Contig": df.get("SEQUENCE",""),
"Start": df.get("START",""),
"End": df.get("END",""),
"Strand": df.get("STRAND",""),
"Pct_Identity": pd.to_numeric(df.get("%IDENTITY",""), errors="coerce"),
"Pct_Coverage": pd.to_numeric(df.get("%COVERAGE",""), errors="coerce"),
})
return out[cols_out]
def best_hit_dedup(df: pd.DataFrame, key_cols):
"""Keep best hit by highest identity, then coverage, then alignment length."""
if df.empty:
return df
d = df.copy()
d["Start_i"] = pd.to_numeric(d["Start"], errors="coerce").fillna(0).astype(int)
d["End_i"] = pd.to_numeric(d["End"], errors="coerce").fillna(0).astype(int)
d["Len"] = (d["End_i"] - d["Start_i"]).abs() + 1
d = d.sort_values(["Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage","Len"], ascending=[False,False,False])
d = d.drop_duplicates(subset=key_cols, keep="first")
return d.drop(columns=["Start_i","End_i","Len"])
def count_hits(path: Path) -> int:
if not path.exists():
return 0
n = 0
with path.open() as f:
for line in f:
if line.startswith("#") or not line.strip():
continue
n += 1
return n
# -------- load + normalize --------
parts = []
for dbname, p in [("MEGARes", megares_tab), ("CARD", card_tab), ("ResFinder", resfinder_tab)]:
df = read_abricate(p)
parts.append(normalize(df, dbname))
amr_all = pd.concat([x for x in parts if not x.empty], ignore_index=True) if any(not x.empty for x in parts) else pd.DataFrame(
columns=["Database","Gene","Product","Accession","Contig","Start","End","Strand","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"]
)
# remove empty genes
amr_all = amr_all[amr_all["Gene"].astype(str).str.len() > 0].copy()
# best per (Database,Gene)
amr_db_gene = best_hit_dedup(amr_all, ["Database","Gene"]) if not amr_all.empty else amr_all
# one row per Gene overall, priority: CARD > ResFinder > MEGARes
priority = {"CARD": 0, "ResFinder": 1, "MEGARes": 2}
if not amr_db_gene.empty:
amr_db_gene["prio"] = amr_db_gene["Database"].map(priority).fillna(9).astype(int)
amr_one = amr_db_gene.sort_values(
["Gene","prio","Pct_Identity","Pct_Coverage"],
ascending=[True, True, False, False]
)
amr_one = amr_one.drop_duplicates(["Gene"], keep="first").drop(columns=["prio"])
amr_one = amr_one.sort_values(["Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
else:
amr_one = amr_db_gene
amr_out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
amr_one.to_csv(amr_out, sep="\t", index=False)
# -------- VFDB --------
vf = normalize(read_abricate(vfdb_tab), "VFDB")
vf = vf[vf["Gene"].astype(str).str.len() > 0].copy()
vf_one = best_hit_dedup(vf, ["Gene"]) if not vf.empty else vf
if not vf_one.empty:
vf_one = vf_one.sort_values(["Gene"]).reset_index(drop=True)
vir_out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
vf_one.to_csv(vir_out, sep="\t", index=False)
# -------- status counts --------
status = pd.DataFrame([
{"Database":"MEGARes", "Hit_lines": count_hits(megares_tab), "File": str(megares_tab)},
{"Database":"CARD", "Hit_lines": count_hits(card_tab), "File": str(card_tab)},
{"Database":"ResFinder", "Hit_lines": count_hits(resfinder_tab), "File": str(resfinder_tab)},
{"Database":"VFDB", "Hit_lines": count_hits(vfdb_tab), "File": str(vfdb_tab)},
])
status_out.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
status.to_csv(status_out, sep="\t", index=False)
print("OK wrote:")
print(" ", amr_out, "rows=", len(amr_one))
print(" ", vir_out, "rows=", len(vf_one))
print(" ", status_out)
PY
log "Finished."
log "Main outputs:"
log " ${AMR_OUT}"
log " ${VIR_OUT}"
log " ${STATUS_OUT}"
log "Raw ABRicate outputs:"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.megares.tab"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.card.tab"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.resfinder.tab"
log " ${OUTDIR}/raw/${SAMPLE}.vfdb.tab"
log "Log:"
log " ${LOGFILE}"
}
main**
Processing Data_Benjamin_DNAseq_2026_GE11174
-
Download the kmerfinder database: https://www.genomicepidemiology.org/services/ –> https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/KmerFinder/ –> https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/KmerFinder/etc/kmerfinder_db.tar.gz
# Download 20190108_kmerfinder_stable_dirs.tar.gz from https://zenodo.org/records/13447056 -
Run nextflow bacass
#–kmerfinderdb /path/to/kmerfinder/bacteria.tar.gz #–kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder_db.tar.gz #–kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/20190108_kmerfinder_stable_dirs.tar.gz nextflow run nf-core/bacass -r 2.5.0 -profile docker \ –input samplesheet.tsv \ –outdir bacass_out \ –assembly_type long \ –kraken2db /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/k2_standard_08_GB_20251015.tar.gz \ –kmerfinderdb /mnt/nvme1n1p1/REFs/kmerfinder/bacteria/ \ -resume
-
KmerFinder summary
From the KmerFinder summary, the top hit is Gibbsiella quercinecans (strain FRB97; NZ_CP014136.1) with much higher score and coverage than the second hit (which is low coverage). So it’s fair to write:
“KmerFinder indicates the isolate is most consistent with Gibbsiella quercinecans.”
…but for a species call (especially for publication), you should confirm with ANI (or a genome taxonomy tool), because k-mer hits alone aren’t always definitive.
-
Using https://www.bv-brc.org/app/ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis to annotate the genome using scaffolded results from bacass. ComprehensiveGenomeAnalysis provides comprehensive overview of the data.
-
Generate the Table 1 Summary of sequence data and genome features under the env gunc_env
activate the env that has openpyxl
mamba activate gunc_env mamba install -n gunc_env -c conda-forge openpyxl -y mamba deactivate
STEP_1
ENV_NAME=gunc_env AUTO_INSTALL=1 THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/make_table1_GE11174.sh
STEP_2
python export_table1_stats_to_excel_py36_compat.py \ –workdir table1_GE11174_work \ –out Comprehensive_GE11174.xlsx \ –max-rows 200000 \ –sample GE11174
STEP_1+2
ENV_NAME=gunc_env AUTO_INSTALL=1 THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/make_table1_with_excel.sh
#For the items “Total number of reads sequenced” and “Mean read length (bp)” pigz -dc GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz | awk ‘END{print NR/4}’ seqkit stats GE11174.rawreads.fastq.gz
-
Antimicrobial resistance gene profiling and Resistome and Virulence Profiling with Abricate and RGI (Reisistance Gene Identifier)
Table 4. Specialty Genes
Source Genes
NDARO 1
Antibiotic Resistance CARD 15
Antibiotic Resistance PATRIC 55
Drug Target TTD 38
Metal Resistance BacMet 29
Transporter TCDB 250
Virulance factor VFDB 33
https://www.genomicepidemiology.org/services/
https://genepi.dk/
conda activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 abricate –list #DATABASE SEQUENCES DBTYPE DATE #vfdb 2597 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #resfinder 3077 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #argannot 2223 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #ecoh 597 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #megares 6635 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #card 2631 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #ecoli_vf 2701 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #plasmidfinder 460 nucl 2025-Oct-22 #ncbi 5386 nucl 2025-Oct-22 abricate-get_db –list #Choices: argannot bacmet2 card ecoh ecoli_vf megares ncbi plasmidfinder resfinder vfdb victors (default ”).
CARD
abricate-get_db –db card
MEGARes (automatically install, if error try MANUAL install as below)
abricate-get_db –db megares
MANUAL install
wget -O megares_database_v3.00.fasta \ “https://www.meglab.org/downloads/megares_v3.00/megares_database_v3.00.fasta” #wget -O megares_drugs_database_v3.00.fasta \ “https://www.meglab.org/downloads/megares_v3.00/megares_drugs_database_v3.00.fasta“
1) Define dbdir (adjust to your env; from your logs it’s inside the conda env)
DBDIR=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3/db
2) Create a custom db folder for MEGARes v3.0
mkdir -p ${DBDIR}/megares_v3.0
3) Copy the downloaded MEGARes v3.0 nucleotide FASTA to ‘sequences’
cp megares_database_v3.00.fasta ${DBDIR}/megares_v3.0/sequences
4) Build ABRicate indices
abricate –setupdb
#abricate-get_db –setupdb abricate –list | egrep ‘card|megares’ abricate –list | grep -i megares
chmod +x run_resistome_virulome.sh ASM=GE11174.fasta SAMPLE=GE11174 THREADS=32 ./run_resistome_virulome.sh
chmod +x run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=GE11174.fasta SAMPLE=GE11174 THREADS=32 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=./vrap_HF/spades/scaffolds.fasta SAMPLE=HF THREADS=32 ~/Scripts/run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 ASM=GE11174.fasta SAMPLE=GE11174 MINID=80 MINCOV=60 ./run_resistome_virulome_dedup.sh
grep -vc ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab grep -vc ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab grep -vc ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab grep -vc ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab
grep -v ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab | grep -v ‘^[[:space:]]$’ | head -n 3 grep -v ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab | grep -v ‘^[[:space:]]$’ | head -n 3 grep -v ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab | grep -v ‘^[[:space:]]$’ | head -n 3 grep -v ‘^#’ resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab | grep -v ‘^[[:space:]]$’ | head -n 3
chmod +x make_dedup_tables_from_abricate.sh OUTDIR=resistome_virulence_GE11174 SAMPLE=GE11174 ./make_dedup_tables_from_abricate.sh
chmod +x run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 \ ASM=GE11174.fasta \ SAMPLE=GE11174 \ OUTDIR=resistome_virulence_GE11174 \ MINID=80 MINCOV=60 \ THREADS=32 \ ./run_abricate_resistome_virulome_one_per_gene.sh
#ABRicate thresholds: MINID=70 MINCOV=50 Database Hit_lines File MEGARes 35 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab CARD 28 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab ResFinder 2 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab VFDB 18 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab
#ABRicate thresholds: MINID=80 MINCOV=60 Database Hit_lines File MEGARes 3 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.megares.tab CARD 1 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.card.tab ResFinder 0 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.resfinder.tab VFDB 0 resistome_virulence_GE11174/raw/GE11174.vfdb.tab
python merge_amr_sources_by_gene.py python export_resistome_virulence_to_excel_py36.py \ –workdir resistome_virulence_GE11174 \ –sample GE11174 \ –out Resistome_Virulence_GE11174.xlsx
Methods sentence (AMR + virulence)
AMR genes were identified by screening the genome assembly with ABRicate against the MEGARes and ResFinder databases, using minimum identity and coverage thresholds of X% and Y%, respectively. CARD-based AMR determinants were additionally predicted using RGI (Resistance Gene Identifier) to leverage curated resistance models. Virulence factors were screened using ABRicate against VFDB under the same thresholds.
Replace X/Y with your actual values (e.g., 90/60) or state “default parameters” if you truly used defaults.
Table 2 caption (AMR)
Table 2. AMR gene profiling of the genome assembly. Hits were detected using ABRicate (MEGARes and ResFinder) and RGI (CARD). The presence of AMR-associated genes does not necessarily imply phenotypic resistance, which may depend on allele type, genomic context/expression, and/or SNP-mediated mechanisms; accordingly, phenotype predictions (e.g., ResFinder) should be interpreted cautiously.
Table 3 caption (virulence)
Table 3. Virulence factor profiling of the genome assembly based on ABRicate screening against VFDB, reporting loci with sequence identity and coverage above the specified thresholds.
-
Generate phylogenetic tree
export NCBI_EMAIL=”j.huang@uke.de” ./resolve_best_assemblies_entrez.py targets.tsv resolved_accessions.tsv
Note the env bengal3_ac3 don’t have the following r-package, using r_env for the plot-step!
#mamba install -y -c conda-forge -c bioconda r-aplot bioconductor-ggtree r-ape r-ggplot2 r-dplyr r-readr
chmod +x build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh export ENV_NAME=/home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 export NCBI_EMAIL=”j.huang@uke.de” ./build_wgs_tree_fig3B.sh
-
DEBUG (recommended): remove one genome and rerun Roary → RAxML; Example: drop GCF_047901425.1 (change to the other one if you prefer).
1.1) remove from inputs so Roary cannot include it
rm -f work_wgs_tree/gffs/GCF_047901425.1.gff rm -f work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_047901425.1.fna rm -rf work_wgs_tree/prokka/GCF_047901425.1 rm -rf work_wgs_tree/genomes_ncbi/GCF_047901425.1 #optional
1.2) remove from accession list so it won’t come back
awk -F’\t’ ‘NR==1 || $2!=”GCF_047901425.1″‘ work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv > work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp \ && mv work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv
2.1) remove from inputs so Roary cannot include it
rm -f work_wgs_tree/gffs/GCA_032062225.1.gff rm -f work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_032062225.1.fna rm -rf work_wgs_tree/prokka/GCA_032062225.1 rm -rf work_wgs_tree/genomes_ncbi/GCA_032062225.1 #optional
2.2) remove from accession list so it won’t come back
awk -F’\t’ ‘NR==1 || $2!=”GCA_032062225.1″‘ work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv > work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp \ && mv work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv.tmp work_wgs_tree/meta/accessions.tsv
3) delete old roary runs (so you don’t accidentally reuse old alignment)
rm -rf work_wgstree/roary*
4) rerun Roary (fresh output dir)
mkdir -p work_wgs_tree/logs ROARY_OUT=”work_wgstree/roary$(date +%s)” roary -e –mafft -p 8 -cd 95 -i 95 \ -f “$ROARY_OUT” \ work_wgs_tree/gffs/*.gff \
work_wgs_tree/logs/roary_rerun.stdout.txt \ 2> work_wgs_tree/logs/roary_rerun.stderr.txt
5) point meta file to new core alignment (absolute path)
echo “$(readlink -f “$ROARY_OUT/core_gene_alignment.aln”)” > work_wgs_tree/meta/core_alignment_path.txt
6) rerun RAxML-NG
rm -rf work_wgs_tree/raxmlng mkdir work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/ raxml-ng –all \ –msa “$(cat work_wgs_tree/meta/core_alignment_path.txt)” \ –model GTR+G \ –bs-trees 1000 \ –threads 8 \ –prefix work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/core
7) Run this to regenerate labels.tsv
bash regenerate_labels.sh
8) Manual correct the display name in vim work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv
#Gibbsiella greigii USA56 #Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6 #Gibbsiella quercinecans strain FRB97 #Brenneria nigrifluens LMG 5956
9) Rerun only the plot step:
Rscript work_wgs_tree/plot/plot_tree.R \ work_wgs_tree/raxmlng/core.raxml.support \ work_wgs_tree/plot/labels.tsv \ 6 \ work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree_like_fig3B.pdf \ work_wgs_tree/plot/core_tree_like_fig3B.png
-
fastaANI and busco explanations
find . -name “*.fna” #./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_004342245.1.fna GCF_004342245.1 Gibbsiella quercinecans DSM 25889 (GCF_004342245.1) #./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_039539505.1.fna GCF_039539505.1 Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6 (GCF_039539505.1) #./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_005484965.1.fna GCF_005484965.1 Brenneria nigrifluens LMG5956 (GCF_005484965.1) #./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_039540155.1.fna GCA_039540155.1 Gibbsiella greigii USA56 (GCA_039540155.1) #./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GE11174.fna #./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_002291425.1.fna GCF_002291425.1 Gibbsiella quercinecans FRB97 (GCF_002291425.1)
mamba activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 fastANI \ -q GE11174.fasta \ -r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_004342245.1.fna \ -o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_quercinecans_DSM_25889.txt fastANI \ -q GE11174.fasta \ -r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_039539505.1.fna \ -o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_papilionis_PWX6.txt fastANI \ -q GE11174.fasta \ -r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_005484965.1.fna \ -o fastANI_out_Brenneria_nigrifluens_LMG5956.txt fastANI \ -q GE11174.fasta \ -r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_039540155.1.fna \ -o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_greigii_USA56.txt fastANI \ -q GE11174.fasta \ -r ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_002291425.1.fna \ -o fastANI_out_Gibbsiella_quercinecans_FRB97.txt cat fastANIout*.txt > fastANI_out.txt
GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_005484965.1.fna 79.1194 597 1890 GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCA_039540155.1.fna 95.9589 1547 1890 GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_039539505.1.fna 97.2172 1588 1890 GE11174.fasta work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_004342245.1.fna 98.0889 1599 1890 GE11174.fasta ./work_wgs_tree/fastas/GCF_002291425.1.fna 98.1285 1622 1890 #在细菌基因组比较里,一个常用经验阈值是:
- ANI ≥ 95–96%:通常认为属于同一物种(species)的范围
- 你这里 97.09% → 很大概率表示 An6 与 HITLi7 属于同一物种,但可能不是同一株(strain),因为还存在一定差异。 是否“同一菌株”通常还要结合:
- 核心基因 SNP 距离、cgMLST
- 组装质量/污染
- 覆盖率是否足够高
#BUSCO 结果的快速解读(顺便一句). The results have been already packaged in the Table 1.
- Complete 99.2%,Missing 0.0%:说明你的组装非常完整(对细菌来说很优秀)
- Duplicated 0.0%:重复拷贝不高,污染/混样风险更低
- Scaffolds 80、N50 ~169 kb:碎片化还可以,但总体质量足以做 ANI/物种鉴定
-
fastANI explanation
From your tree and the fastANI table, GE11174 is clearly inside the Gibbsiella quercinecans clade, and far from the outgroup (Brenneria nigrifluens). The ANI values quantify that same pattern.
1) Outgroup check (sanity)
-
GE11174 vs Brenneria nigrifluens (GCF_005484965.1): ANI 79.12% (597/1890 fragments)
- 79% ANI is way below any species boundary → not the same genus/species.
- On the tree, Brenneria sits on a long branch as the outgroup, consistent with this deep divergence.
- The relatively low matched fragments (597/1890) also fits “distant genomes” (fewer orthologous regions pass the ANI mapping filters).
2) Species-level placement of GE11174
A common rule of thumb you quoted is correct: ANI ≥ 95–96% ⇒ same species.
Compare GE11174 to the Gibbsiella references:
-
vs GCA_039540155.1 (Gibbsiella greigii USA56): 95.96% (1547/1890)
- Right at the boundary. This suggests “close but could be different species” or “taxonomy/labels may not reflect true species boundaries” depending on how those genomes are annotated.
- On the tree, G. greigii is outside the quercinecans group but not hugely far, which matches “borderline ANI”.
-
vs GCF_039539505.1 (Gibbsiella papilionis PWX6): 97.22% (1588/1890)
-
vs GCF_004342245.1 (G. quercinecans DSM 25889): 98.09% (1599/1890)
-
vs GCF_002291425.1 (G. quercinecans FRB97): 98.13% (1622/1890)
These are all comfortably above 96%, especially the two quercinecans genomes (~98.1%). That strongly supports:
GE11174 belongs to the same species as Gibbsiella quercinecans (and is closer to quercinecans references than to greigii).
This is exactly what your tree shows: GE11174 clusters in the quercinecans group, not with the outgroup.
3) Closest reference and “same strain?” question
GE11174’s closest by ANI in your list is:
- FRB97 (GCF_002291425.1): 98.1285%
- DSM 25889 (GCF_004342245.1): 98.0889%
- Next: PWX6 97.2172%
These differences are small, but 98.1% ANI is not “same strain” evidence by itself. Within a species, different strains commonly sit anywhere from ~96–99.9% ANI depending on diversity. To claim “same strain / very recent transmission,” people usually look for much tighter genome-wide similarity:
- core-genome SNP distance (often single digits to tens, depending on organism and context)
- cgMLST allele differences
- recombination filtering (if relevant)
- assembly QC/contamination checks
- and confirming that alignment/ANI coverage is high and not biased by missing regions
Your fragment matches (e.g., 1622/1890 for FRB97) are reasonably high, supporting that the ANI is meaningful, but it still doesn’t equate to “same strain.”
4) How to phrase the combined interpretation (tree + ANI)
A clear summary you can use:
- The phylogenetic tree places GE11174 within the Gibbsiella quercinecans lineage, with Brenneria nigrifluens as a distant outgroup.
-
fastANI supports this:
- ~98.1% ANI to G. quercinecans FRB97 and DSM 25889 → strong same-species support.
- 97.2% to G. papilionis → still same-species range, but more distant than the quercinecans references.
- 95.96% to G. greigii → borderline; consistent with being a close neighboring lineage but not the best species match for GE11174.
- 79.1% to Brenneria → confirms it is an appropriate outgroup and far outside the species/genus boundary.
- Therefore, GE11174 is very likely Gibbsiella quercinecans (species-level), and appears most similar to FRB97/DSM 25889, but additional high-resolution analyses are required to assess “same strain.”
If you want, paste the fastANI line for GE11174 vs GE11174? (or run fastANI against a broader set), and/or your core SNP distances from the Roary alignment, and I can help you write a tighter “strain-level” conclusion.
#TODO_NEXT_MONDAY: * phylogenetic tree + fastaANI + nf-core/pairgenomealign (compare to the closest isoalte https://nf-co.re/pairgenomealign/2.2.1/)
* #summarize all results with a mail to send them back, mentioned that we can submit the genome to NCBI to obtain a high-quality annotation. What strain name would you like to assign to this isolate?
* If they agree, I can submit the two new isolates to the NCBI-database!-
submit both sequences in a batch to NCBI-server!
-
Find the more “closest isolate” from GenBank (robust approach) for STEP_7
4. Find the more “closest isolate” from GenBank (robust approach)
# download all available genomes for the genus Gibbsiella (includes assemblies + metadata) #--assembly-level" flag: must be 'chromosome', 'complete', 'contig', 'scaffold' datasets download genome taxon Gibbsiella --include genome,gff3,gbff --assembly-level complete,chromosome,scaffold --filename gibbsiella.zip unzip -q gibbsiella.zip -d gibbsiella_ncbi mamba activate /home/jhuang/miniconda3/envs/bengal3_ac3 # make a Mash sketch of your isolate mash sketch -o isolate bacass_out/Unicycler/GE11174.scaffolds.fa # sketch all reference genomes (example path—adjust) find gibbsiella_ncbi -name "*.fna" -o -name "*.fasta" > refs.txt mash sketch -o refs -l refs.txt # get closest genomes mash dist isolate.msh refs.msh | sort -gk3 | head -n 20 > top20_mash.txt ## What your Mash results mean * The **best hits** to your assembly (`GE11174.scaffolds.fa`) are: * **GCA/GCF_002291425.1** (shows up twice: GenBank **GCA** and RefSeq **GCF** copies of the *same assembly*) * **GCA/GCF_004342245.1** (same duplication pattern) * **GCA/GCF_047901425.1** (FRB97; also duplicated) * Mash distances around **0.018–0.020** are **very close** (typically same species; often same genus and usually within-species). * The `0` in your output is just Mash’s p-value being printed as 0 due to underflow (i.e., extremely significant). So yes: your isolate looks **very close to those Gibbsiella genomes**, and FRB97 being in that set is consistent with your earlier KmerFinder result.
5. — Remove duplicates (GCA vs GCF)
Right now you’re seeing the same genome twice (GenBank + RefSeq). For downstream work, keep one. Example: keep only **GCF** if available, else GCA: ```bash # Take your top hits, prefer GCF over GCA cat top20_mash.txt \ | awk '{print $2}' \ | sed 's|/GCA_.*||; s|/GCF_.*||' \ | sort -u ``` But easiest: just manually keep one of each pair: * keep `GCF_002291425.1` (drop `GCA_002291425.1`) * keep `GCF_004342245.1` * keep `GCF_047901425.1` (and maybe keep `GCA_032062225.1` if it’s truly different and you want a more distant ingroup point)