LT manuscript TODOs
gene_x 0 like s 1237 view s
Tags: research, ChIP-seq
-
Define "promoter types" by examining the frequency and distribution of the 'GRGGC' motif on both + and - strands within the promoter region, and categorize promoters based on the identified "promoter types."
-
Investigate the reasons for observing only a small proportion of peaks in the promoter regions in my analysis (e.g., 203 out of 1938 peaks in NHDF samples).
-
Evaluate the consistency of peaks between replicates for both NHDF and K331A samples.
-
Identify the overlap between peaks and integration sites.
-
Perform enhancer analysis using the additional data for H3K4me1 and H3K27ac marks, obtained from public repositories. /home/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_sT_immune_evasion_PUBLISHING/Data_Denise_ChIPSeq_Protocol2/Data_H3K27ac/Raw_Data
#H3K4me3_H3K27ac__H3K27me3_H3K9me3 V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_H3K4me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K4me3_D1 V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_H3K4me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K4me3_D2 V_8_1_6_p604_d8_D1_H3K4me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p604_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K4me3_D1 V_8_1_5_p604_d8_D2_H3K4me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p604_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K4me3_D2 V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_H3K27me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K27me3_D1 V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_H3K27me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K27me3_D2 V_8_1_6_p604_d8_D1_H3K27me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p604_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K27me3_D1 V_8_1_5_p604_d8_D2_H3K27me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p604_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K27me3_D2 V_8_1_7_p601_d8_D1_H3K9me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K9me3_D1 V_8_1_7_p601_d8_D2_H3K9me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K9me3_D2 V_8_1_7_p604_d8_D1_H3K9me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p604_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K9me3_D1 V_8_1_7_p604_d8_D2_H3K9me3.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p604_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K9me3_D2 V_8_1_8_p601_d8_D1_H3K27ac.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p601_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K27ac_D1 V_8_1_8_p601_d8_D2_H3K27ac.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p601_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p601_H3K27ac_D2 V_8_1_8_p604_d8_D1_H3K27ac.fastq.gz,V_8_1_6_p604_d8_D1_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K27ac_D1 V_8_1_8_p604_d8_D2_H3K27ac.fastq.gz,V_8_1_5_p604_d8_D2_input.fastq.gz,p604_H3K27ac_D2 #H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public #https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSM733662 #https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSM1003526 NHDF_H3K4me1_r1.fastq.gz NHDF_H3K4me1_r2.fastq.gz NHDF_H3K27ac_r1.fastq.gz NHDF_H3K27ac_r2.fastq.gz NHDF_Control_r1.fastq.gz NHDF_Control_r2.fastq.gz -
In the PCA plot, adjust the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis to their actual scales, and exclude d3 samples.
-
Identify the significant genes by conducting analyses focused on the specific sequencing data of interest (for example, only input the LT_d8 and control_d8 data for the LT_vs_control analysis), and then compare the lists of significant genes derived from these targeted analyses with those from the comprehensive analysis.
#Error during "macs2 callpeak" (rnaseq) jhuang@hamm:~/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public$ nextflow run NGI-ChIPseq/main.nf --reads '/mnt/h1/jhuang/DATA/Data_Denise_LT_DNA_Binding/ChIPseq_histone_hg38/H3K27ac_H3K4me1_public/Raw_Data/*.fastq.gz' --genome hg38 --macsconfig macs.config --saveReference --saveAlignedIntermediates --singleEnd --blacklist_filtering -profile standard --project NHDF_enhancer_analysis_hg38 -resumenew
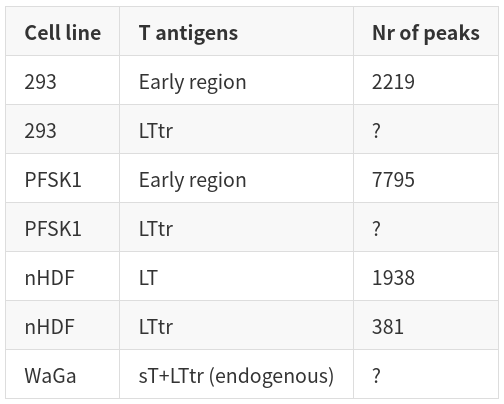
| Cell line | T antigens | Nr of peaks | | ----------- | ----------- | ----------- | | 293 | Early region | 2219 | | 293 | LTtr | ? | | PFSK1 | Early region | 7795 | | PFSK1 | LTtr | ? | | nHDF | LT | 1938 | | nHDF | LTtr | 381 | | WaGa | sT+LTtr (endogenous) | ? |
old
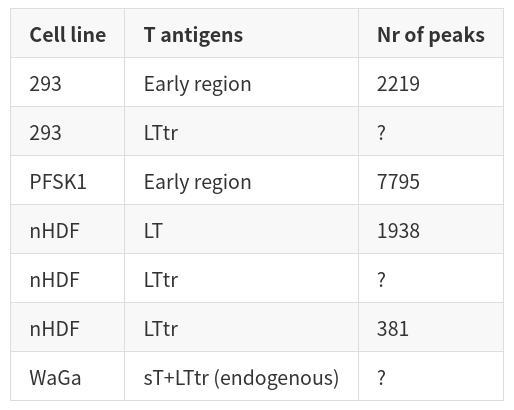
| Cell line | T antigens | Nr of peaks | | ----------- | ----------- | ----------- | | 293 | Early region | 2219 | | 293 | LTtr | ? | | PFSK1 | Early region | 7795 | | nHDF | LT | 1938 | | nHDF | LTtr | ? | | nHDF | LTtr | 381 | | WaGa | sT+LTtr (endogenous) | ? |
-
A brief overview of each cell line and their relevance to MCPyV:
-
HEK293:
- Origin: Human embryonic kidney cells, but with characteristics of immature neuronal cells.
- MCPyV: These cells are often used in virology research due to their high transfection efficiency. They are not naturally permissive to MCPyV infection, but they can be used to study the virus by introducing viral genes through transfection.
-
PFSK-1:
- Origin: Derived from a primary cerebral tumor of a 22-month-old child, these cells have neuronal properties.
- MCPyV: Not typically associated with MCPyV research, as these cells are of neural origin. MCC typically does not arise from neural tissue.
-
nHDF (Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts):
- Origin: These are primary cells derived from normal human dermal skin.
- MCPyV: While not derived from Merkel cells, fibroblasts like nHDF can be used in studies to understand the impact of MCPyV on skin cells or to provide a non-cancerous control in MCPyV studies.
-
WaGa:
- Origin: A cell line derived from human Merkel cell carcinoma.
- MCPyV: WaGa cells are MCPyV-positive, meaning they contain the virus, and are used in research to understand the biology of MCPyV-associated MCC.
-
MKL-1:
- Origin: Also a cell line derived from human Merkel cell carcinoma.
- MCPyV: MKL-1 cells are MCPyV-positive and have been used extensively in studies to understand MCPyV’s role in Merkel cell carcinoma pathogenesis.
Each of these cell lines offers a different context for studying the biology of MCPyV, its infection mechanism, the cellular response to the virus, and the development of MCC. The HEK293 line is often used for molecular cloning and gene expression studies due to its ease of transfection and high growth rate. In contrast, WaGa and MKL-1 cells, being derived from MCC, provide a more disease-relevant system to study the virus' oncogenic mechanisms.
In virology and cancer research, choosing the appropriate cell line is crucial, as it can significantly affect the relevance and applicability of the findings. The HEK293 cells would provide a basic understanding of the virus-host interactions at the molecular level, whereas WaGa and MKL-1 cells would be used to study the virus in the context of its natural disease state. PFSK-1 and nHDF might serve as non-MCC comparators or be used in MCPyV research for more specialized purposes.
-
-
Sample code explanation
Markdown | Less | Pretty
--- | --- | ---
Still | renders | nicely
1 | 2 | 3
| Item | Price | # In stock | |--------------|-----------|------------| | Juicy Apples | 1.99 | 7 | | Bananas | 1.89 | 5234 |
| Sample Code | Sample Name |
| ----------- | ----------- |
| untreated_d0_DonorI | untreated_Day0 |
| untreated_d0_DonorII | untreated_Day0 |
| p601_d3_DonorII | mCherry-control_Day3 |
| p604_d3_DonorII | sT_Day3 |
| p601_d8_DonorII | mCherry-control_Day8 |
| p604_d8_DonorII | sT_Day8 |
| p601_d3_DonorI | mCherry-control_Day3 |
| p604_d3_DonorI | sT_Day3 |
| p601_d8_DonorI | mCherry-control_Day8 |
| p604_d8_DonorI | sT_Day8 |
| p600_d3_DonorII | GFP-control_Day3 |
| p605_d3_DonorII | LTtr_Day3 |
| p600_d8_DonorII | GFP-control_Day8 |
| p605_d8_DonorII | LTtr_Day8 |
| p600_d3_DonorI | GFP-control_Day3 |
| p605_d3_DonorI | LTtr_Day3 |
| p600_d8_DonorI | GFP-control_Day8 |
| p605_d8_DonorI | LTtr_Day8 |
| p602_d8_DonorII | LT_Day8 |
| p602_d8_DonorI | LT_Day8 |
| p600and601_d12_DonorI | GFP+mCherry-control_Day12 |
| p604and605_d12_DonorI | sT+LTtr_Day12 |
| p600and601_d9_DonorII | GFP+mCherry-control_Day9 |
| p604and605_d9_DonorII | sT+LTtr_Day9 |
| p602_d3_DonorI | LT_Day3 |
| p602_d3_DonorII | LT_Day3 |
| p602and604_d3_DonorI | sT+LT_Day3 |
| p602and604_d3_DonorII | sT+LT_Day3 |
点赞本文的读者
还没有人对此文章表态
本文有评论
xxx说:
Markdown | Less | Pretty --- | --- | --- *Still* | `renders` | **nicely** 1 | 2 | 3
看文章,发评论,不要沉默
最受欢迎文章
- Motif Discovery in Biological Sequences: A Comparison of MEME and HOMER
- Why Do Significant Gene Lists Change After Adding Additional Conditions in Differential Gene Expression Analysis?
- Calling peaks using findPeaks of HOMER
- PiCRUST2 Pipeline for Functional Prediction and Pathway Analysis in Metagenomics
- Should the inputs for GSVA be normalized or raw?
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Kraken2 Installation and Usage Guide
- pheatmap vs heatmap.2
- Setup conda environments
- Guide to Submitting Data to GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus)
最新文章
- 足突(Podosome)、胞外囊泡(Extracellular Vesicle)与基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)综合解析
- NCBI BioSample Submission Strategy for PJI and Nasal Microbiota Study
- Human RNA-seq processing for Data_Ben_RNAseq_2025
- 基因组与表型特性研究:一株药物敏感的鲍曼不动杆菌显示出增强的毒力相关特性和应激耐受性
最多评论文章
- Updating Human Gene Identifiers using Ensembl BioMart: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The top 10 genes
- Retrieving KEGG Genes Using Bioservices in Python
推荐相似文章
Merkel细胞多瘤病毒大T抗原(LT)、截短的大T抗原(LTtr; MCC350)和小T抗原(sT)对初级新生儿人类真皮成纤维细胞(nHDFs)中的mRNA水平的影响
足突(Podosome)、胞外囊泡(Extracellular Vesicle)与基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)综合解析